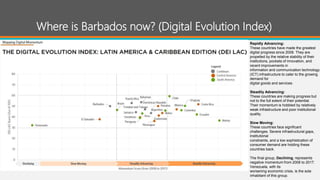
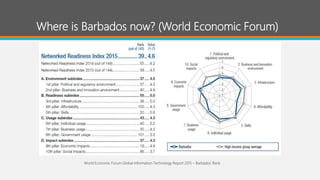
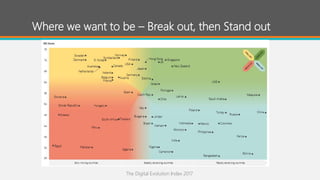
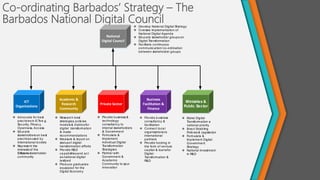
The document proposes the Digital Barbados Initiative to address Barbados' stagnating economy by leveraging the global digital economy. It finds Barbados ranks low in key digital metrics and participation in the digital economy. The initiative's vision is for Barbados to be a global digital leader that unleashes its people's potential. A National Digital Council multi-stakeholder framework would oversee coordination of digital transformation efforts across government, businesses, and citizens. The council would facilitate collaboration, identify partners, and educate on digital transformation benefits and roles to make Barbados a leading digital society.