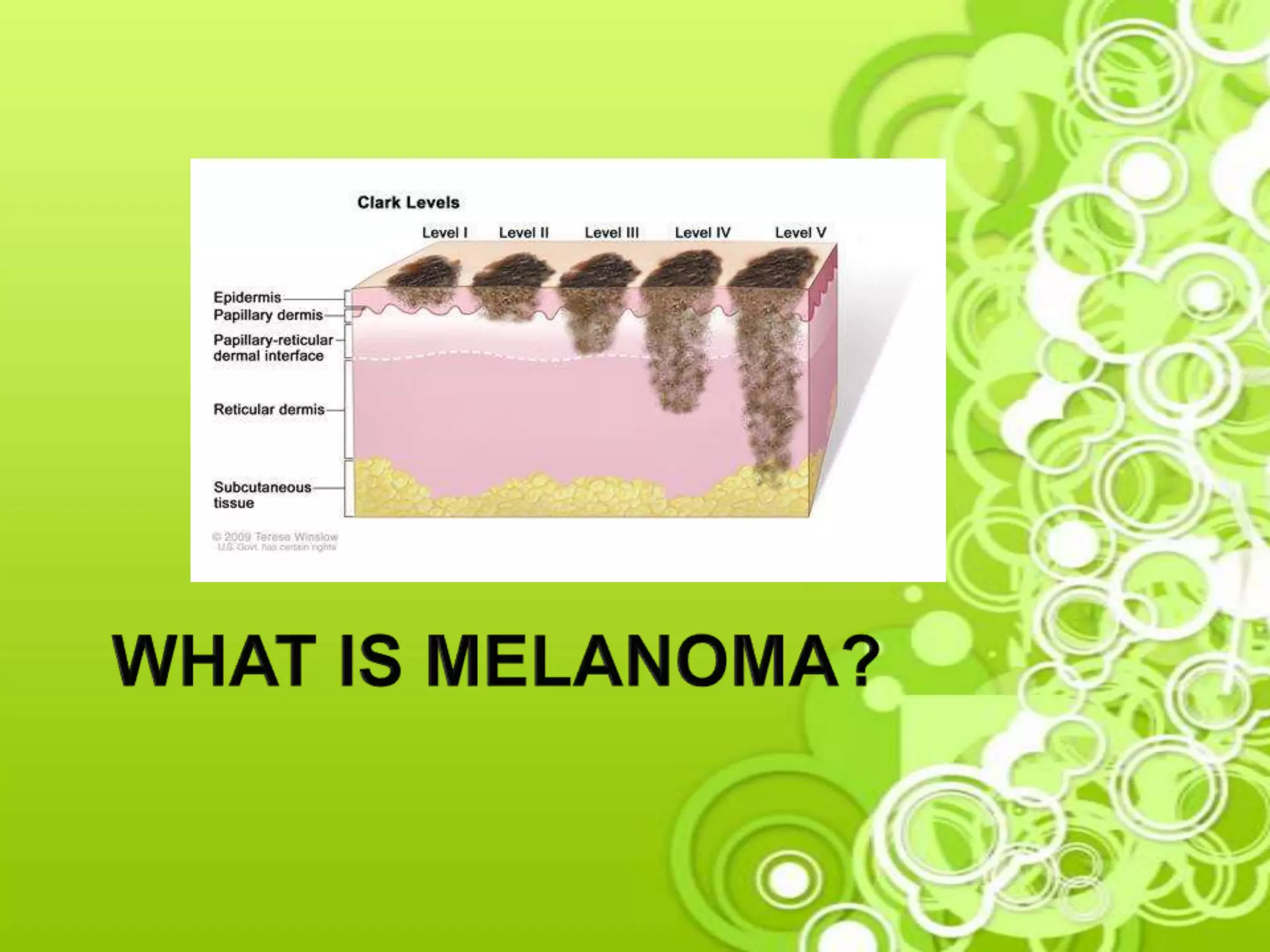
