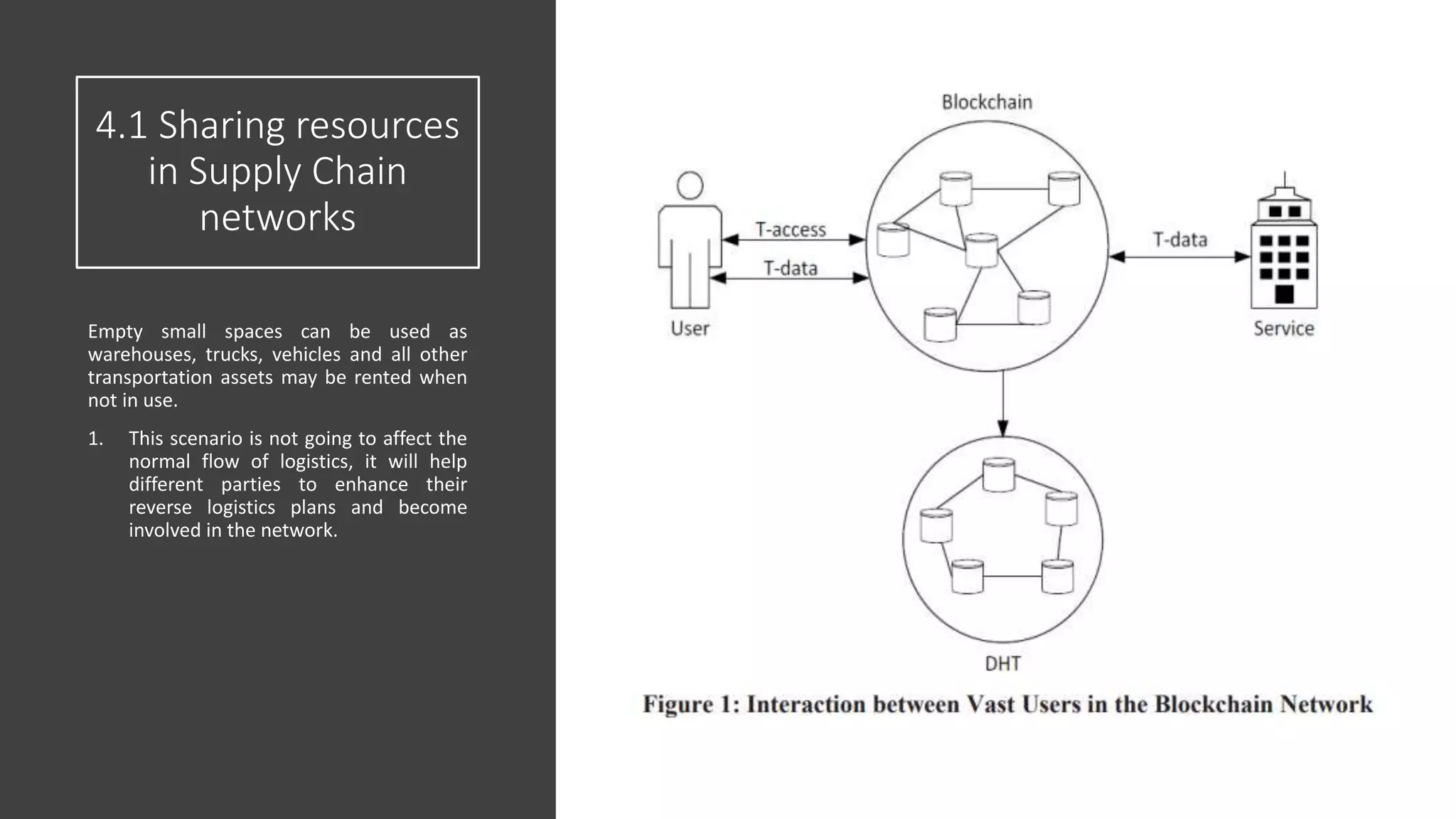
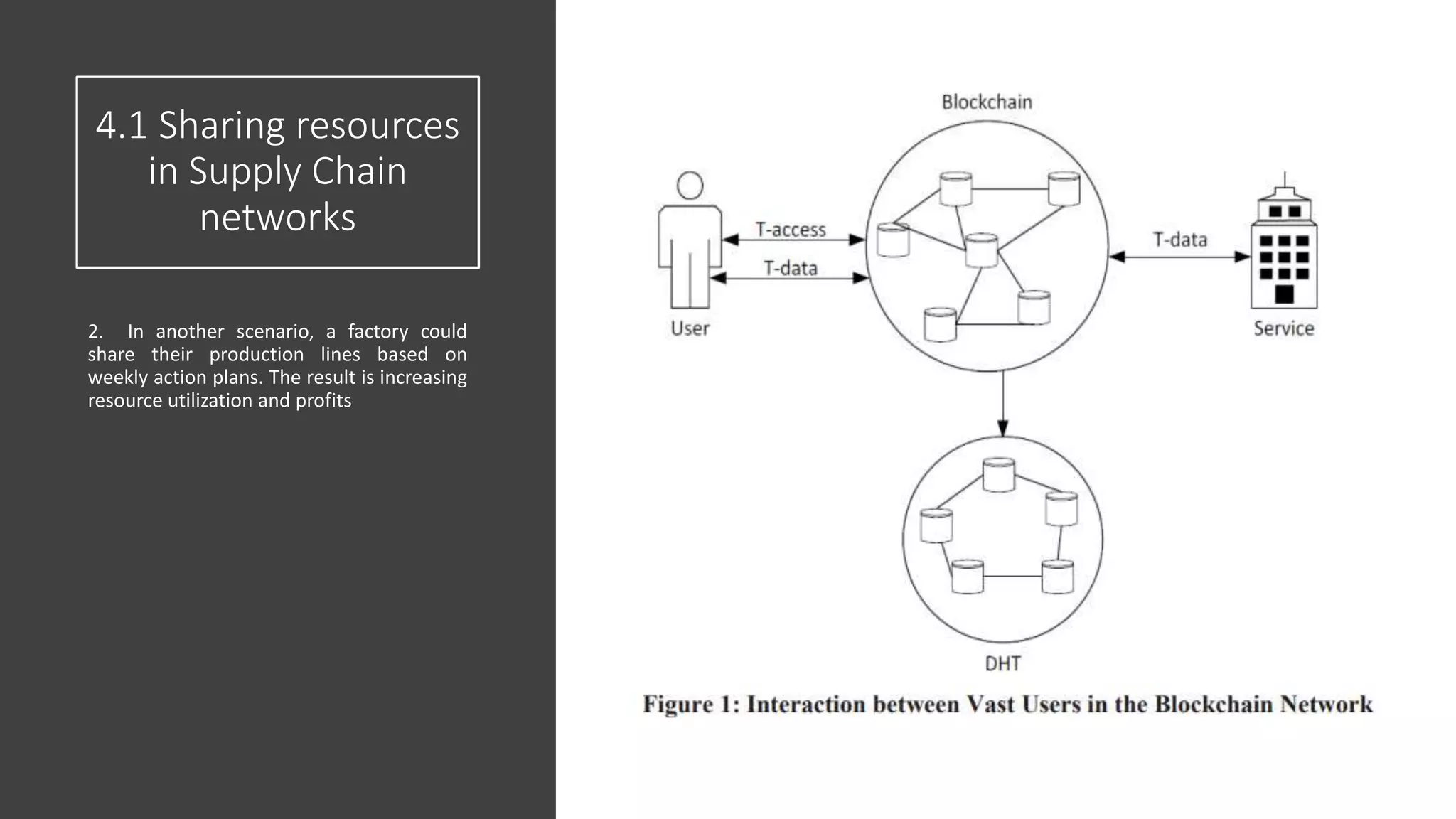
The document discusses the integration of blockchain technology with supply chain management to enhance transparency, traceability, and resource sharing among global networks. It outlines previous works, examines various applications of blockchain, and proposes scenarios for improving supply chain performance through better data management. The conclusion emphasizes that applying blockchain can address existing challenges in supply chains and improve overall efficiency and profitability.