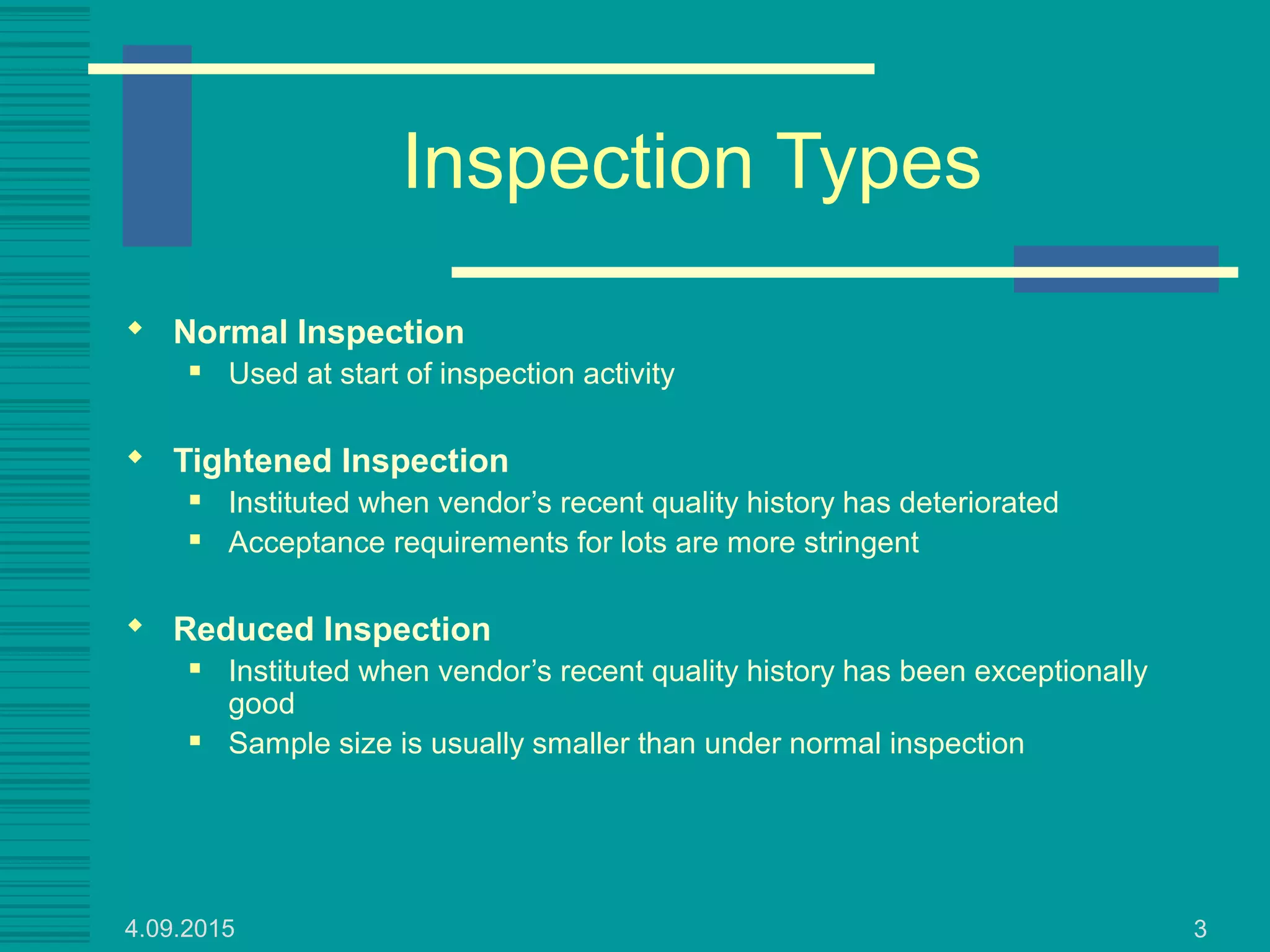
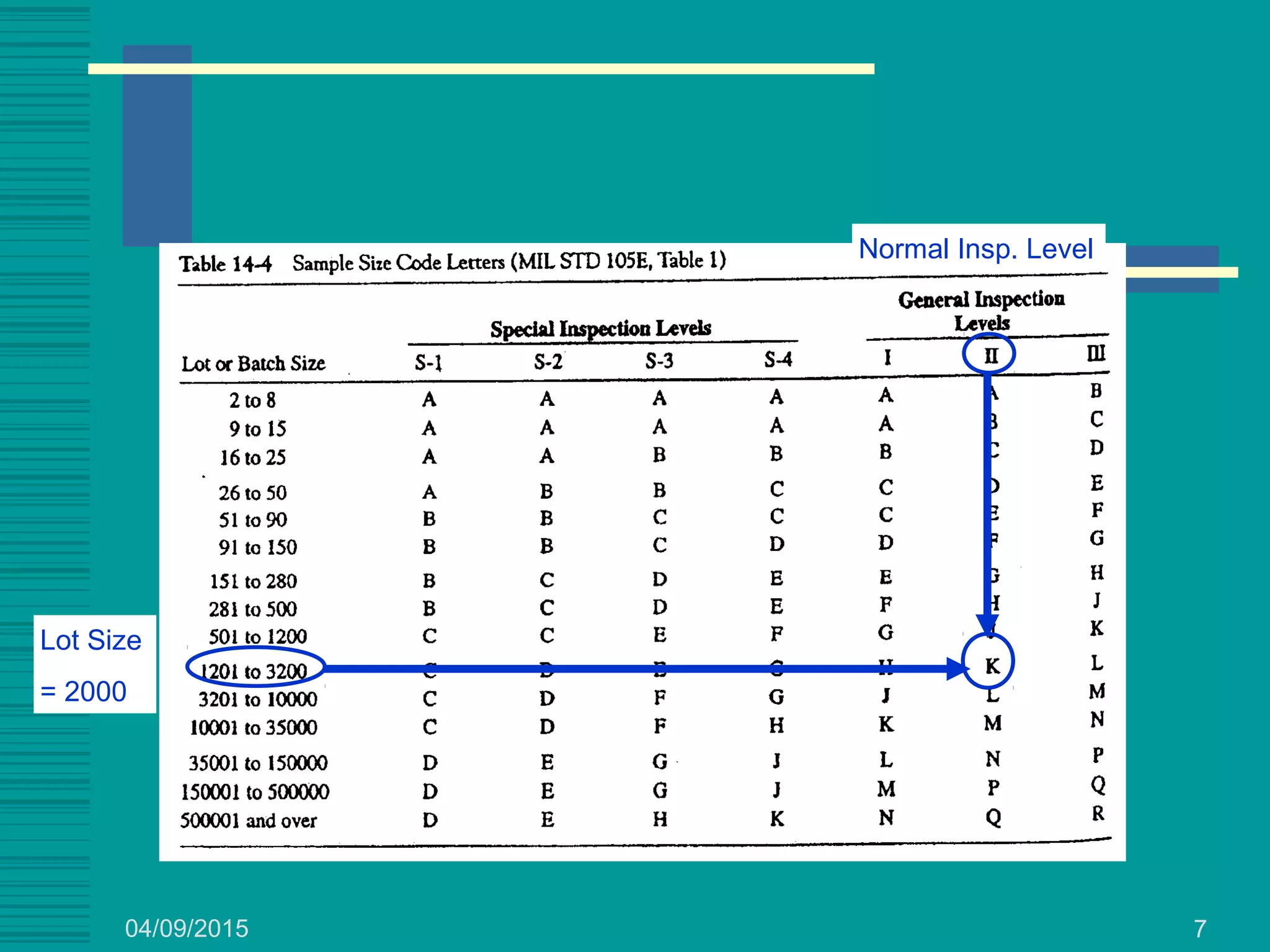
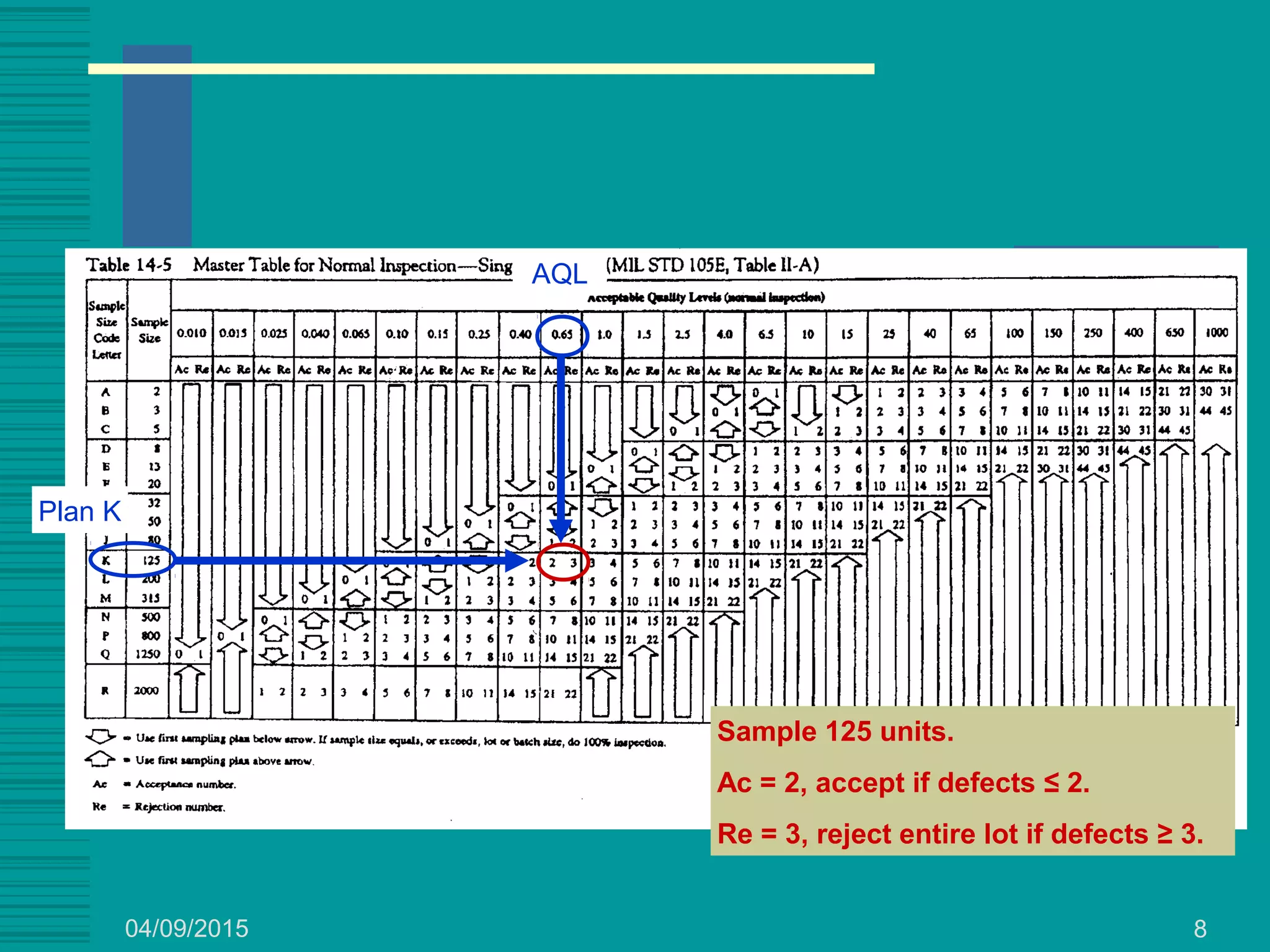
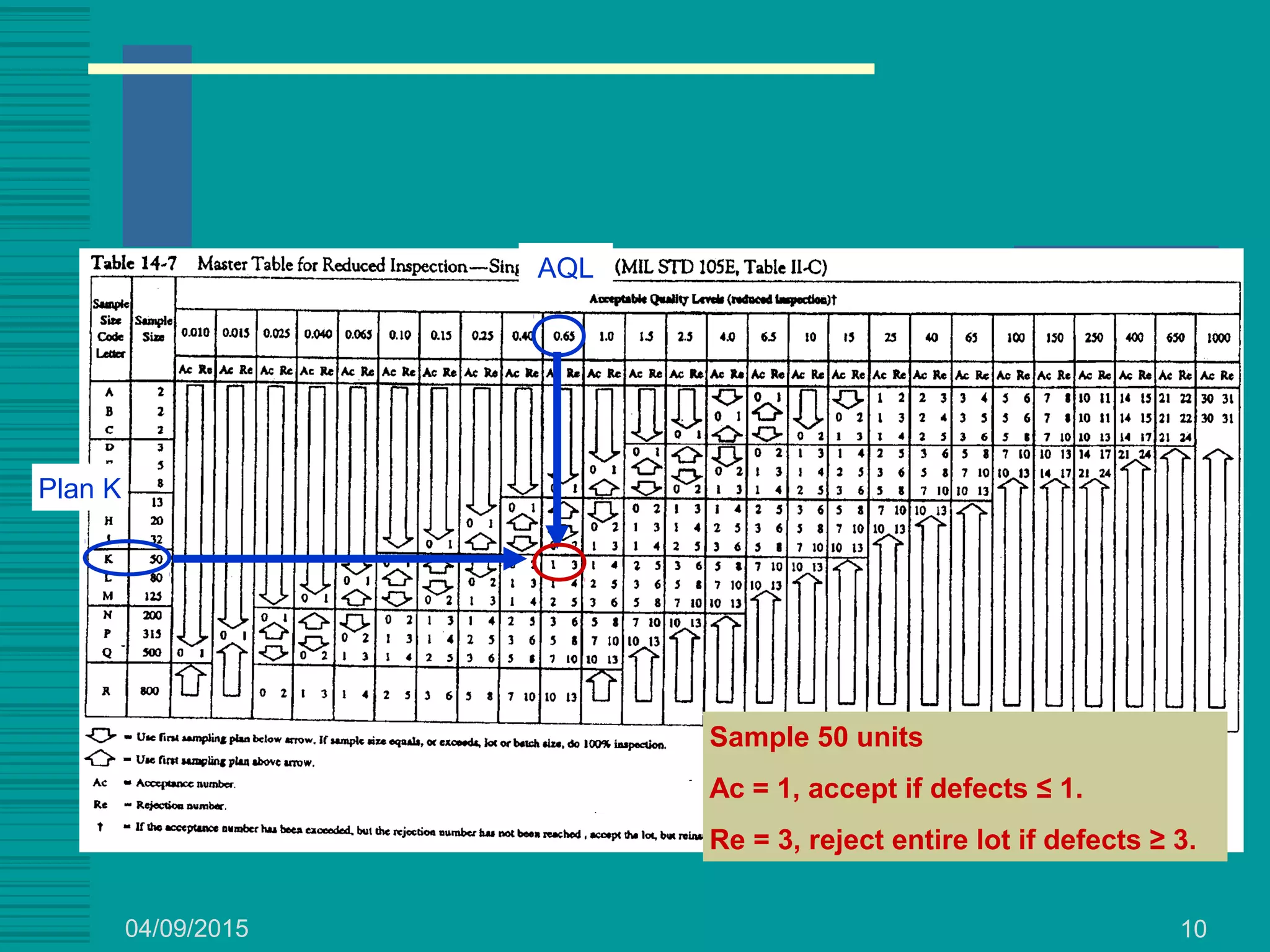
