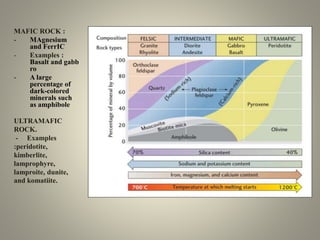
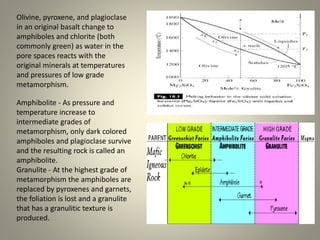
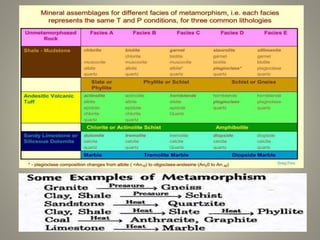
This document summarizes the metamorphism of different rock types including ultramafic, mafic, pelitic, and calcareous rocks. Ultramafic rocks like peridotite and serpentinite can transform into serpentine, anthophyllite, olivine, and pyroxene minerals. Mafic rocks like basalt metamorphose into amphiboles and chlorite at low grades and amphibolite at intermediate grades, and granulite at highest grades. Pelitic rocks contain chlorite, muscovite, quartz and albite. Calcareous rocks like limestone coarsen but change little, while impure limestone forms diverse calcium-magnesium-sil