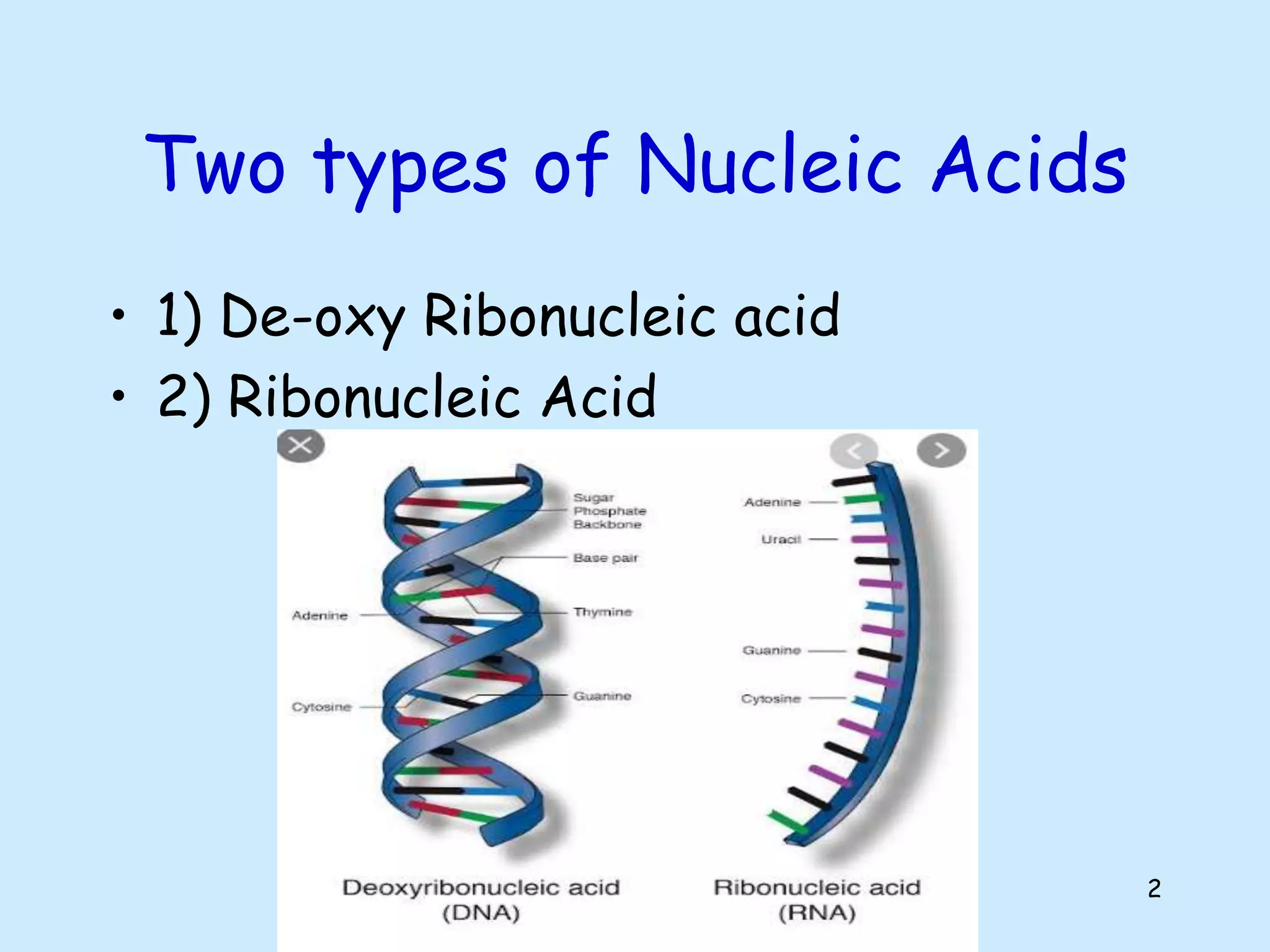
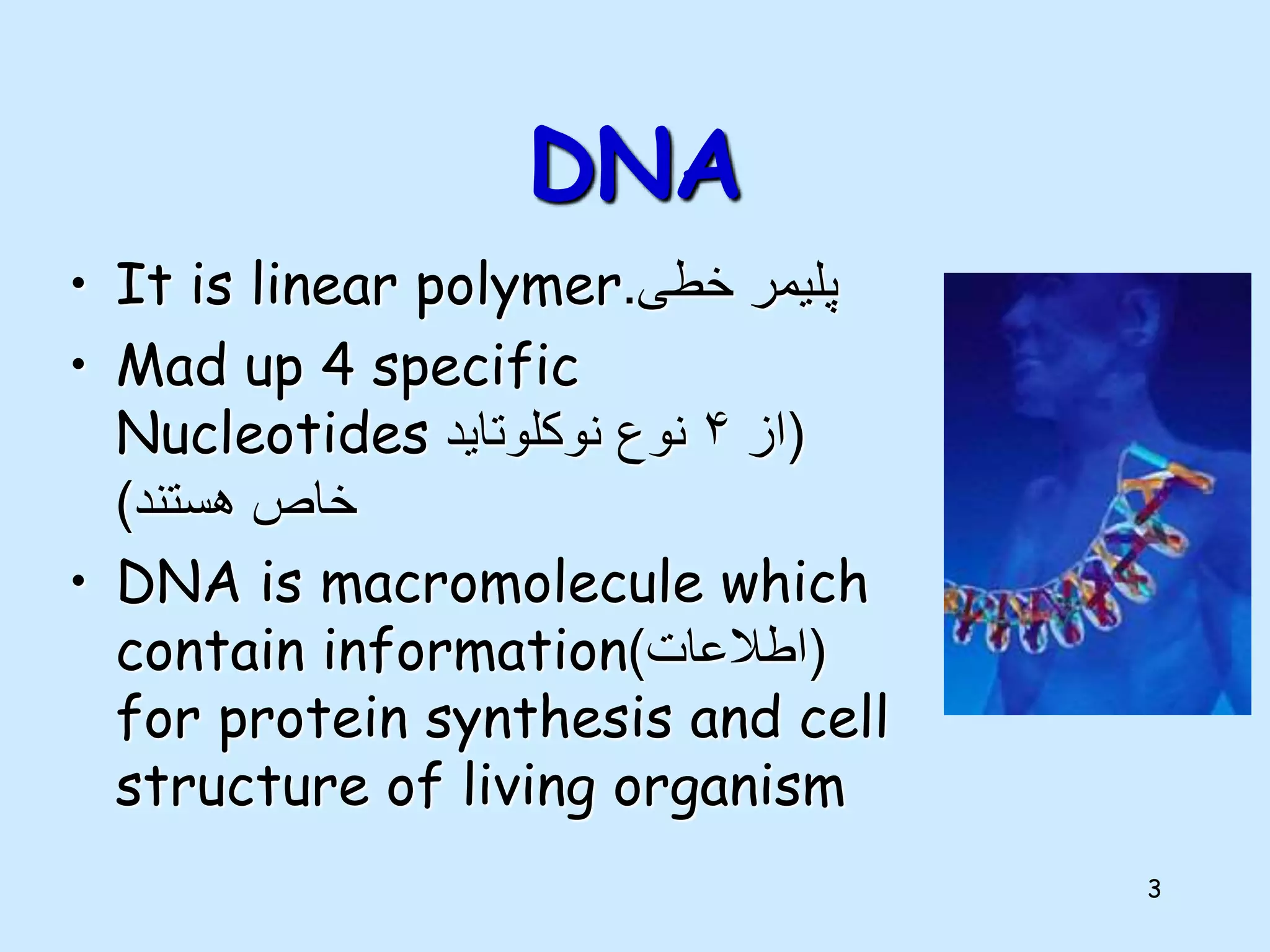
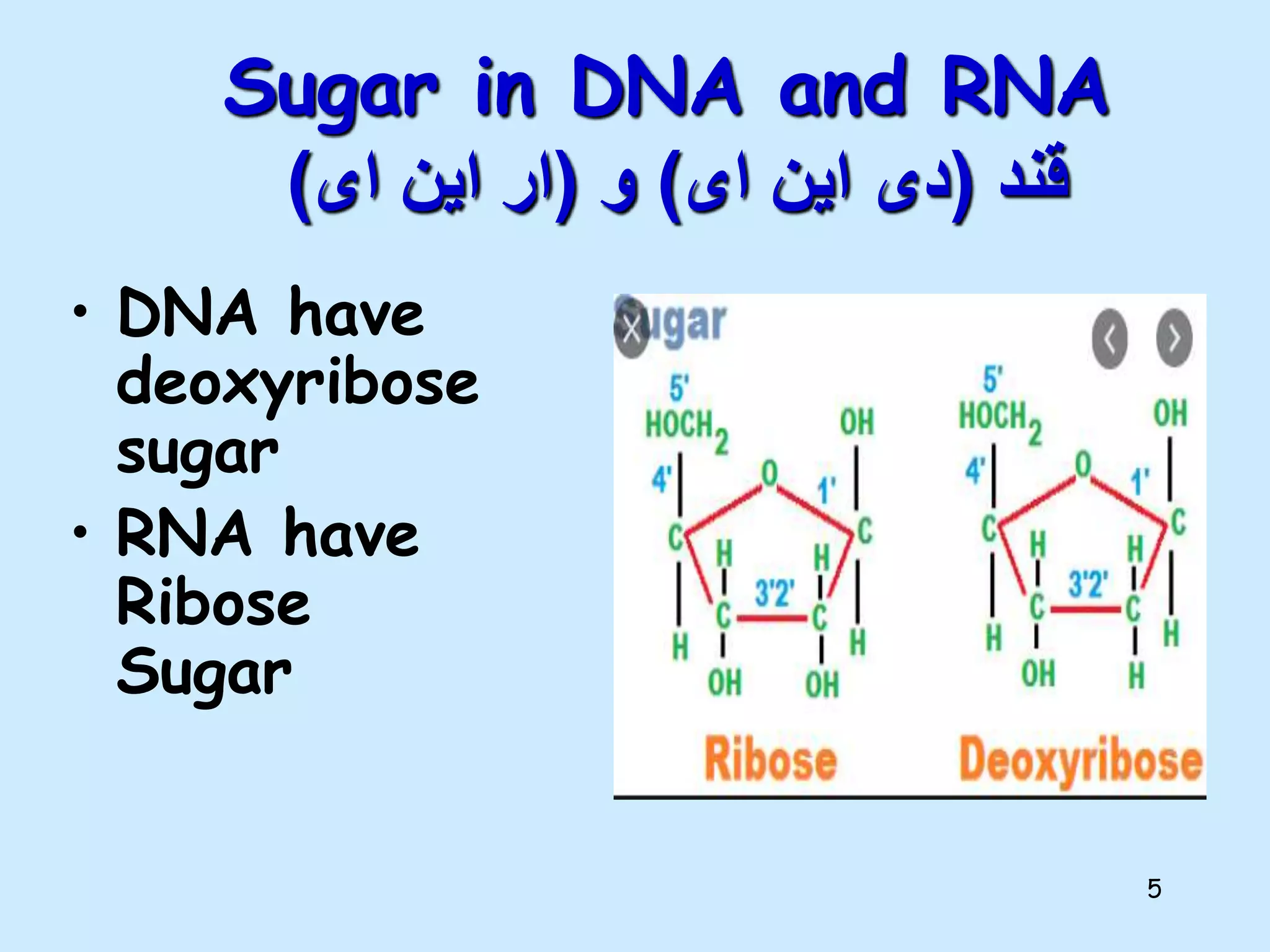
