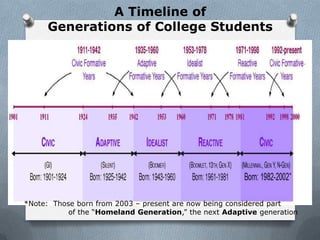
This document discusses generational characteristics with a focus on Millennials. It defines a generation as those born within a 20 year period who experience formative events together between ages 10-18. Millennials are defined as those born between 1982-2002. Critical events during their formative years included 9/11, wars in the Middle East, school shootings, and the rise of technology and social media. The document outlines characteristics of Millennials including being civic-minded, ambitious, pressured, and team-oriented. It also discusses how they approach academics, social life, technology, and expectations of rules and authority.