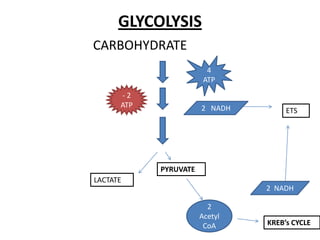
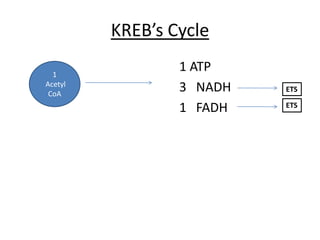
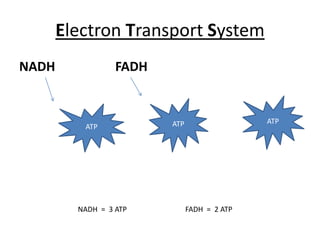
The document summarizes different metabolic pathways that cells use to generate energy in the form of ATP. It discusses the phosphagen system which provides a quick burst of energy through creatine phosphate. Glycolysis breaks down carbohydrates to generate some ATP along with NADH. The Krebs cycle further breaks down products from glycolysis to produce more ATP, NADH, and FADH which feed into the electron transport system to generate the most ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Aerobic glycolysis of one carbohydrate molecule can ultimately generate 38 ATP through these metabolic pathways.