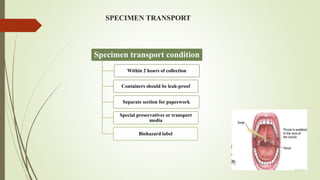
The document provides an overview of the importance of microbial culture in diagnosing infectious diseases and guiding antibiotic therapy. It outlines the workflow of a microbiology department, emphasizing the need for proper specimen collection and handling to avoid contamination and incorrect results. Additionally, it discusses the growing public health threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and the department's goals to educate the public and enhance clinical microbiology services in Afghanistan.