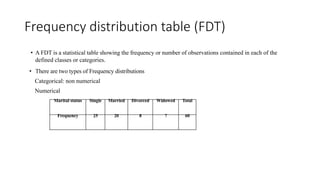
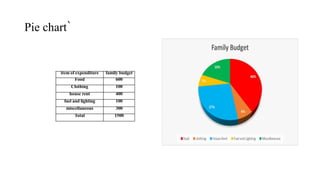
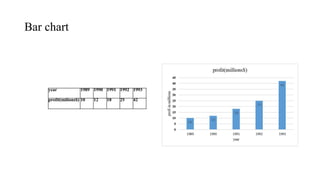
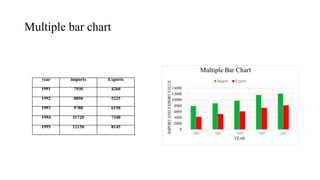
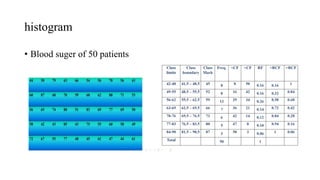
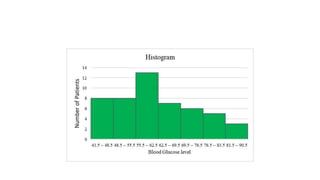
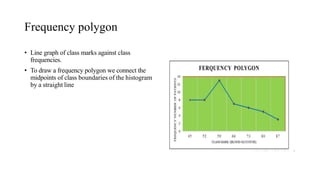
This document discusses various methods for presenting data, including textual, tabular, and graphical methods. It provides examples of each type of presentation: a frequency distribution table showing marital status data; a numerical frequency distribution of children per family; and examples of common graphs like pie charts, bar charts, histograms, and frequency polygons. The key methods discussed are tabular (e.g. frequency tables), bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, histograms, and frequency polygons for summarizing both categorical and numerical data visually.