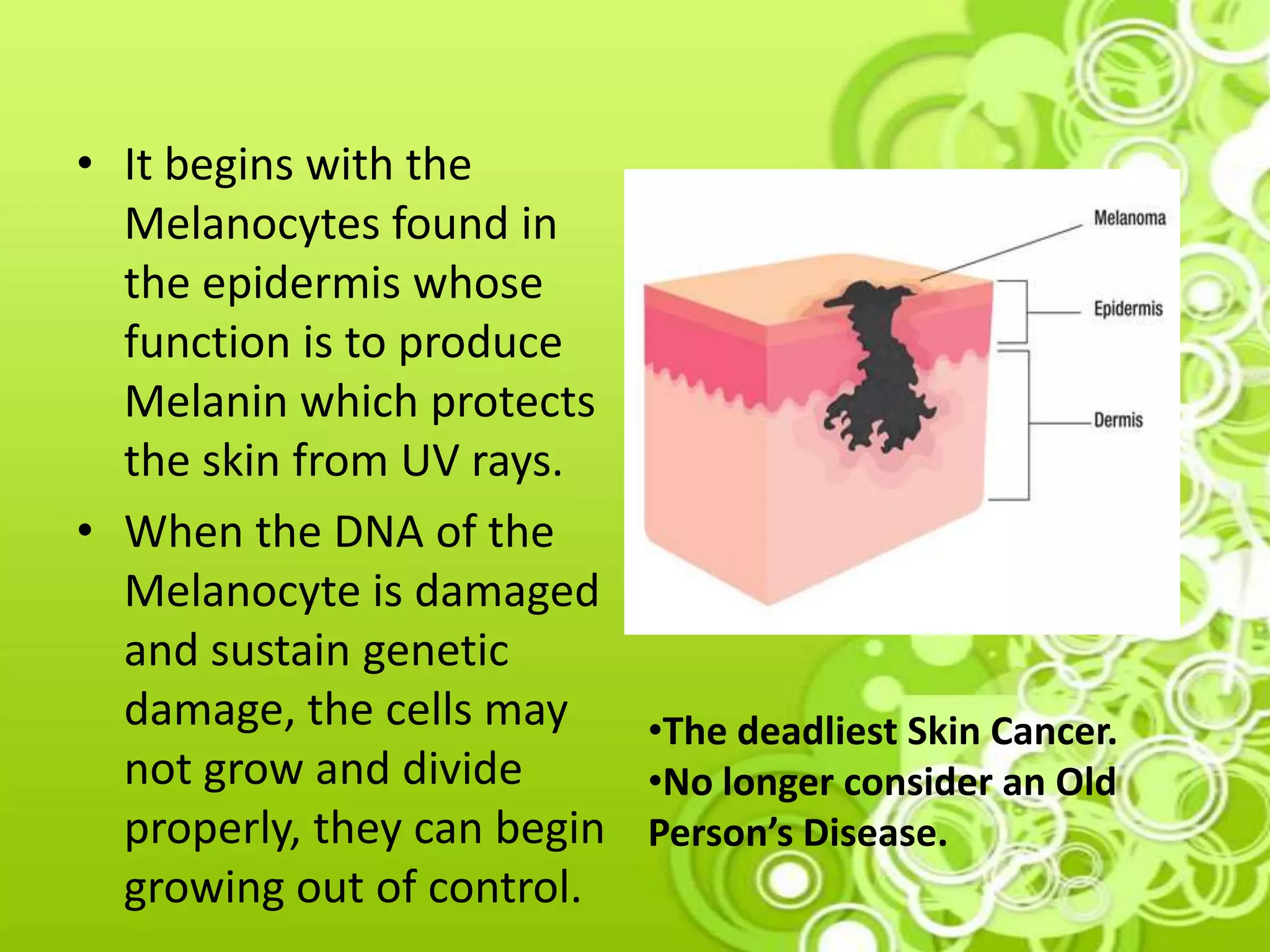
