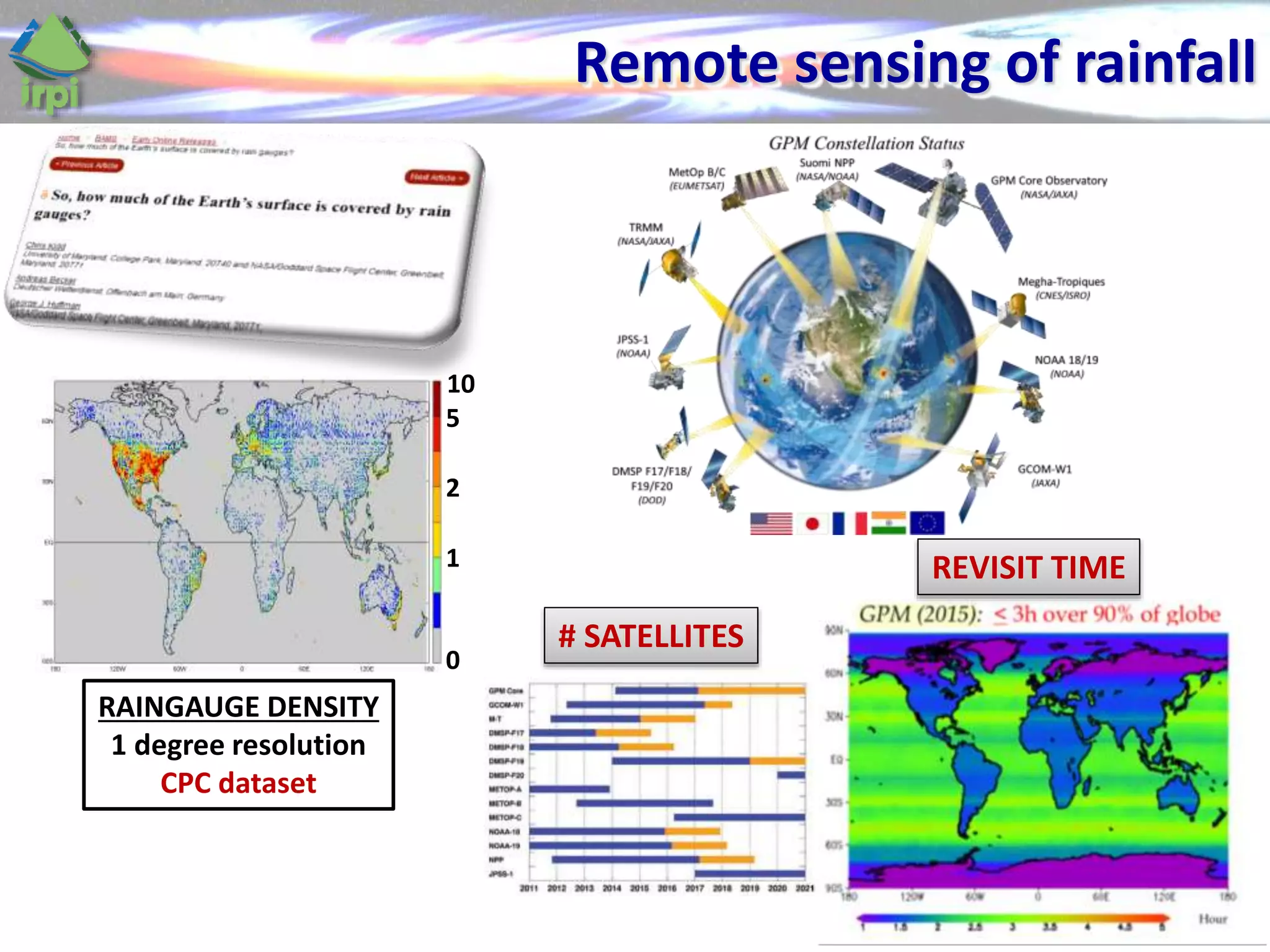
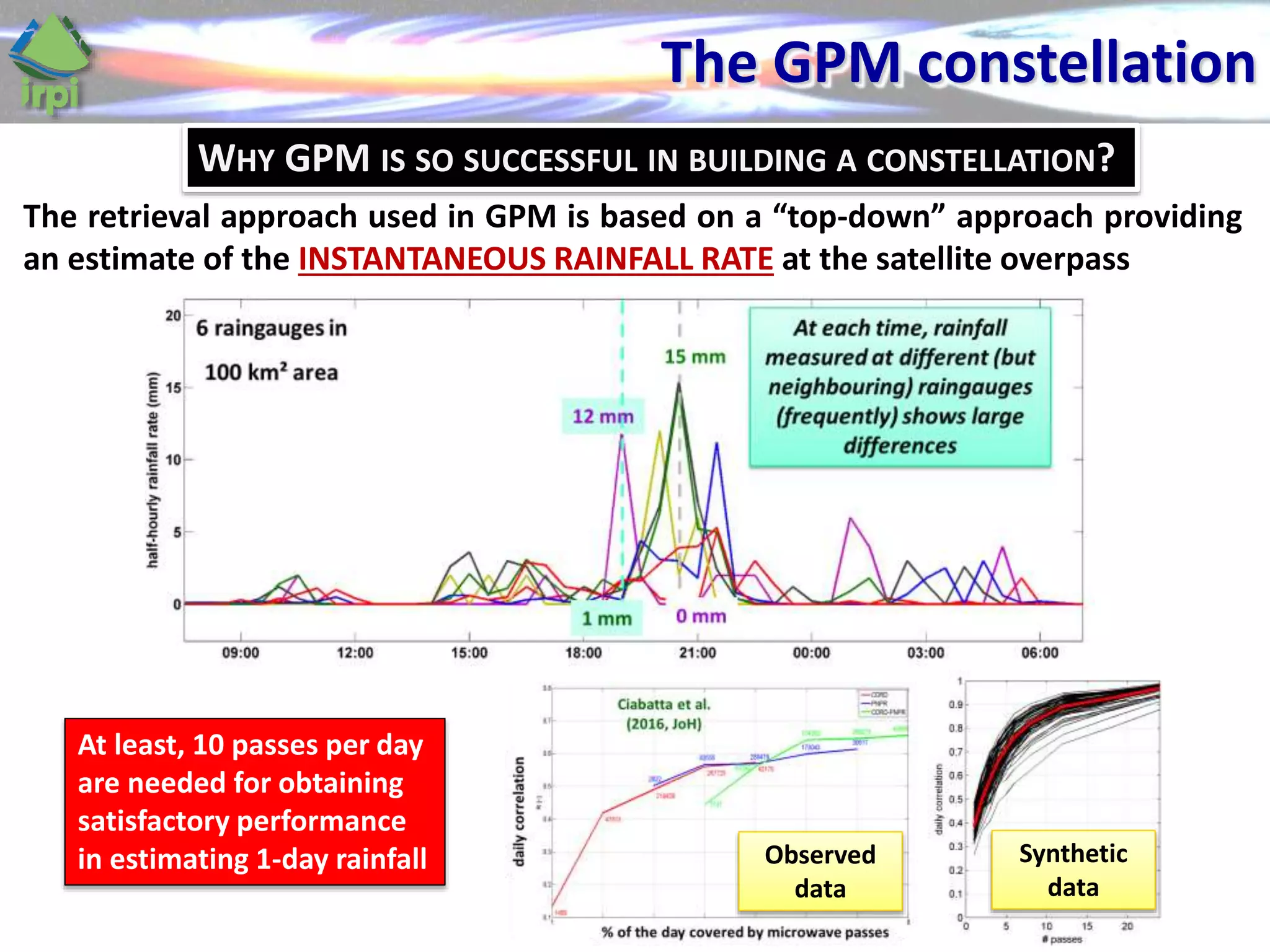
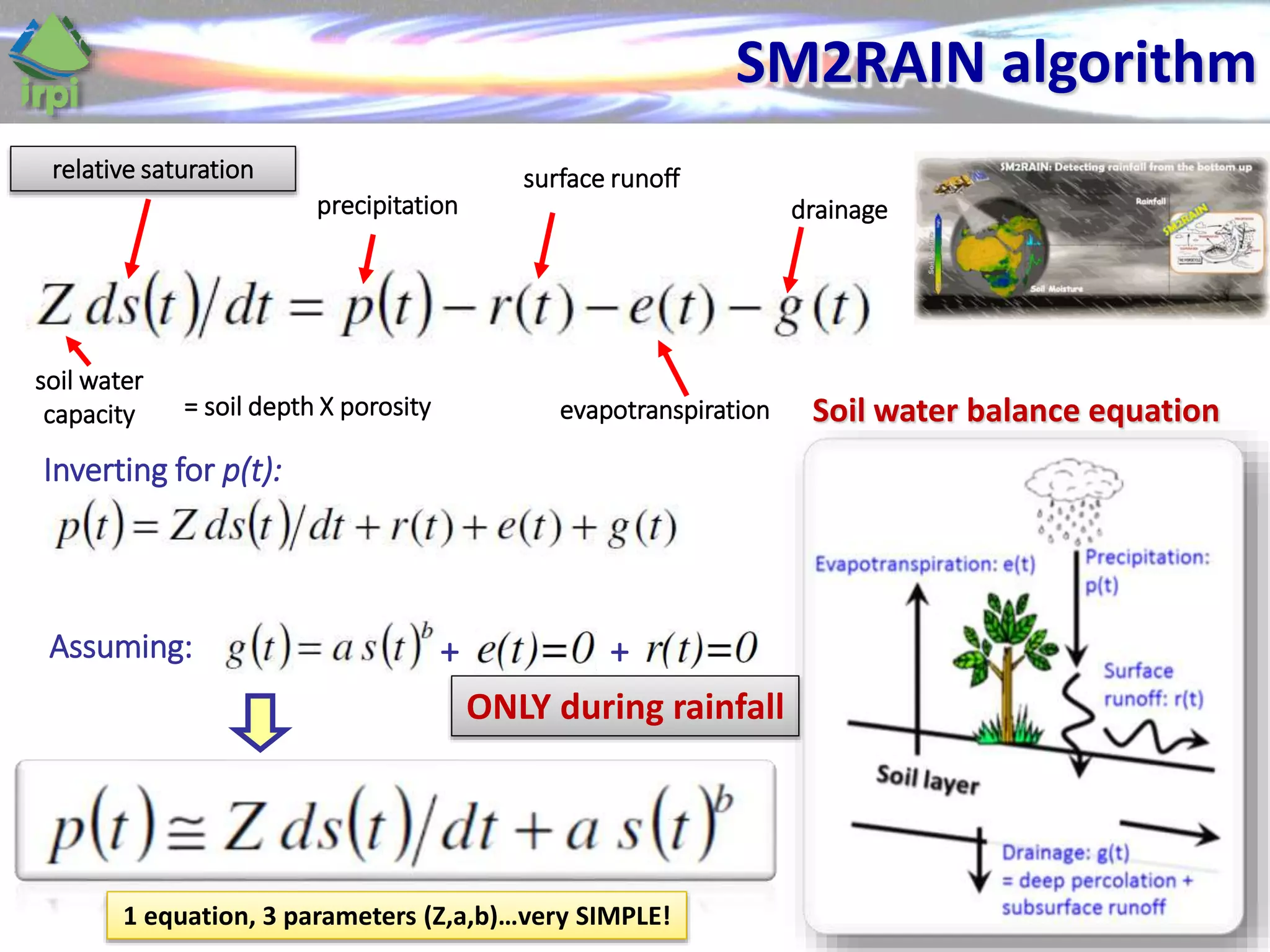
