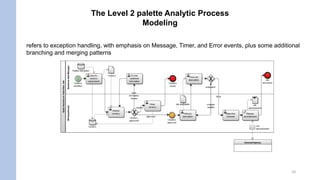
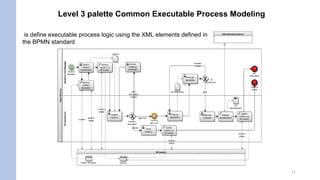
This document discusses key concepts in BPMN (Business Process Modeling Notation) modeling including:
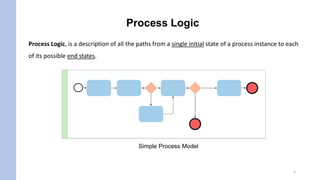
- Process logic describes all possible paths from start to end of a process instance.
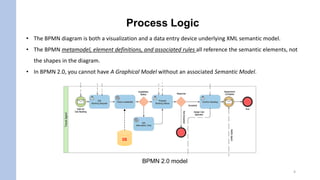
- A BPMN diagram represents both a visualization and underlying XML semantic model. The shapes do not define the model, rather they reference the underlying semantic elements.
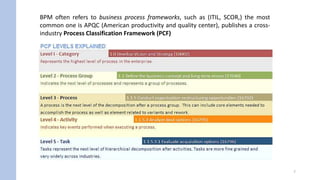
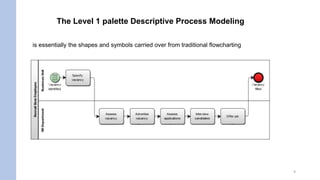
- Activities represent discrete units of work with a start and end, while a process is a sequence of activities from start to defined end states. Process modeling involves understanding how activities and processes are defined.