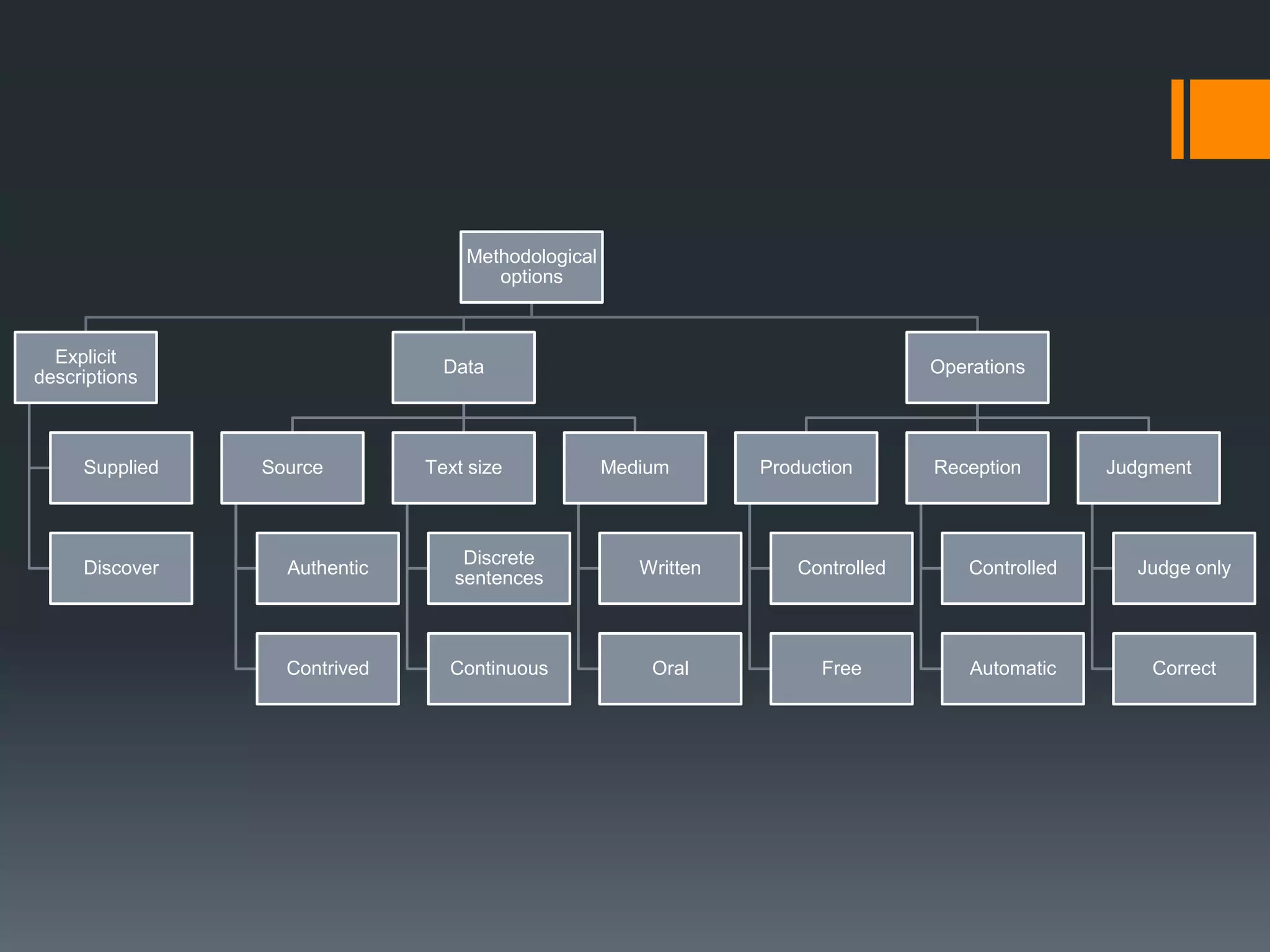
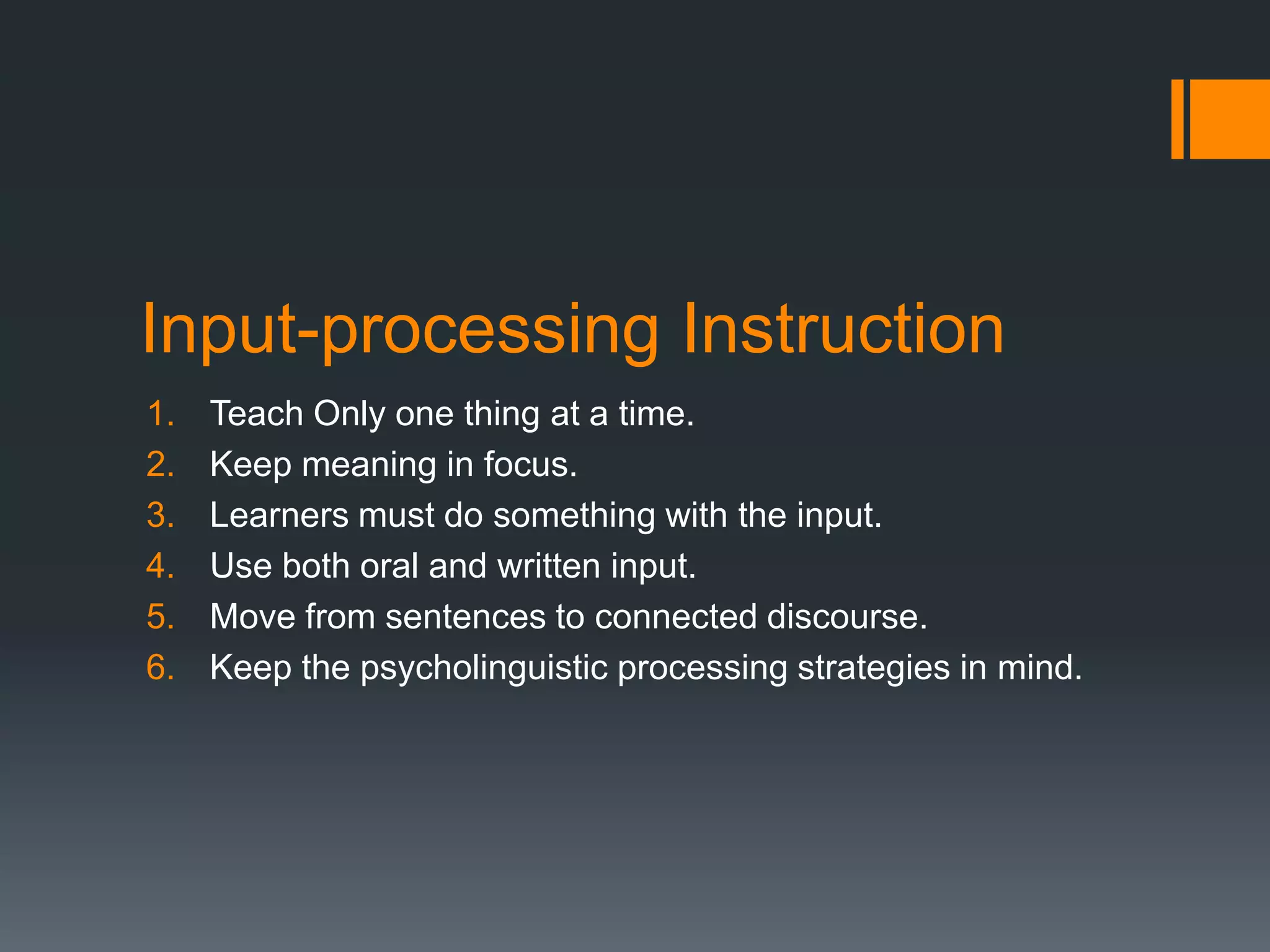
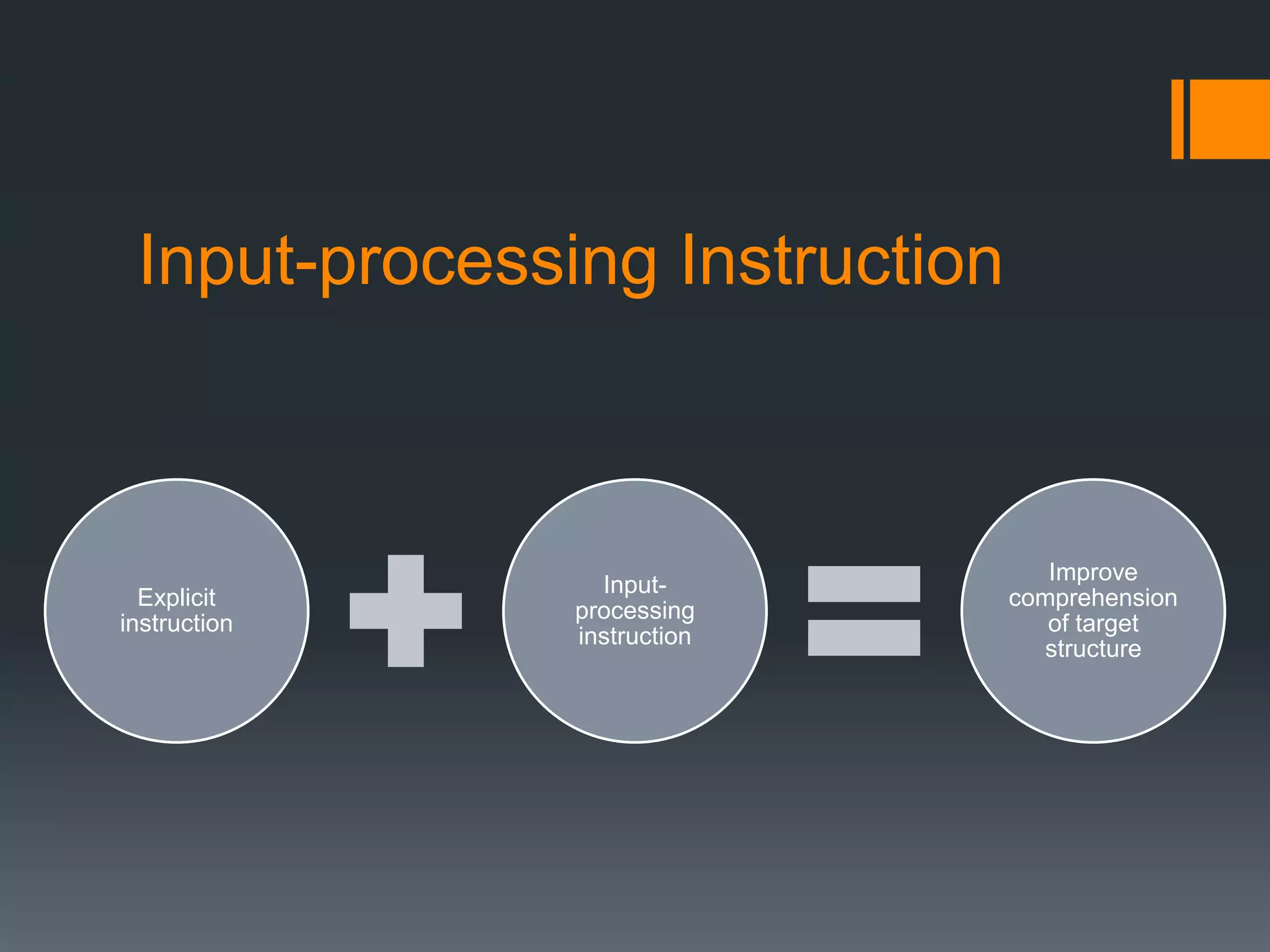
This document outlines and analyzes different methodological options for teaching grammar based on Rod Ellis's (2002) work. It finds that most grammar practice books rely on explicit descriptions and controlled production exercises. However, it suggests discovery-based learning, noticing grammatical features through input processing, and tasks that raise learner consciousness as more effective based on SLA research. The document concludes that while traditional approaches remain common, teaching materials should incorporate insights from SLA theory for more effective grammar instruction.