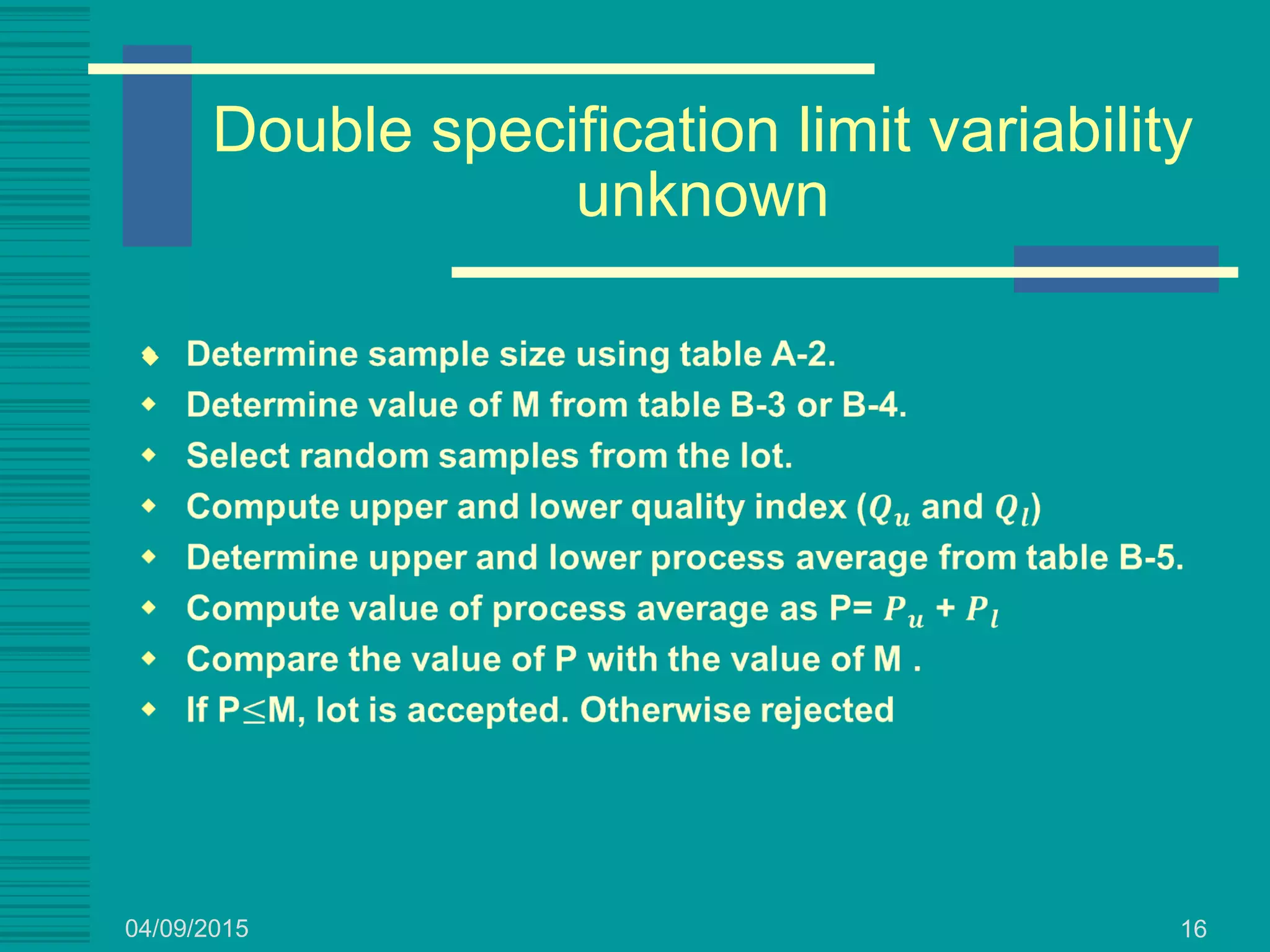
This document discusses military standards for acceptance sampling, including Military Standard 105E and Military Standard 414. MIL STD 105E provides sampling schemes for attributes data using single, double, or multiple sampling plans. It describes normal, tightened, and reduced inspection levels based on a vendor's quality history. MIL STD 414 provides variables acceptance sampling plans that use sample sizes based on lot size and inspection level, assuming the quality characteristic is normally distributed. It includes plans based on sample standard deviation, range, and known process standard deviation. The document provides examples of using these standards to determine acceptance sampling plans.