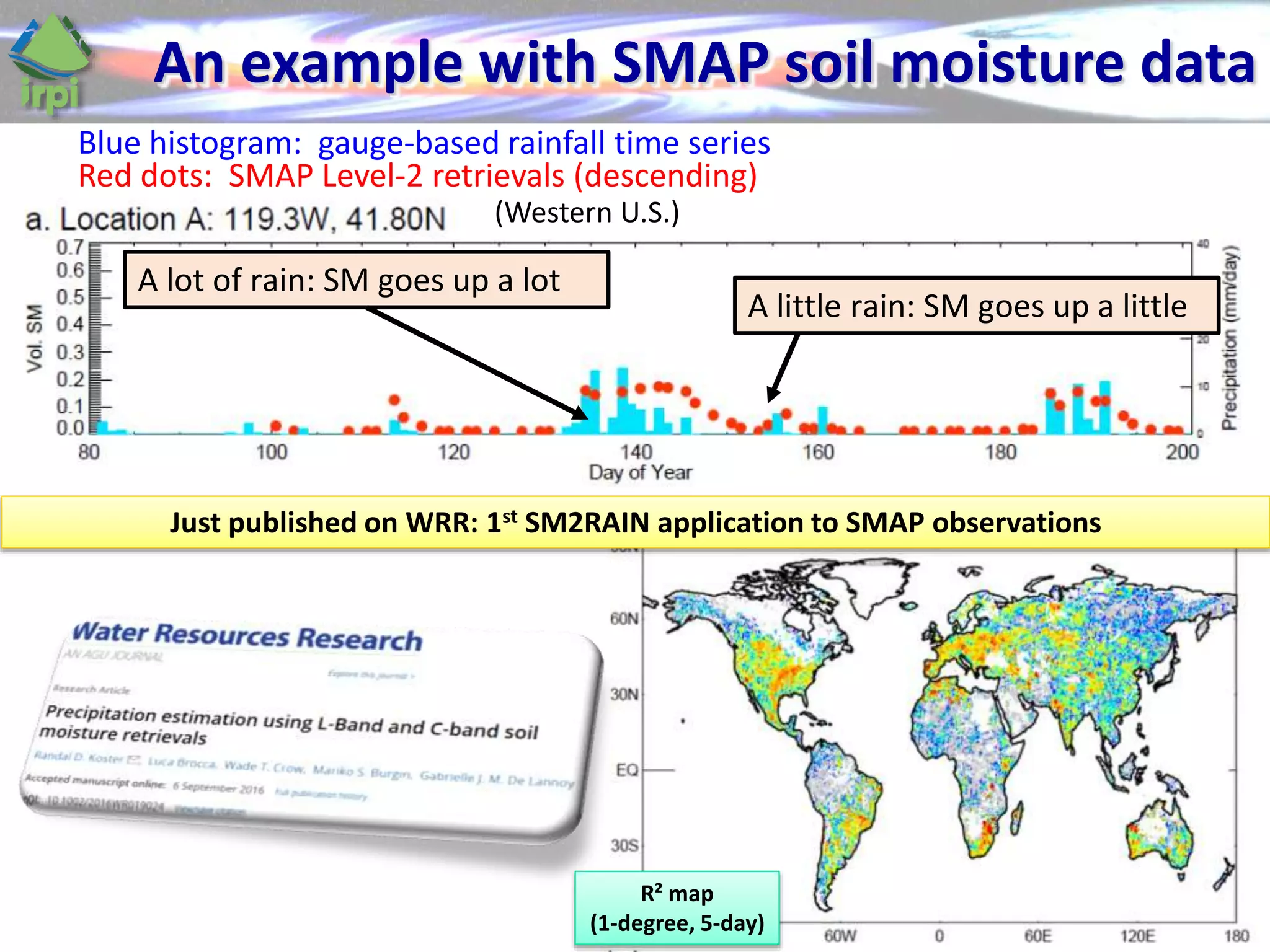
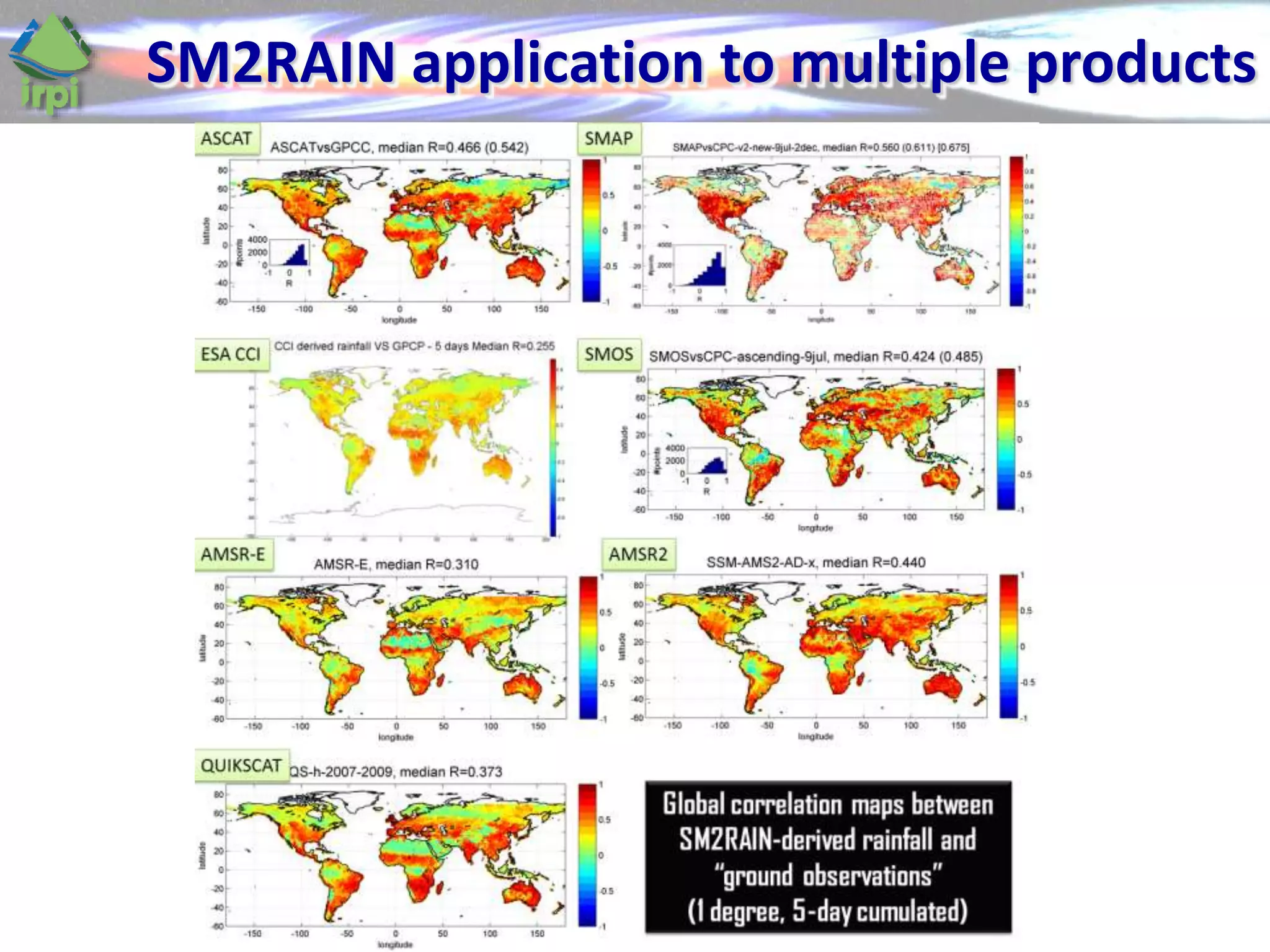
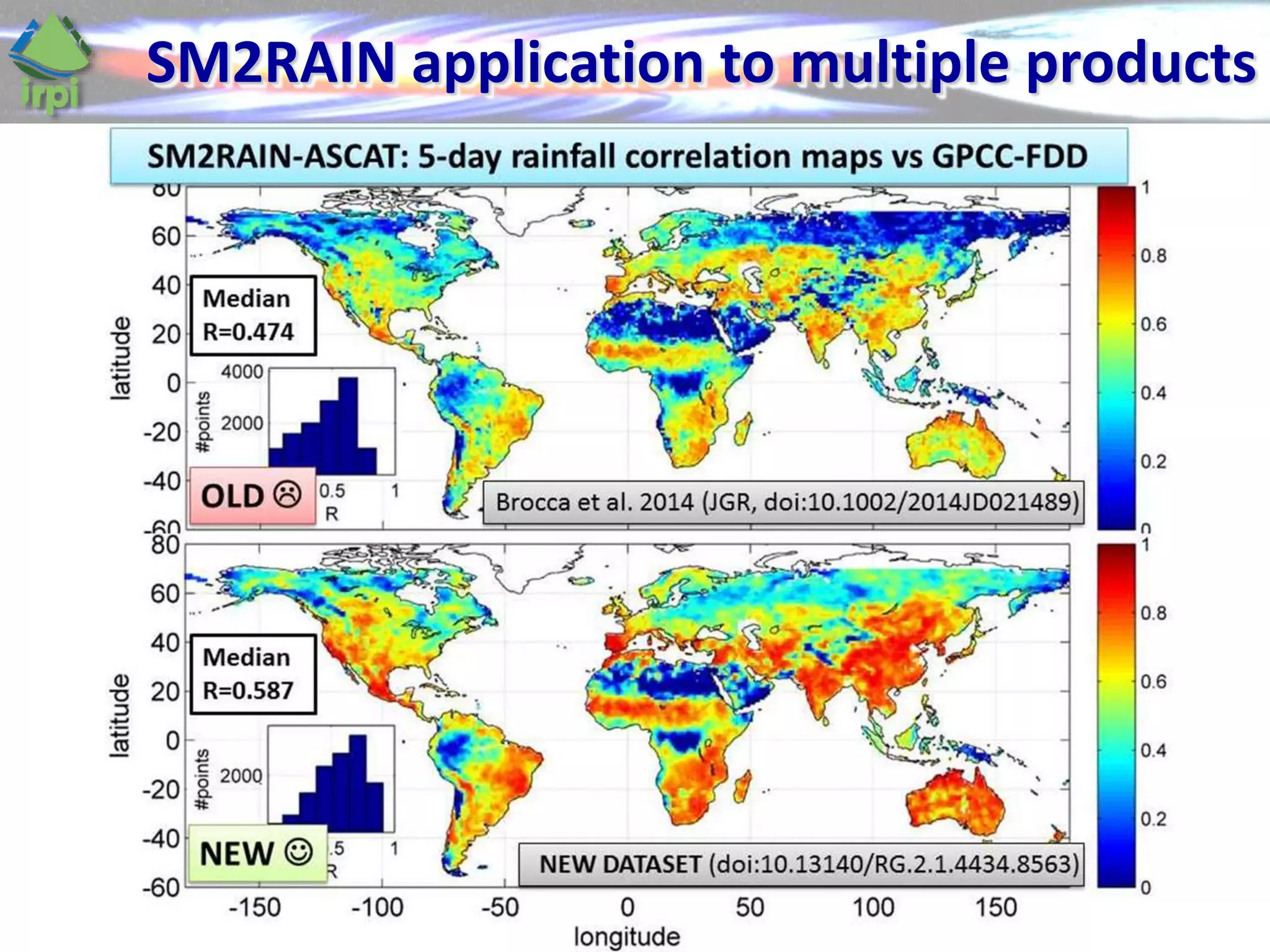
