Embed presentation
Downloaded 94 times
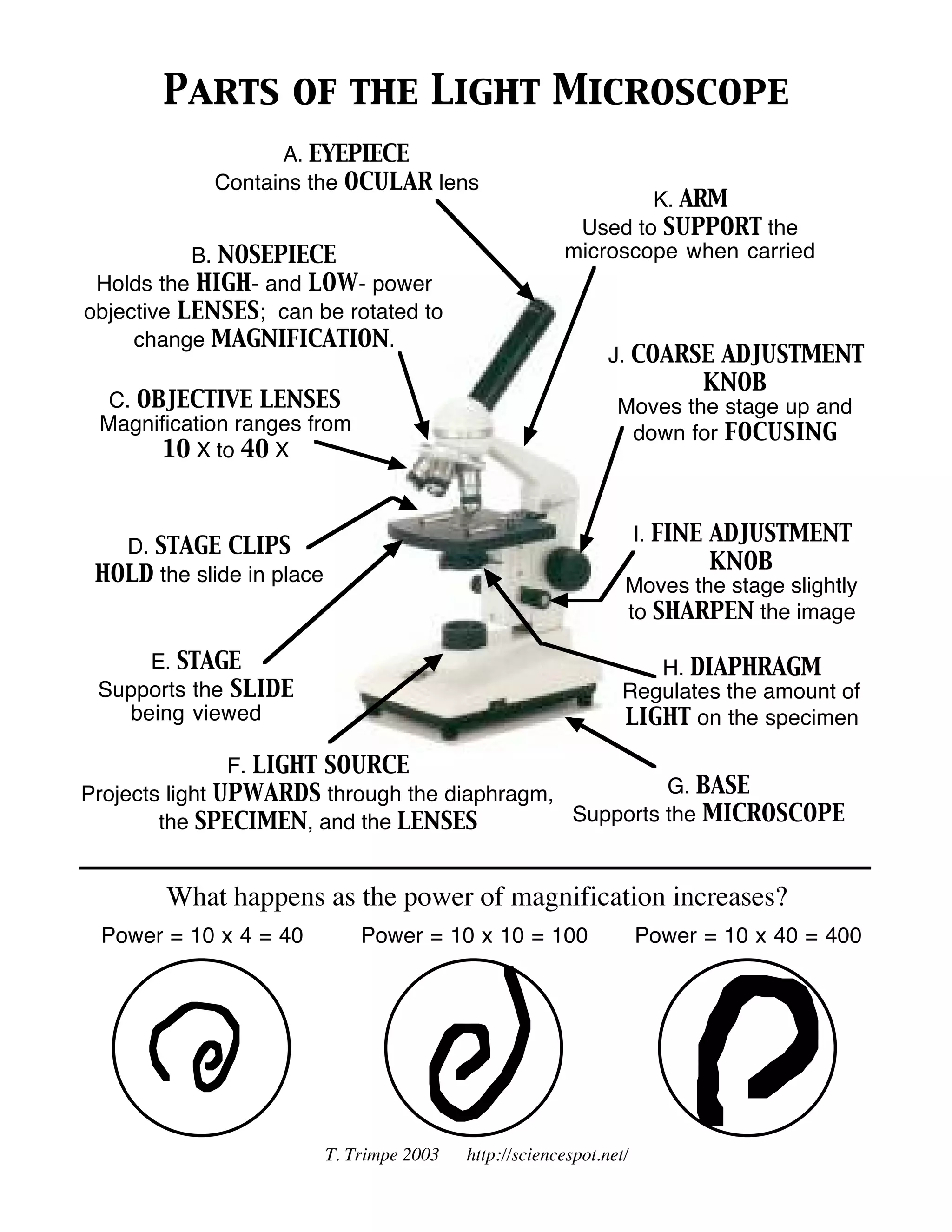

The document describes the main parts of a light microscope and their functions. It includes labels and descriptions for each part: the eyepiece contains the ocular lens, the coarse adjustment knob moves the stage up and down for focusing, and the fine adjustment knob moves the stage slightly to sharpen the image. As the power of magnification increases, the level of magnification and detail visible also increases.

