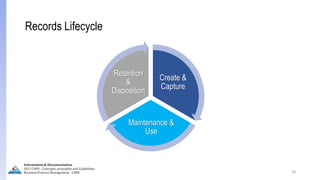
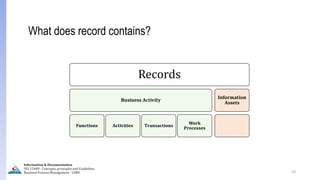
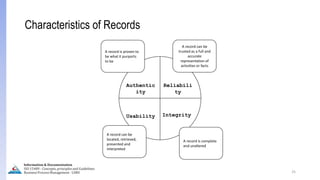
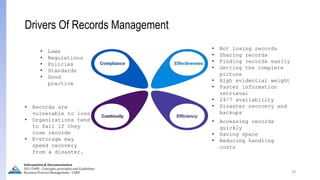
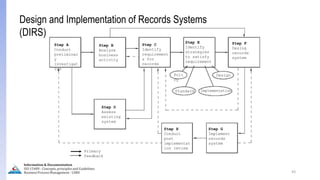
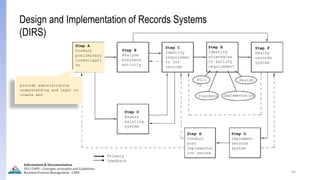
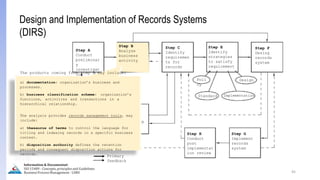
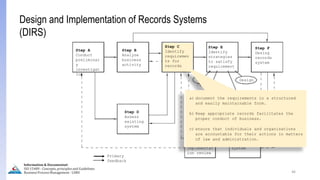
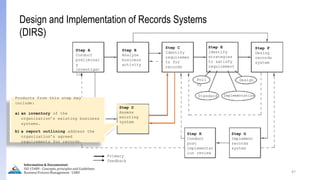
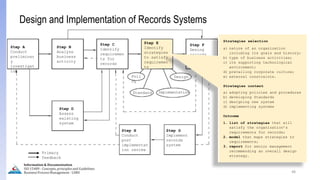
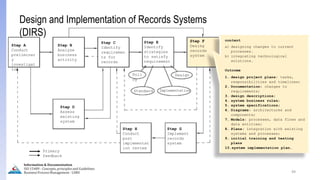
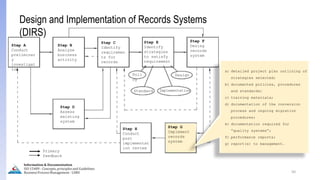
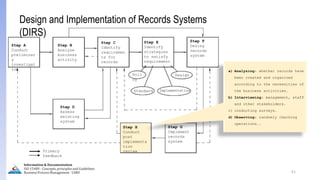
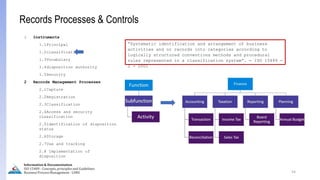
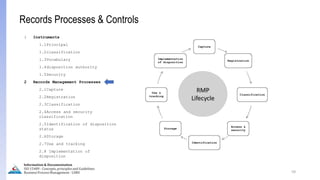
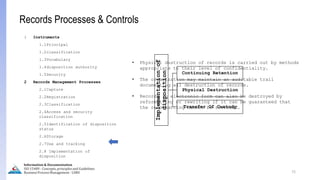
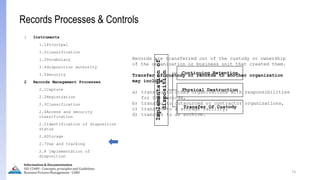
The document provides an overview of ISO 15489, which defines concepts and principles for records management. It discusses key aspects of records management including the records lifecycle of creation, maintenance, and disposition. It also defines what constitutes a record and a document, and outlines the importance of effective records management for organizations. Records management ensures records and information are captured and accessible to meet legal and operational needs.