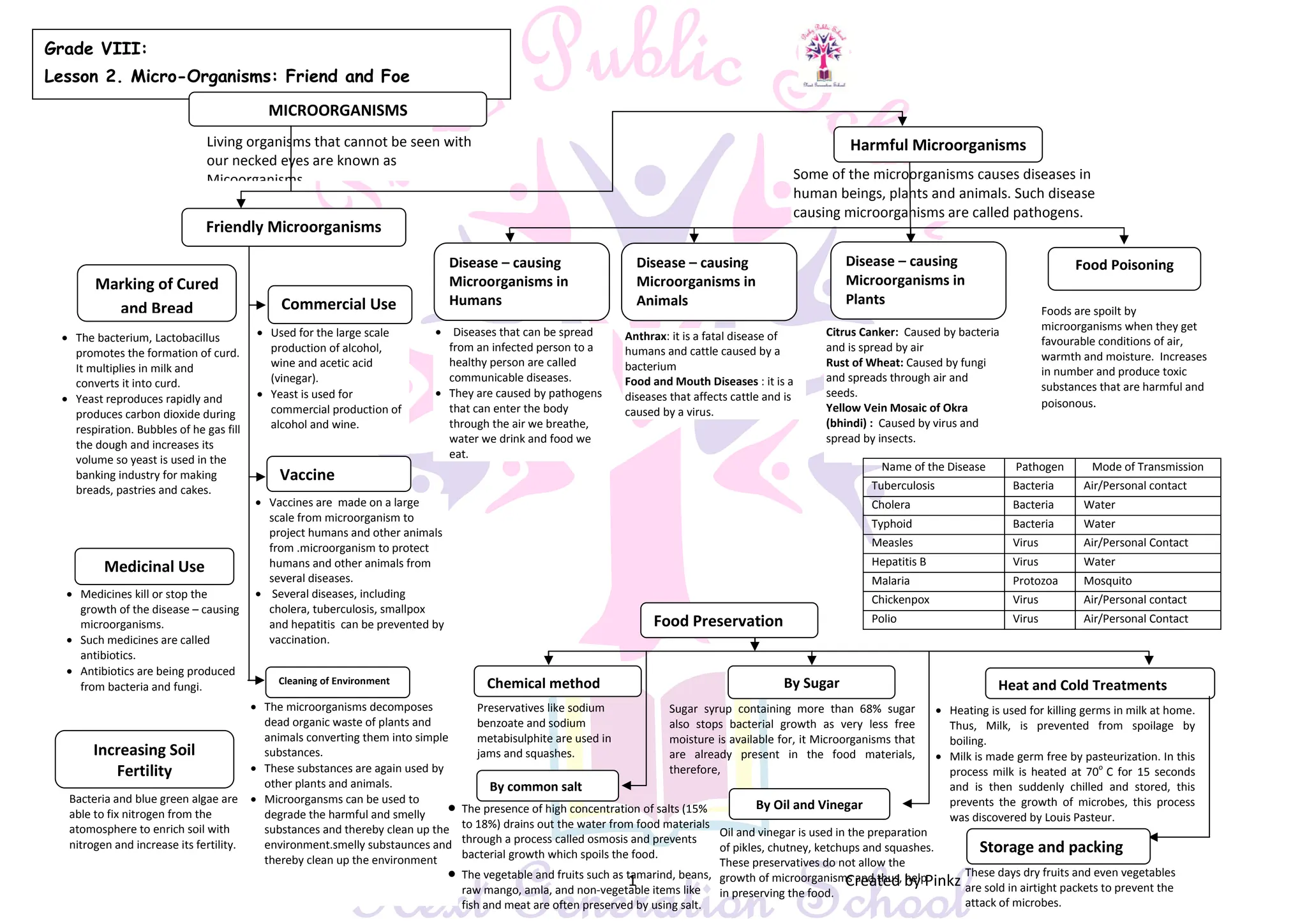
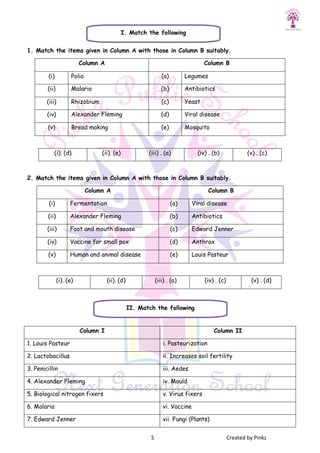
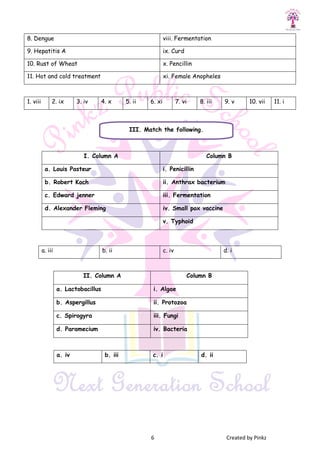
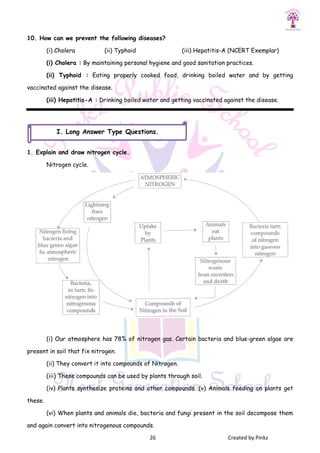
This document discusses microorganisms and their roles as both helpful and harmful to humans and the environment. It describes how certain microorganisms like Lactobacillus and yeast are used in food production to make curd, bread, alcohol, and more. It also explains how microorganisms can cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants. Pathogens and the diseases they cause like anthrax, foot and mouth disease, and yellow vein mosaic are identified. Methods of preventing disease transmission and food spoilage through techniques like vaccination, antibiotics, food preservation, and sanitation are outlined.