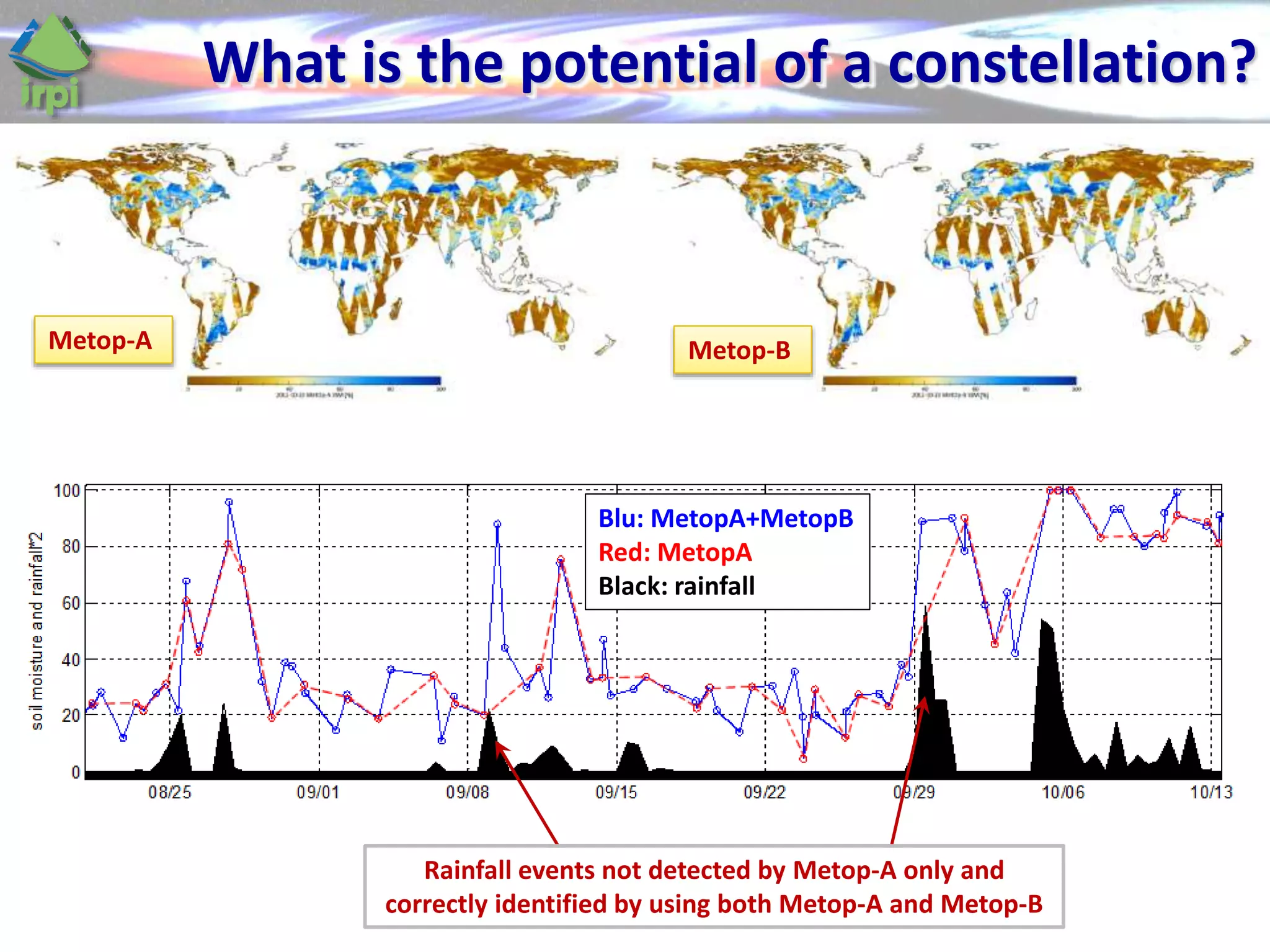
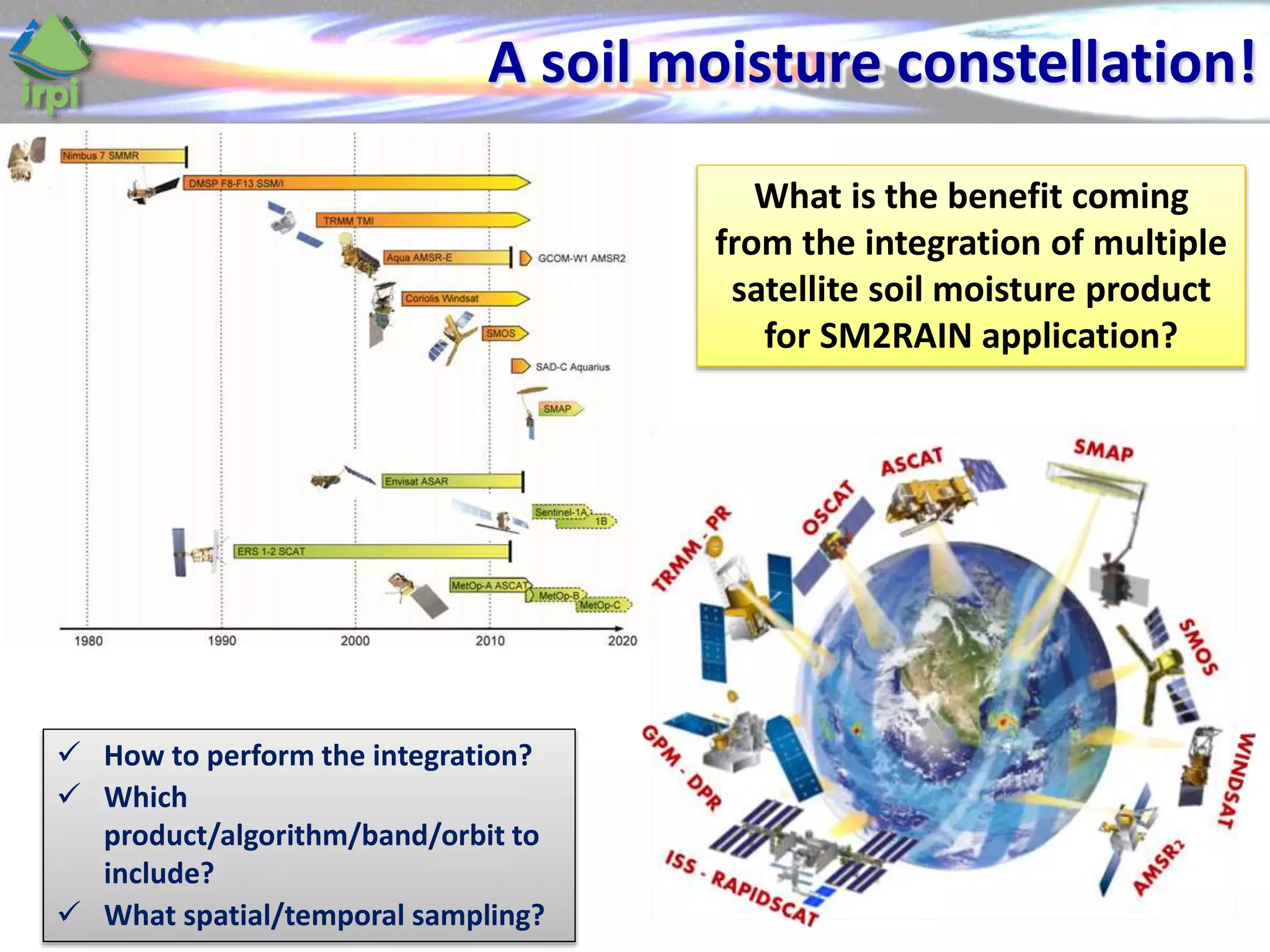
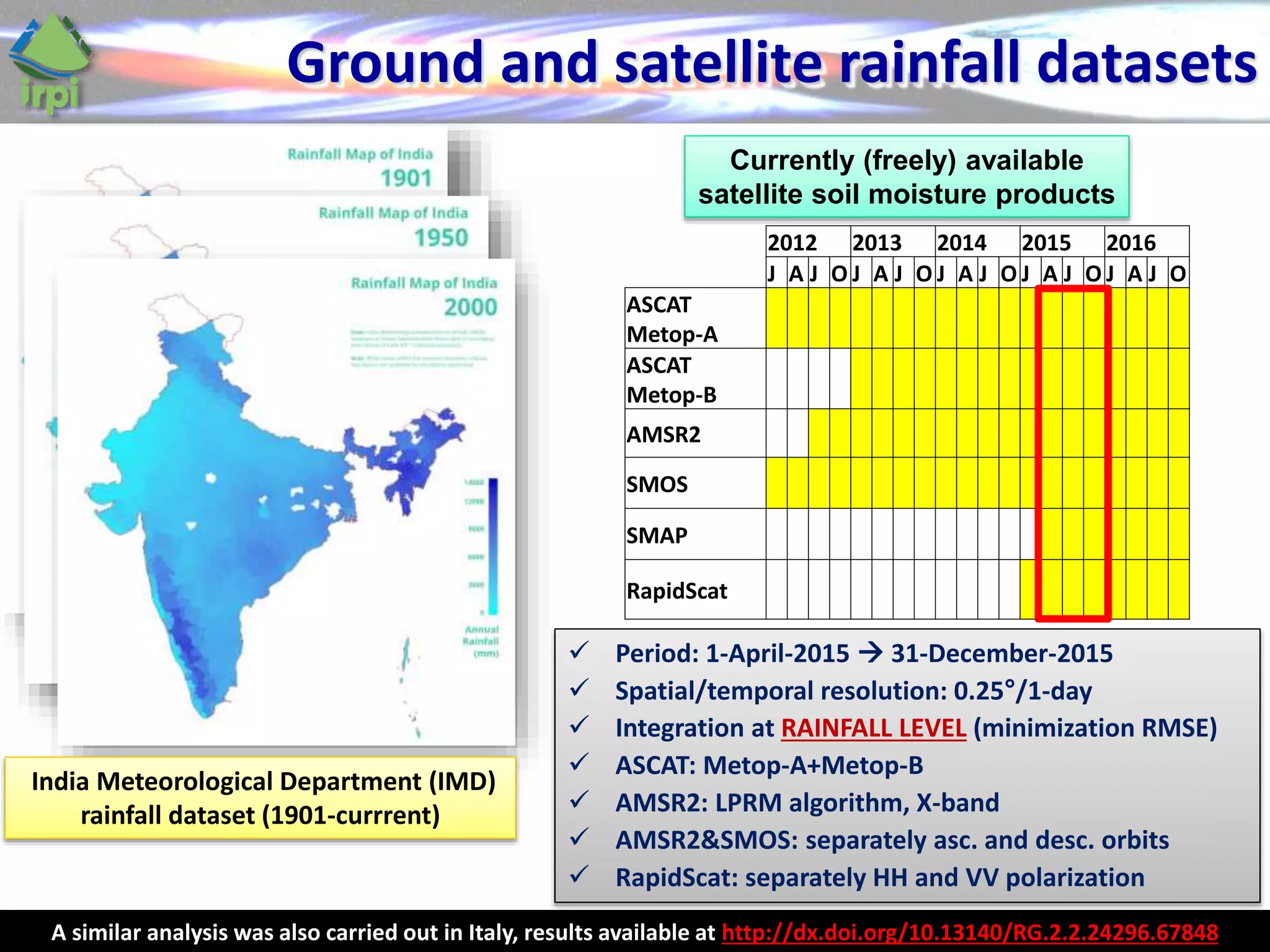
