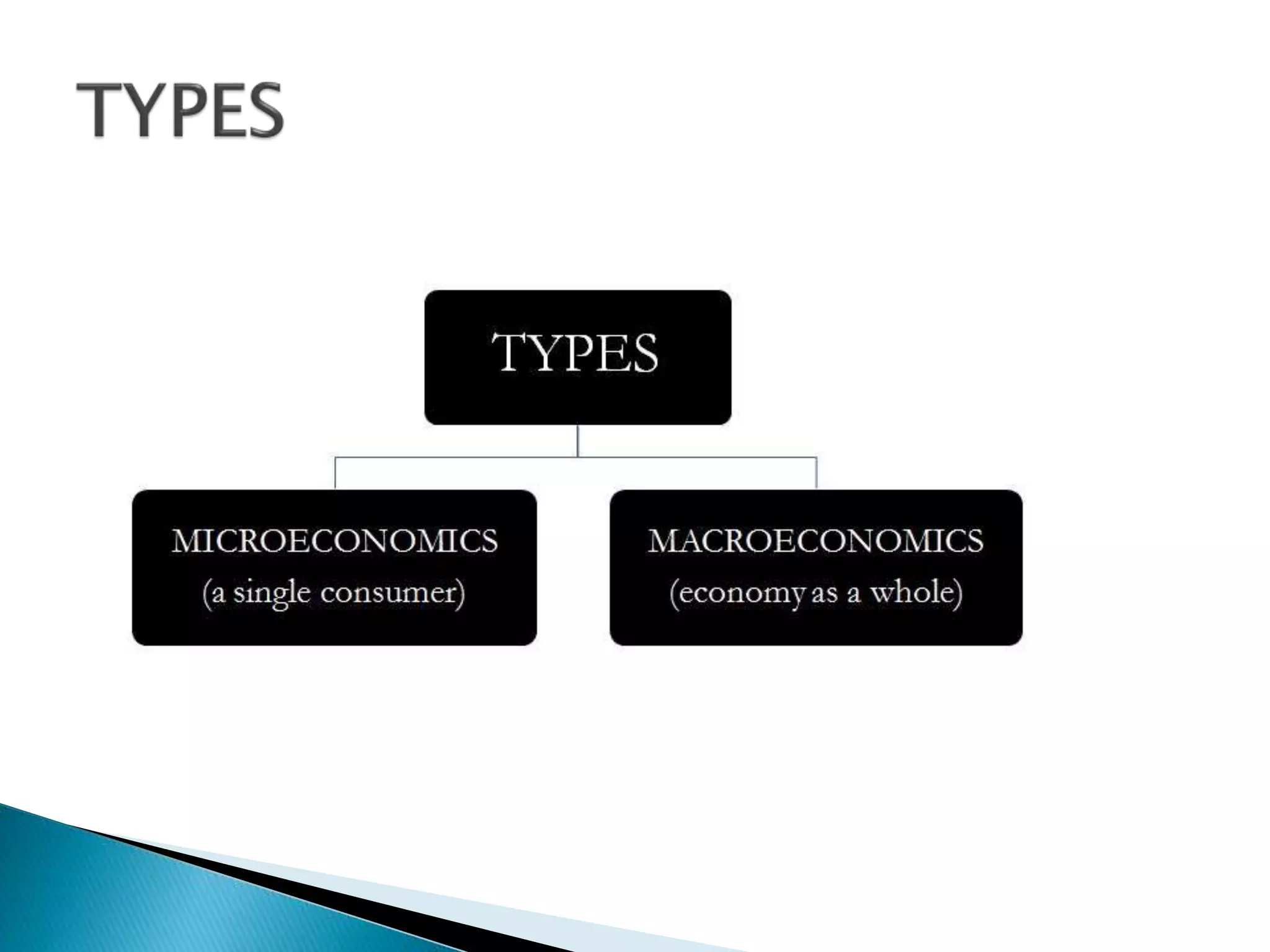
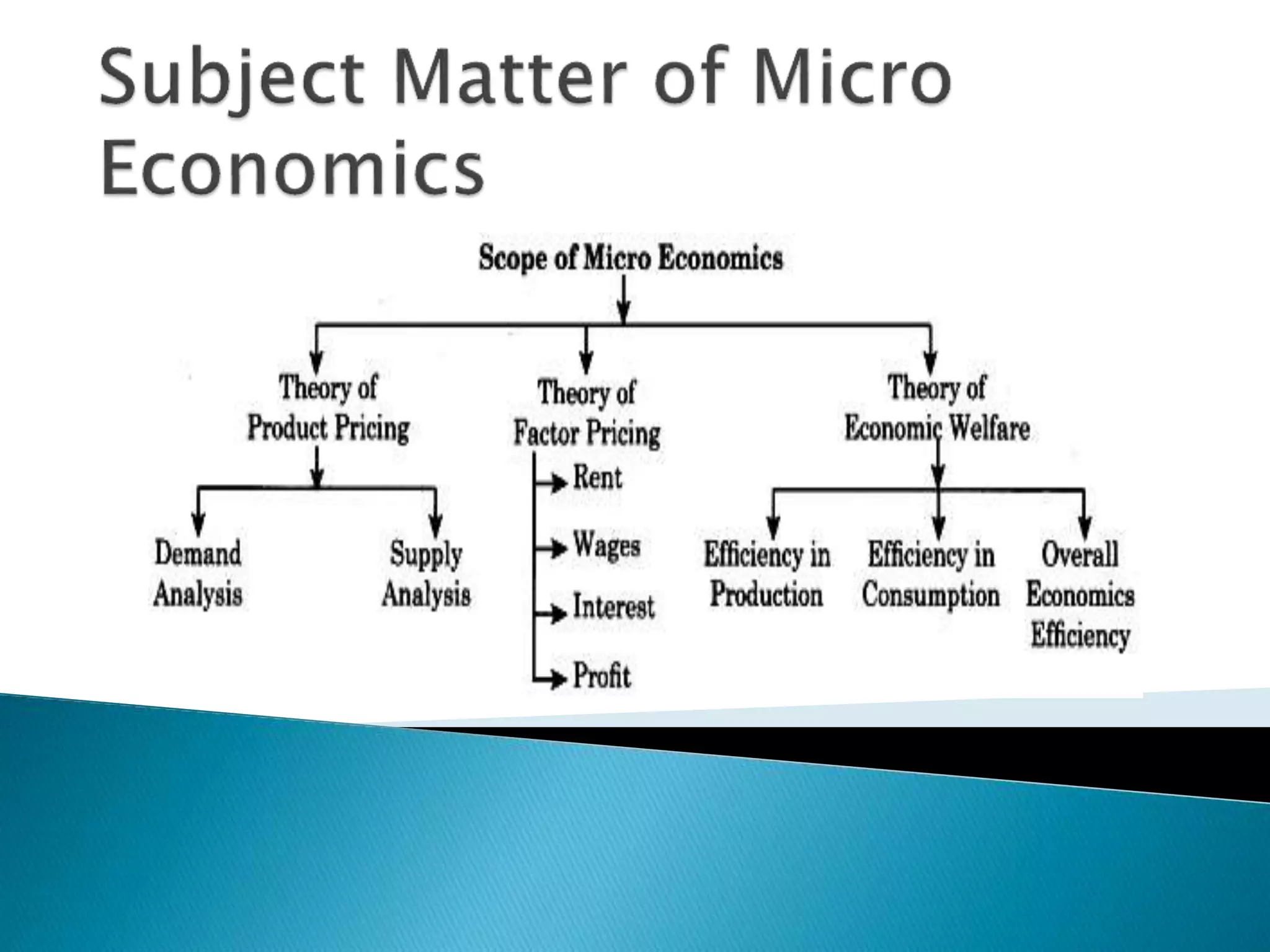
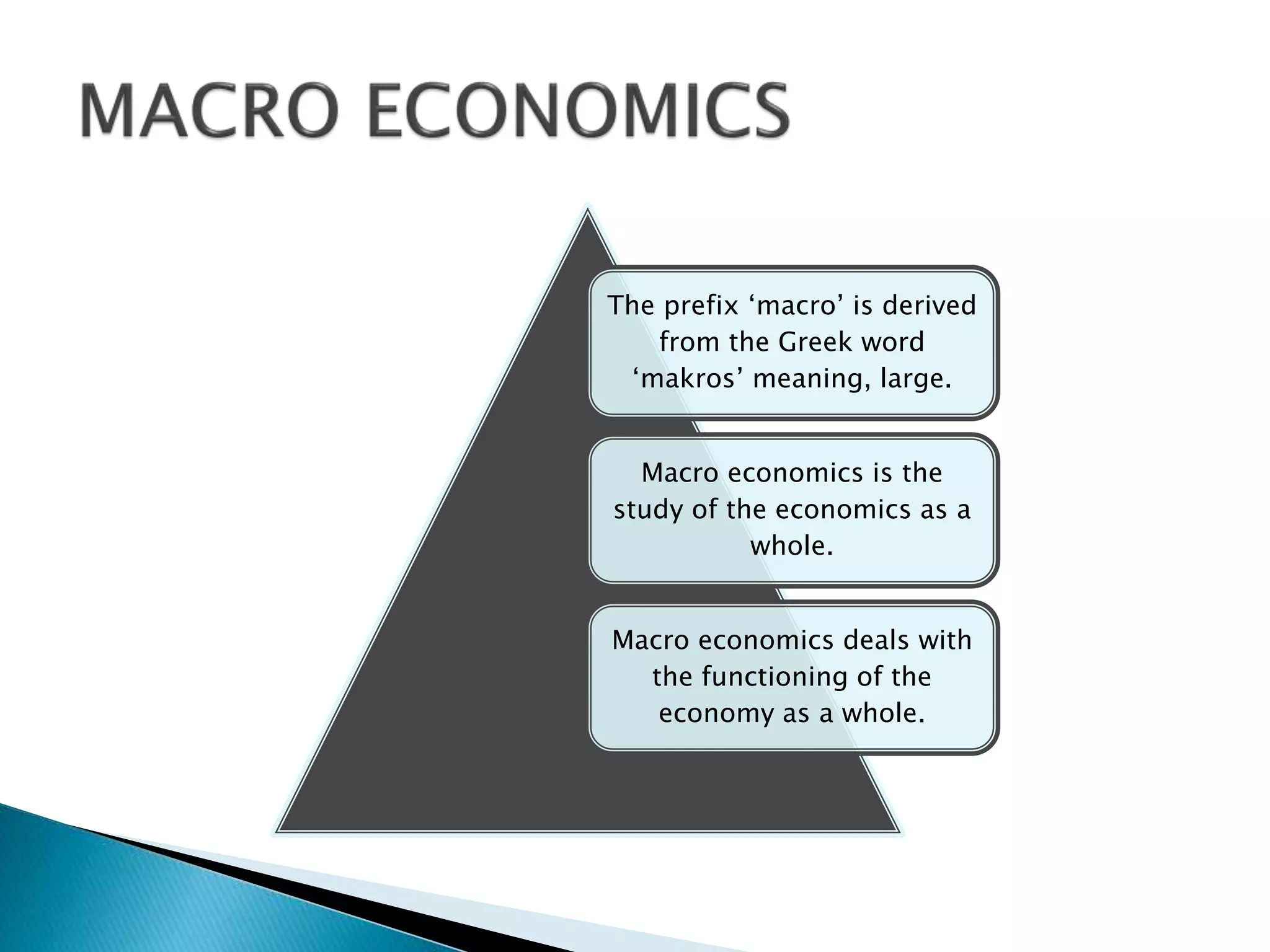
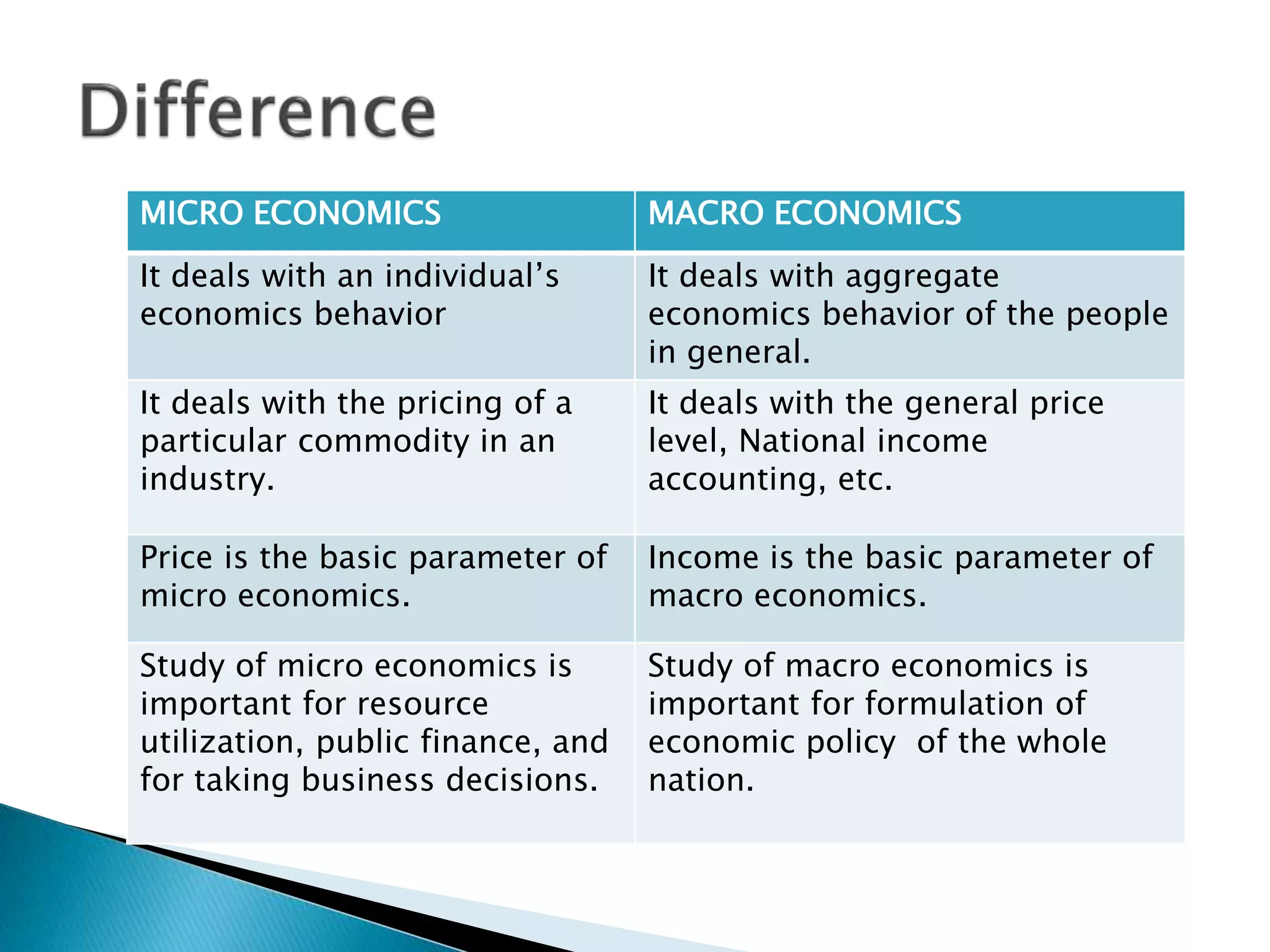
