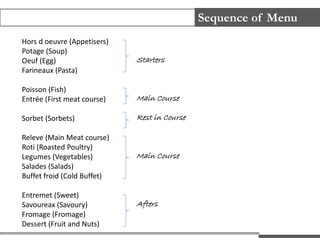
The document discusses various types of menus including a la carte, table d'hote, cyclic, and carte du jour as well as the importance of menu planning in determining business performance, restaurant theme, type of menu offered, level of service, and profitability. It also covers principles of menu planning such as variety, balance, nutrition, flexibility, and truthfulness. Finally, it provides tips for menu design, writing, and sequencing courses from appetizers to desserts.