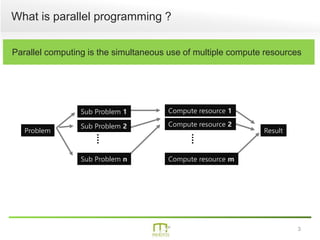
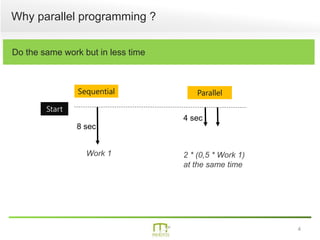
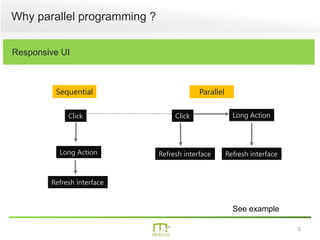
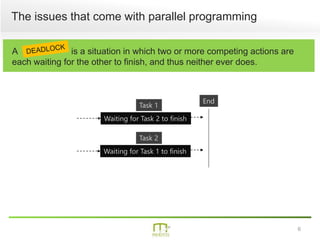
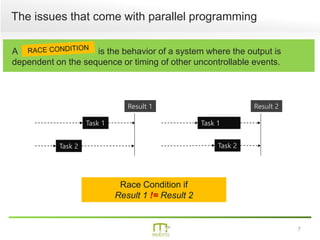
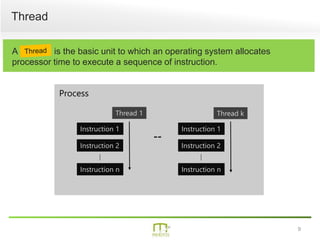
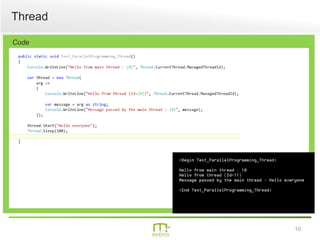
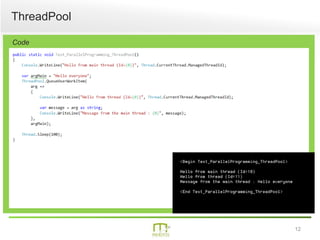
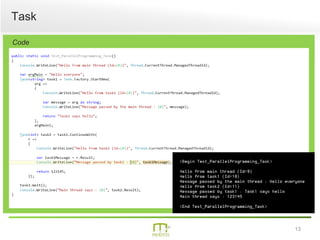
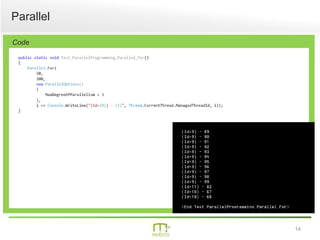
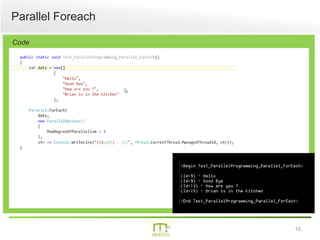
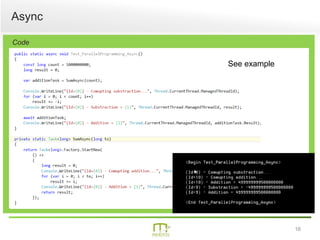
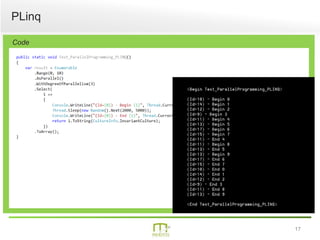
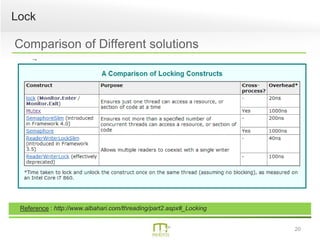
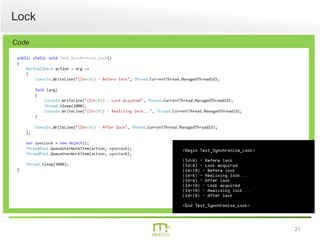
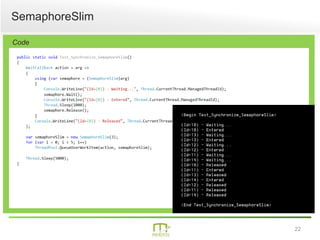
This document summarizes a presentation on parallel programming in .NET. It introduces parallel programming and why it is useful for performing work faster and creating responsive user interfaces. It discusses common issues like deadlocks and race conditions. It then covers different techniques for parallel programming in C#, including using threads, thread pools, tasks, Parallel class, async programming, and PLINQ. It also discusses synchronization techniques like locks, mutexes, and signaling with wait/pulse and barriers. Finally, it discusses storing shared items and provides an overview of thread-safe collection classes in .NET.