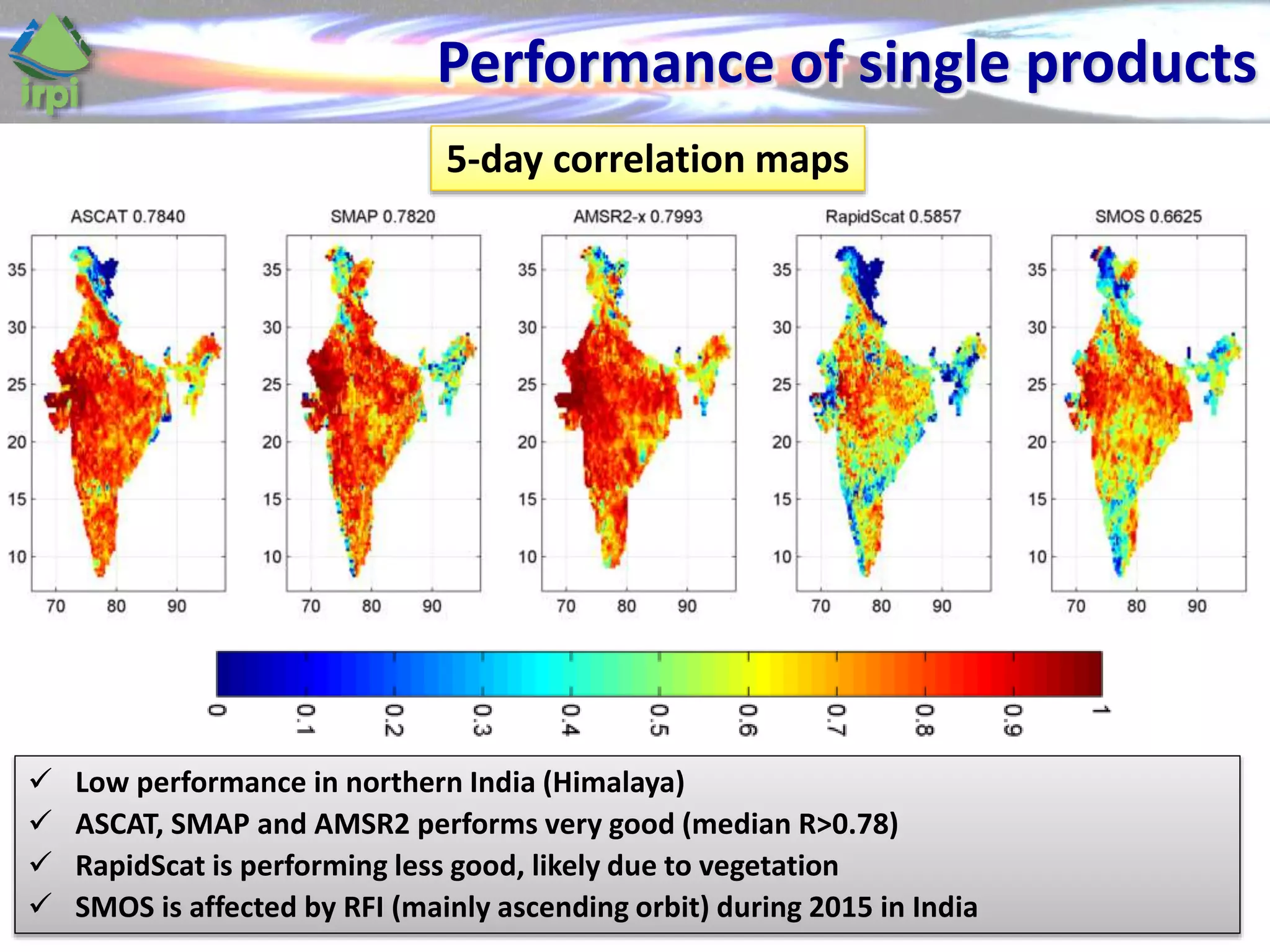
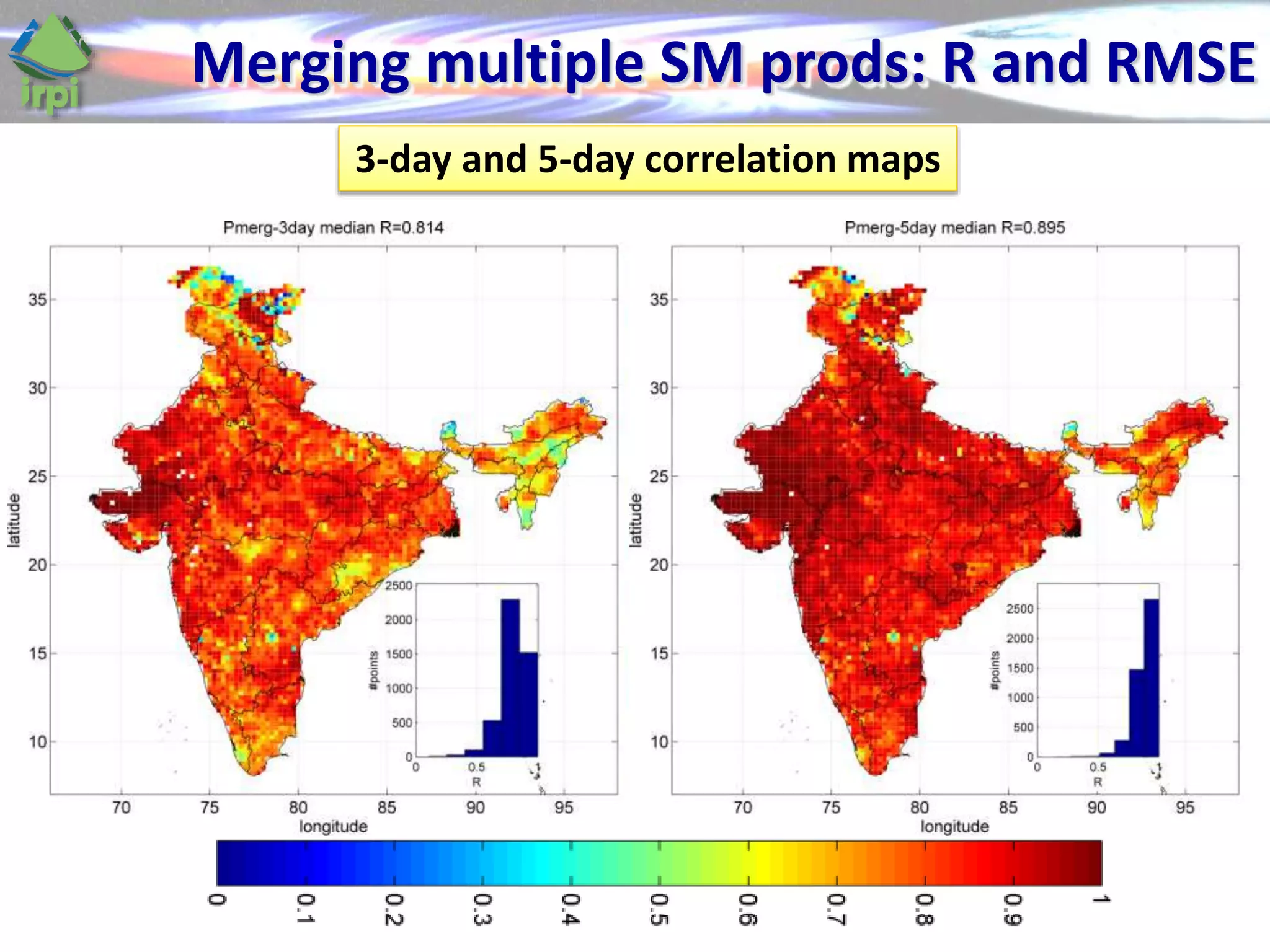
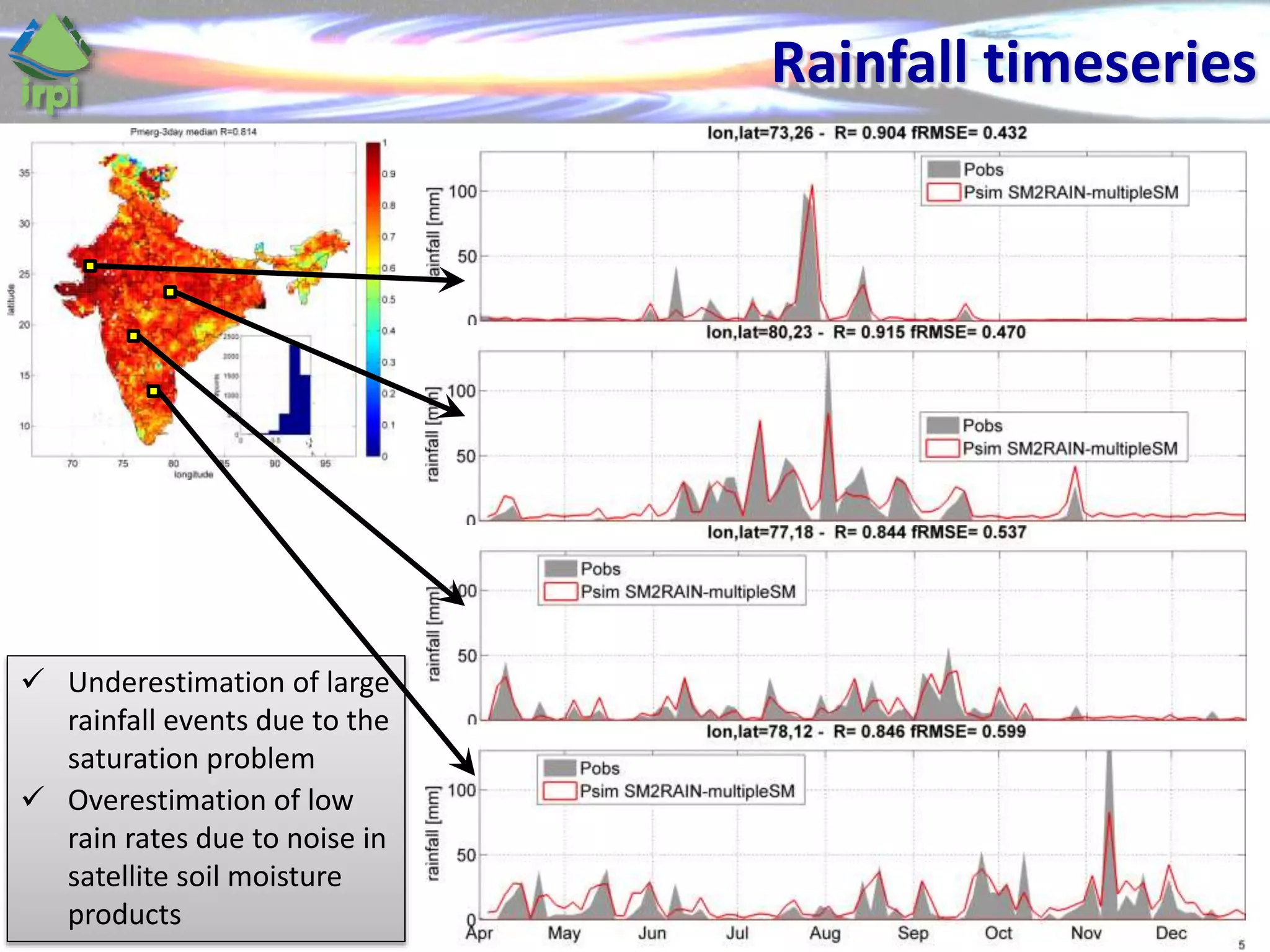
