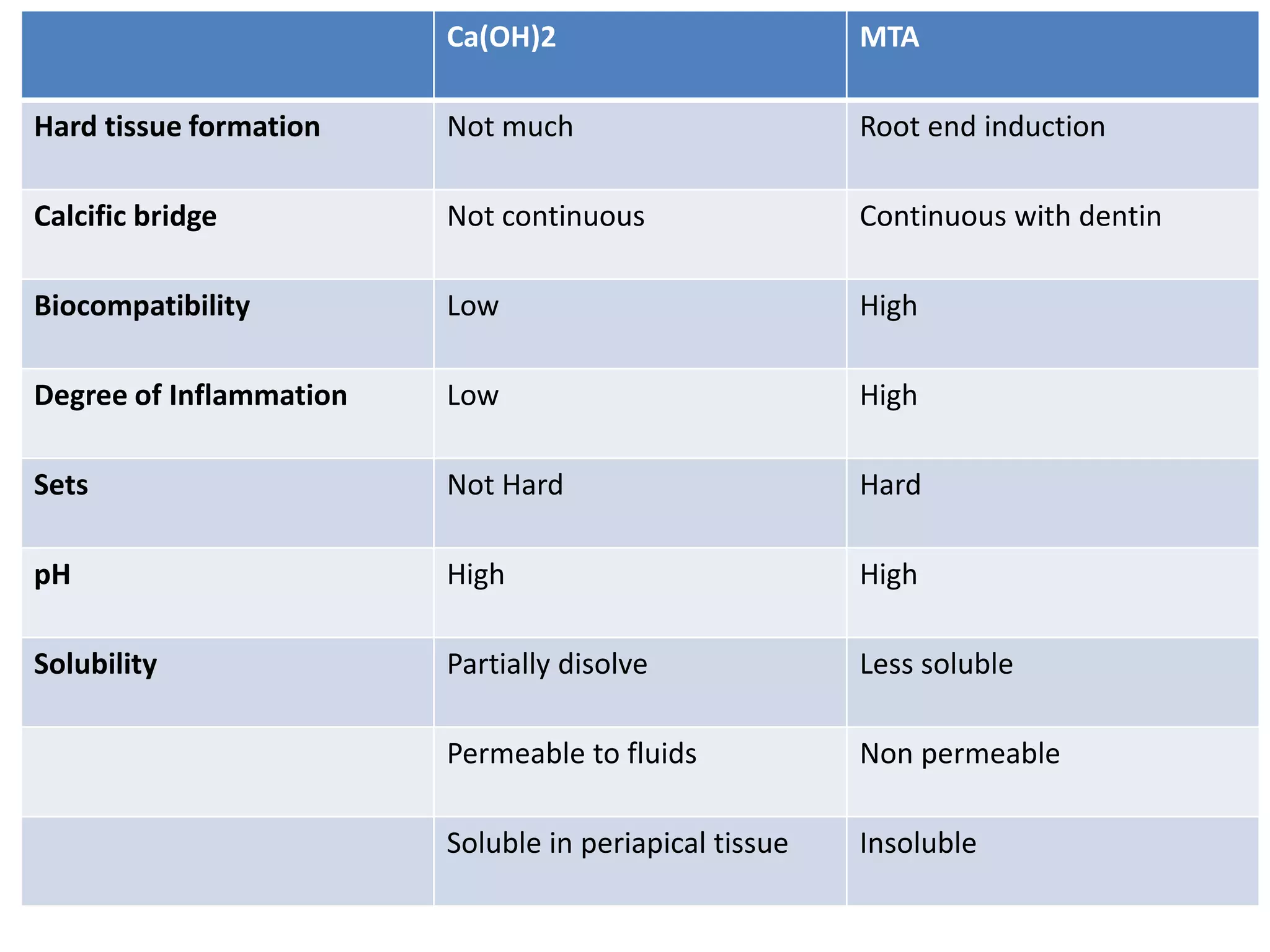
The document provides a comprehensive overview of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), highlighting its composition, properties, and clinical applications in dentistry, particularly in endodontics. MTA is lauded for its biocompatibility, sealing ability, and various uses such as direct pulp capping and root end filling, with a notable comparison to calcium hydroxide. The document concludes by emphasizing MTA's advantages, including reduced treatment time and improved patient outcomes.
![Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
[MTA]
Dept. of Conservative & Endodontics
Kantipur Dental College
Chetan Basnet
BDS 4th Batch](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mineraltrioxideaggregate-151027184900-lva1-app6891/75/Mineral-trioxide-aggregate-1-2048.jpg)




























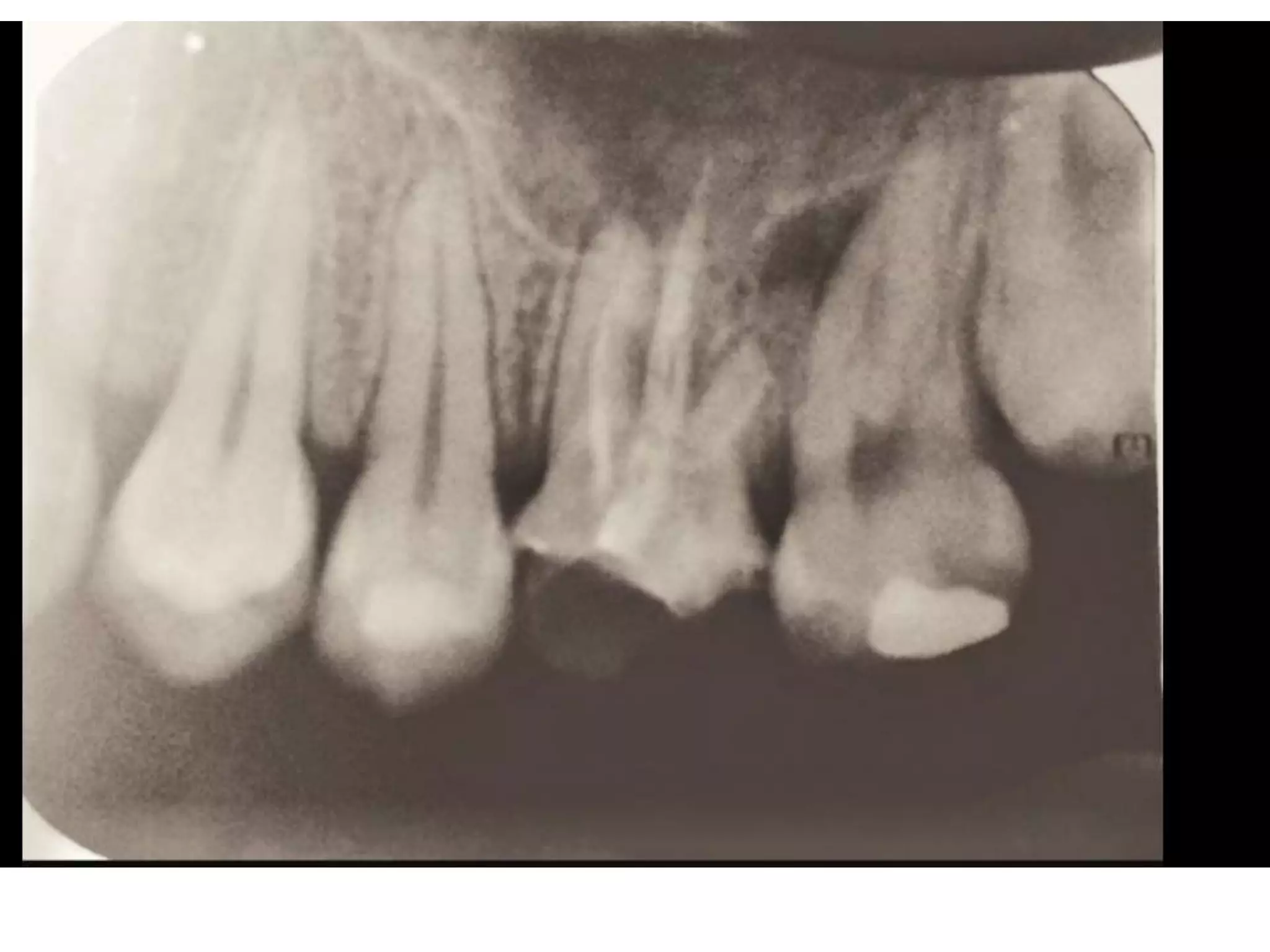
![Treatment Plan:
• Oral Prophylaxis and oral Hygiene Instructions
• Prefabrication of post on palatal site and composite builup wrt 26
• Restoration wrt :17, 16, 36, 46
BUT
When treatment was started and caries excavation was done PERFORATION
was noted on sub-palatal floor and patient was informed about the
cause of bad smell.
The patient desired extraction of same teeth but was advised to save the teeth
and repair perforation. After getting the CONSENT of patient the furcation
repair was stared by using MINERAL TRIOXIDE AGGREGATE [MTA].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mineraltrioxideaggregate-151027184900-lva1-app6891/75/Mineral-trioxide-aggregate-34-2048.jpg)