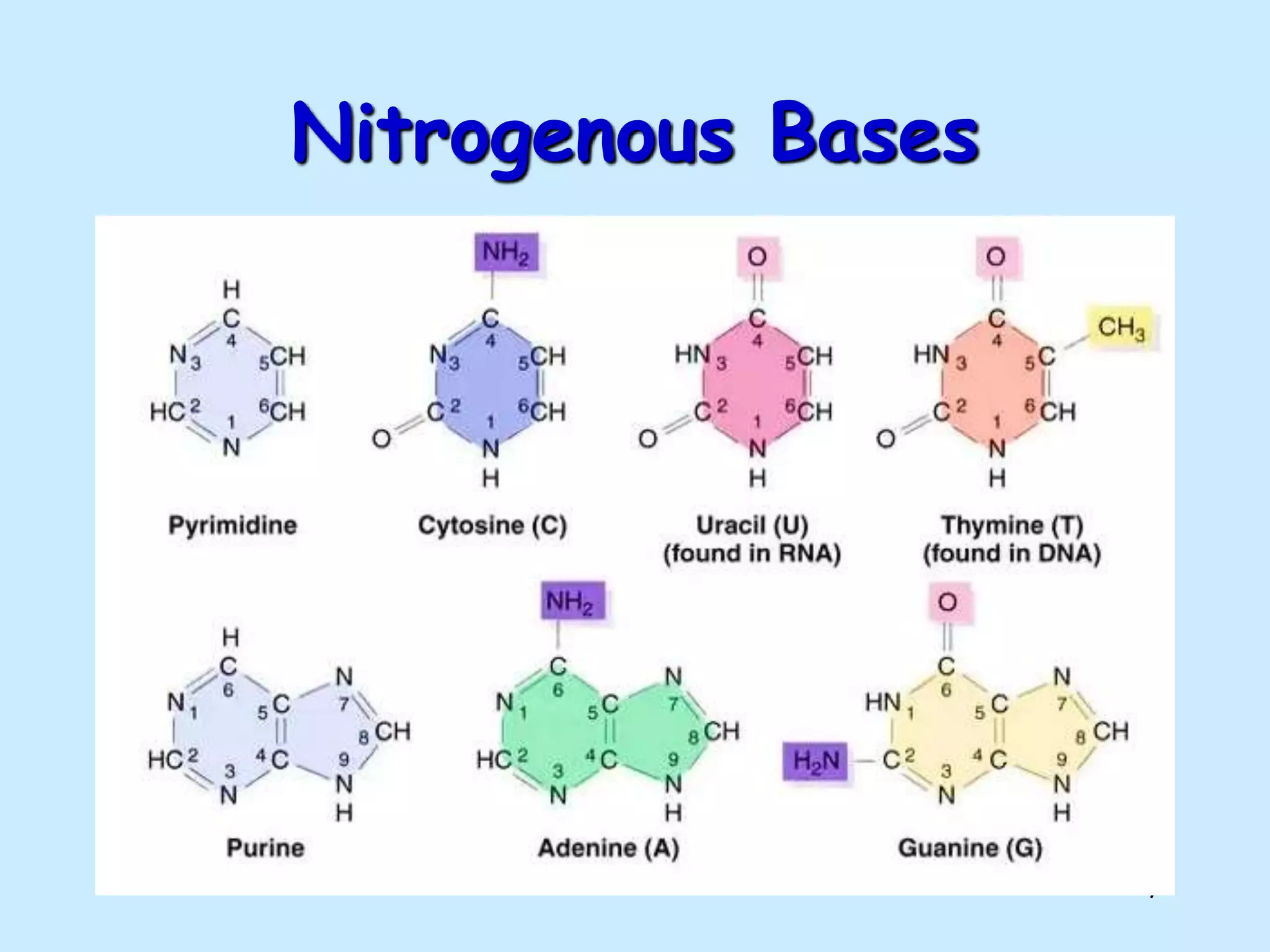
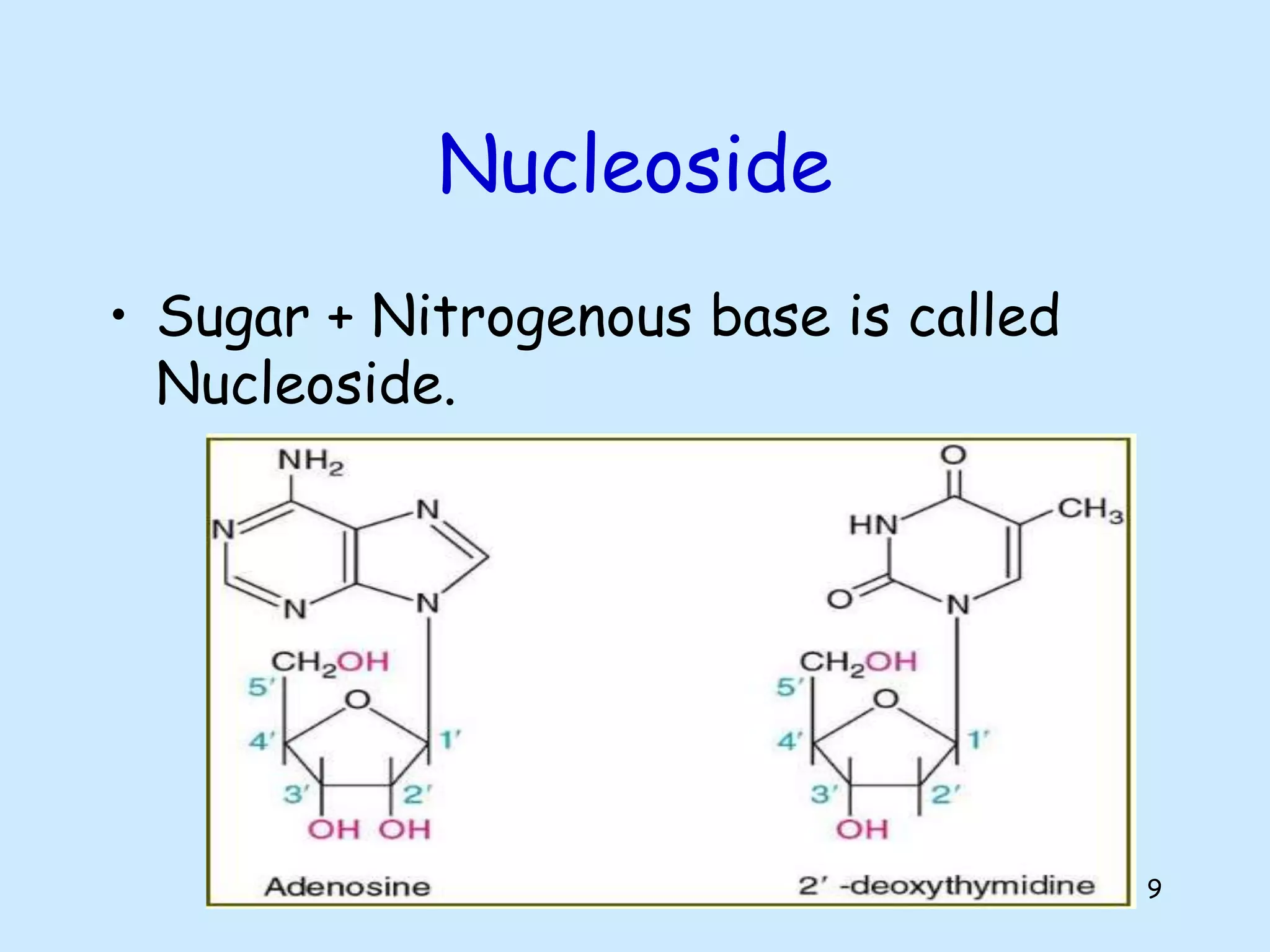