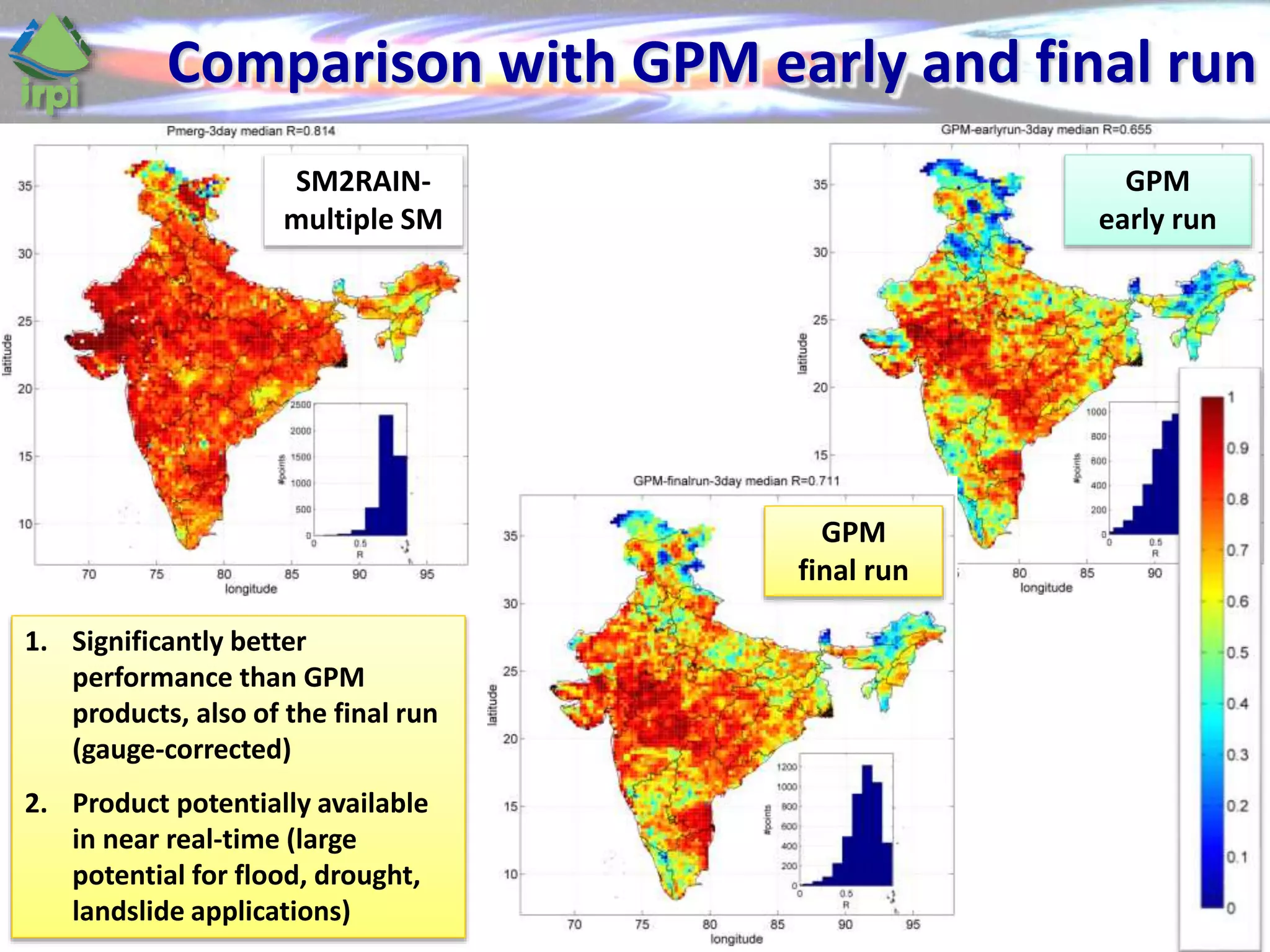
The document discusses the use of satellite soil moisture data for rainfall estimation through a new approach called 'sm2rain'. It highlights the algorithm's performance in estimating rainfall accurately by integrating multiple satellite soil moisture products and compares it with traditional methods. The results indicate significant improvement in rainfall estimation, especially beneficial for flood and drought management.