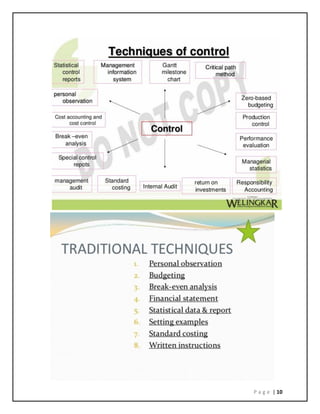
The document is a micro project report submitted by students Tushar Singh, Pankaj Yadav and Yogi Shah for their management course. It includes a proposal, literature review, methodology, outputs and evaluation of a study on controlling methods in management. The students addressed various course outcomes related to basic management principles, planning, organizing, directing and controlling. They received a certificate for satisfactorily completing the micro project. The report discusses traditional and modern control techniques such as personal observation, statistical reports and return on investment. The students developed skills in teamwork, research, time management and technical writing through this project.








![P a g e | 15
Annexure – IV
Micro Project Evaluation Sheet
Name of Student: Tushar, Pankaj, Yogi Enrollment No: 1700040135 - 1700040137
Name of Program: Computer Engineering Semester: Sixth
Course Title: Management Course Code: 22509
Title of the Micro-Project: To Study The Managerial Skills.
Cos addressed by Micro Project:
1. Use basic management principles to execute daily activities. [ ✓ ]
2. Use principles of planning and organizing for accomplishment of tasks [ ✓ ]
3. Use principles of directing and controlling for implementing the plans [ ✓ ]
4. Apply principles of safety management in all activities [ ✓ ]
5. Understand various provision of industrial acts [ ✓ ]
Sr.
No.
Characteristic to be assessed
Poor
( Marks1-
3 )
Average
(Marks 4-
5 )
Good
(Marks 6-
8)
Excellent
( Marks9-
10)
Sub
Total
A. Process and Product Assessment (Convert Above Total marks out of 6 Marks)
1 Relevance to the course
2 Information Collection
3
Completion of the Target as per
project proposal
4
Analysis of Data and
representation
5 Quality of Prototype/Model
6 Report Preparation
B. Individual Presentation / Viva (Convert above total marks out of 4 marks)
7 Presentation
8 Defense](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microprojectmgt-230403165015-db128b72/85/MICRO_PROJECT_MGT-pdf-15-320.jpg)