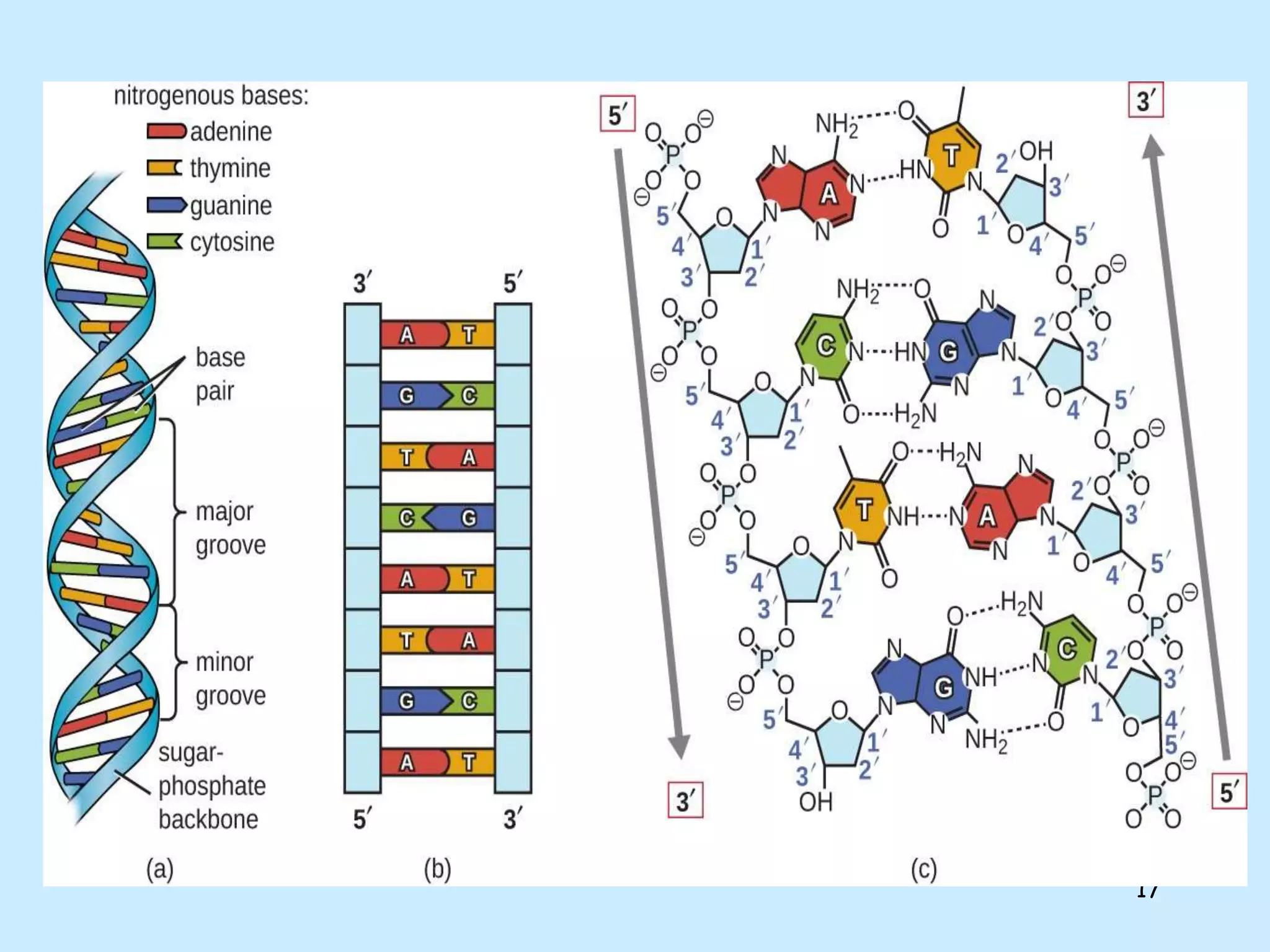
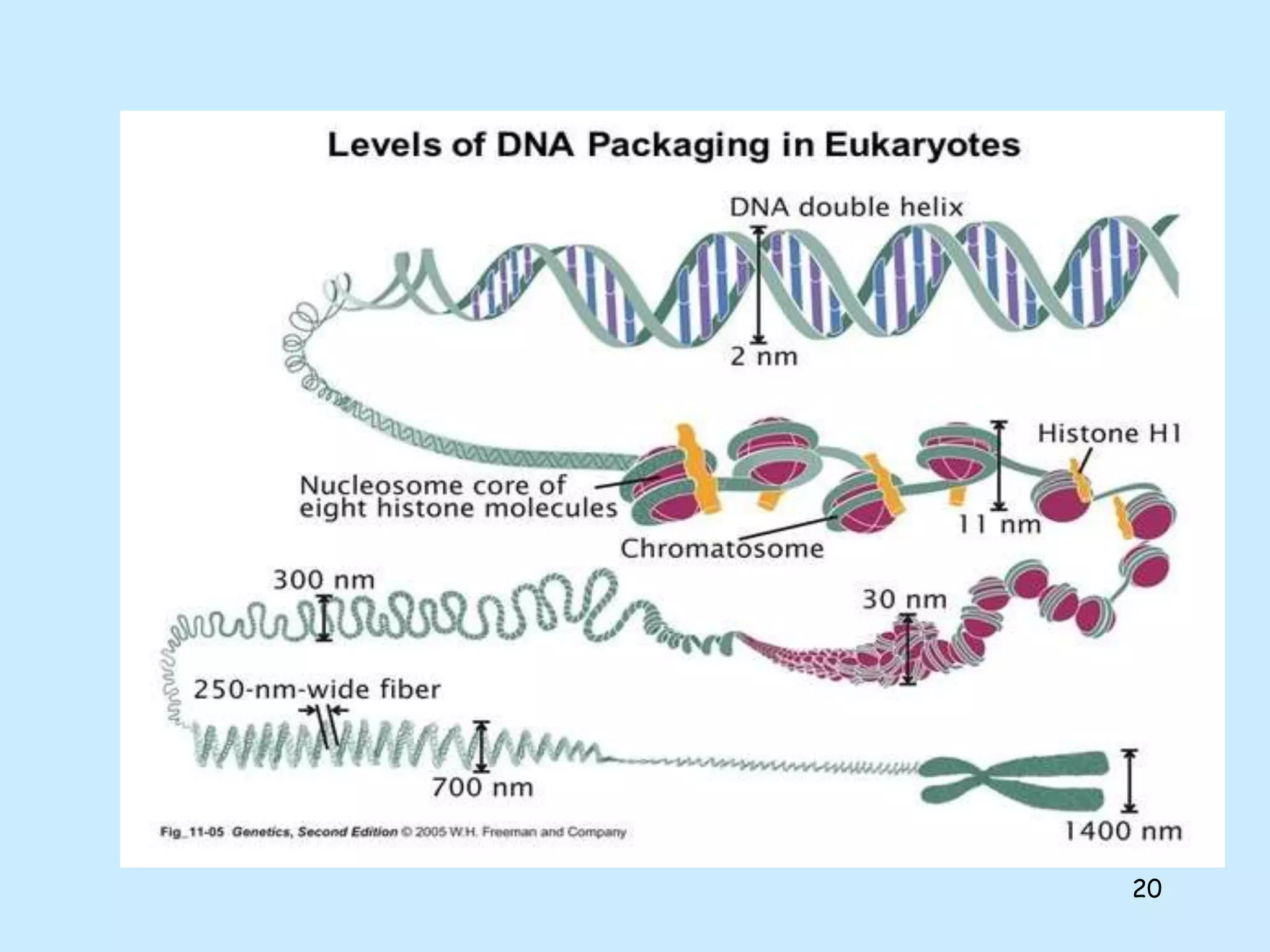
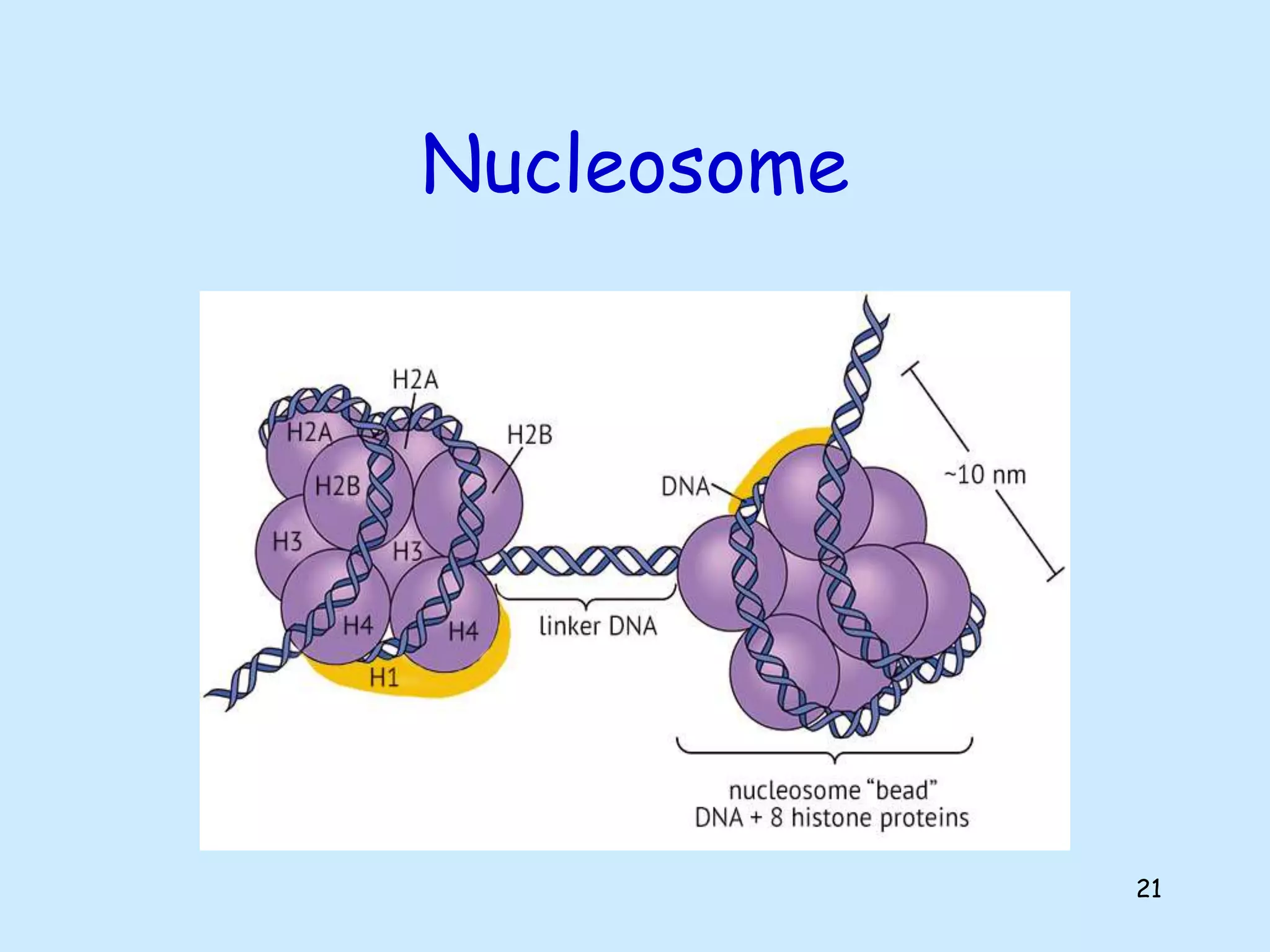
The lecture by Shahid Zadran discusses two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA, detailing their structures and components, which include nucleotides made up of nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphate groups. DNA is characterized by its double helix structure and Chargaff's rule, where adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine. The document also explains the primary and secondary structures of nucleic acids, emphasizing the importance of hydrogen bonds and the anti-parallel nature of DNA strands.