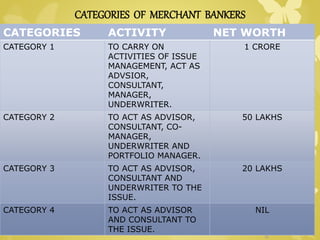
The document discusses the history and evolution of merchant banking in India. It provides details about modern merchant banking services, categories of merchant bankers based on net worth, and differences between merchant banks and commercial banks. Key points covered include that merchant banking originated in Italy and France in the 17th-18th centuries and was introduced to India through Grindlays Bank in 1967. Modern merchant banks provide services like management advising, underwriting, and portfolio management.