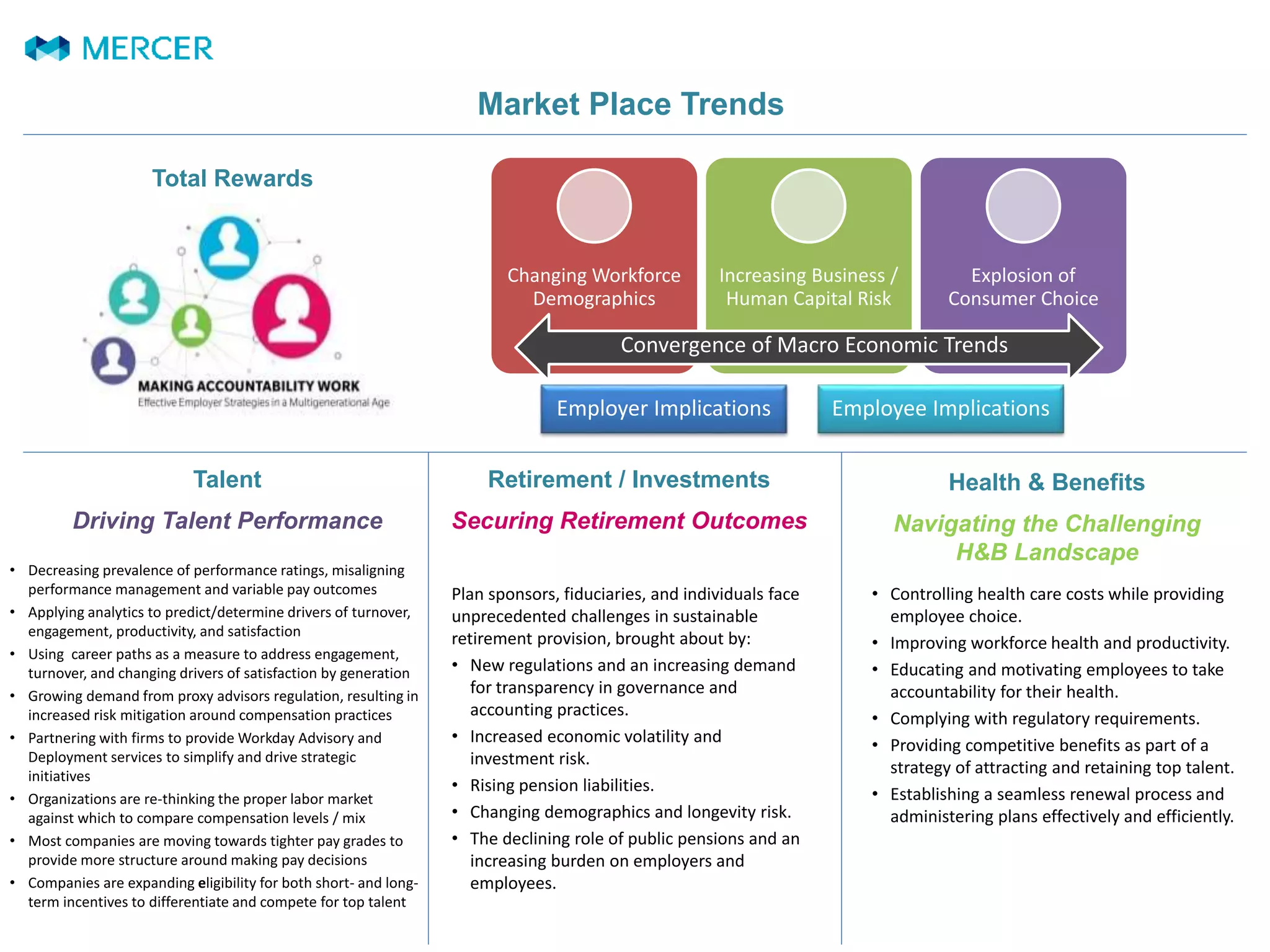
This document summarizes trends in total rewards programs including talent, retirement, health benefits, and incentives. Key points include:
- Companies are applying analytics to predict turnover and engagement, and using career paths to address different generational needs.
- Regulatory pressure is increasing risk mitigation around compensation. Many are moving to tighter pay grades and expanding short- and long-term incentives.
- Controlling healthcare costs while providing choice and accountability is a challenge. Compliance and attracting talent are priorities.
- Retirement benefits face challenges around regulations, volatility, liabilities, and changing demographics. Employers bear more responsibility.
- The review found Employer XYZ's programs generally aligned with markets, with opportunities to