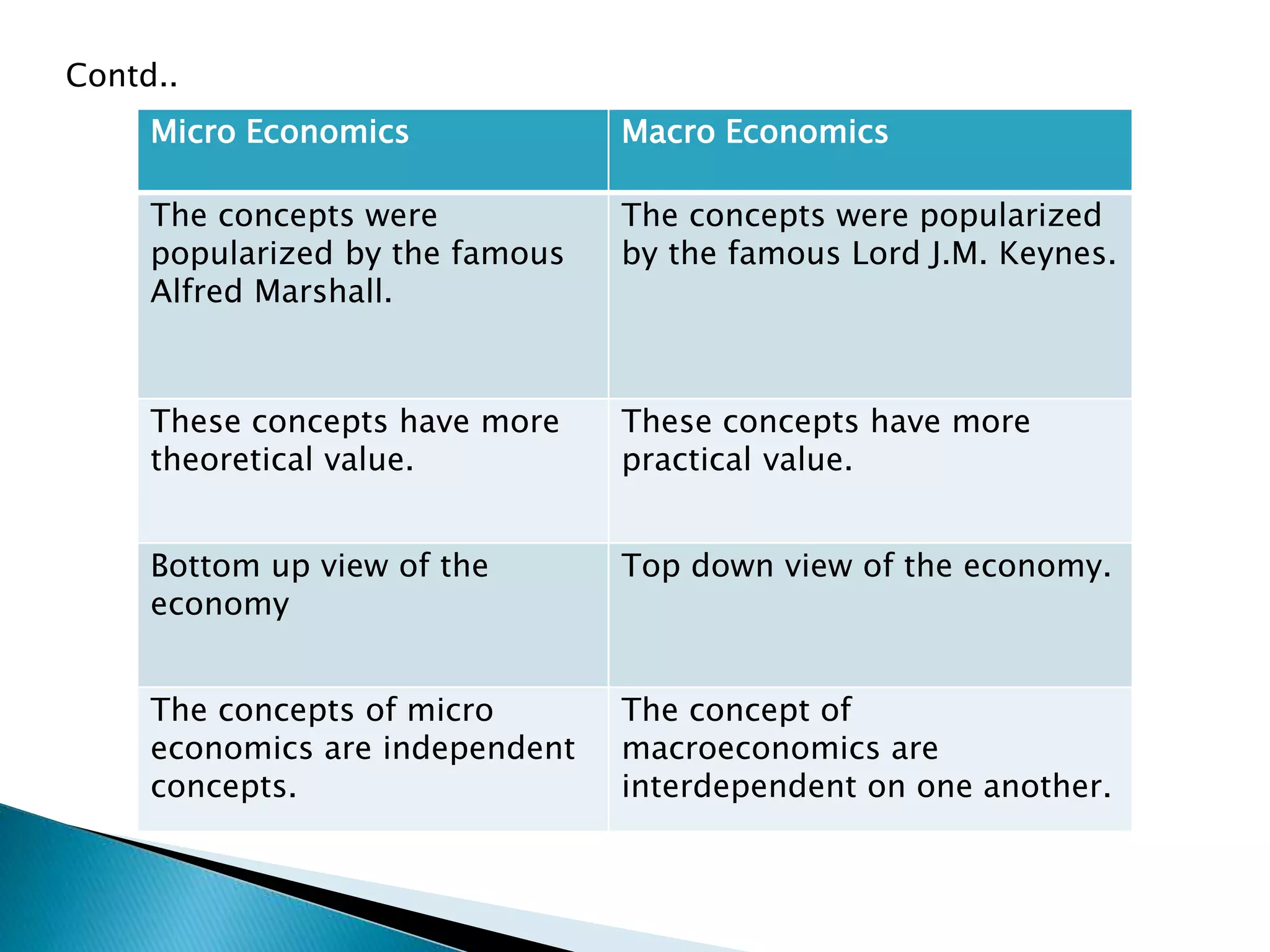
Microeconomics studies individual economic decision-making units and variables, like households, firms, and industries. It examines how these units interact in markets and how resource allocation, price determination, and production are determined. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, looks at aggregate economic measures for an entire economy, such as total output and income, unemployment rates, and price levels. It studies topics like national income accounting and the effects of fiscal and monetary policy. While microeconomics takes a bottom-up view of markets, macroeconomics takes a top-down perspective of the overall functioning of the economy.