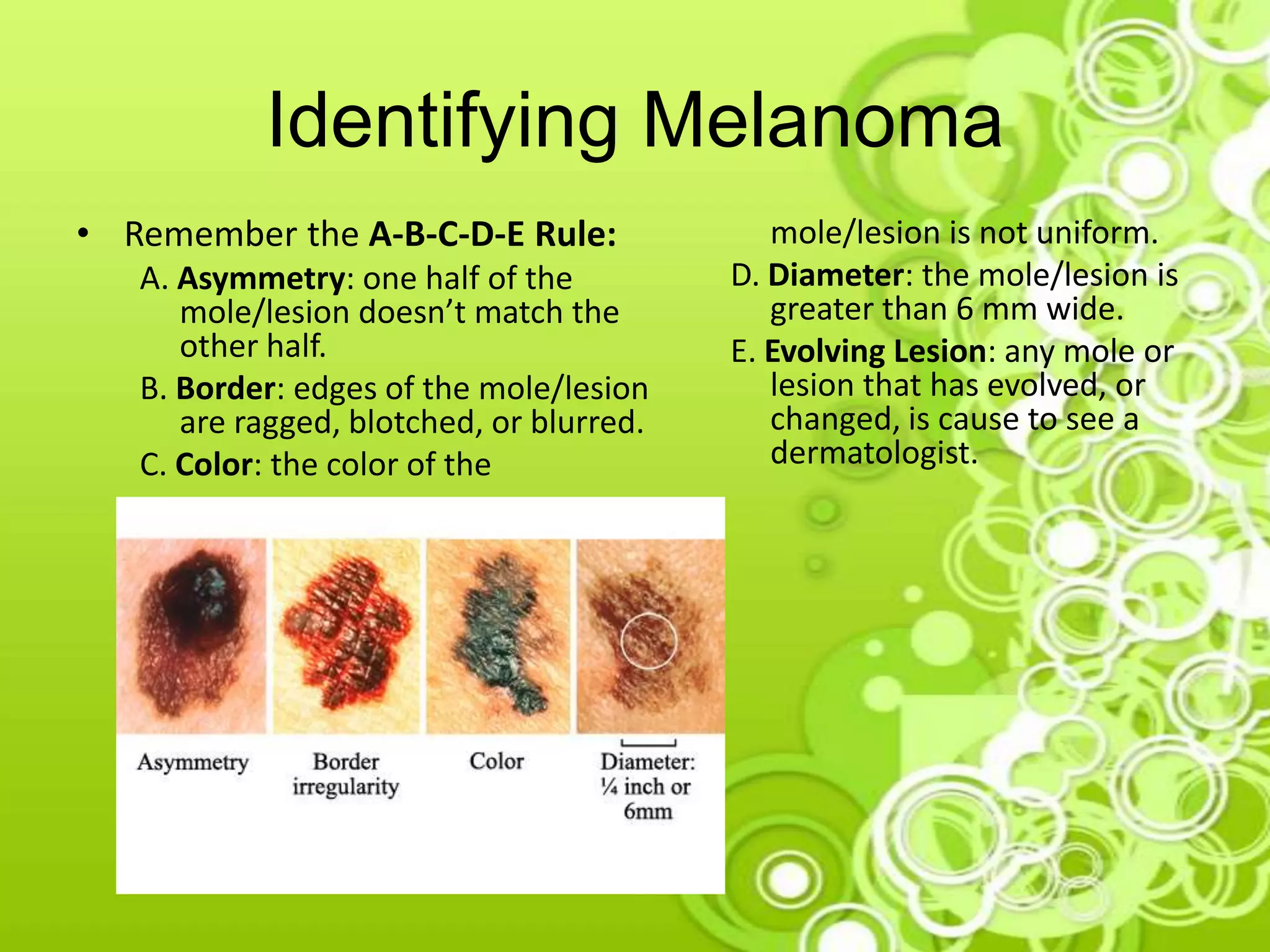
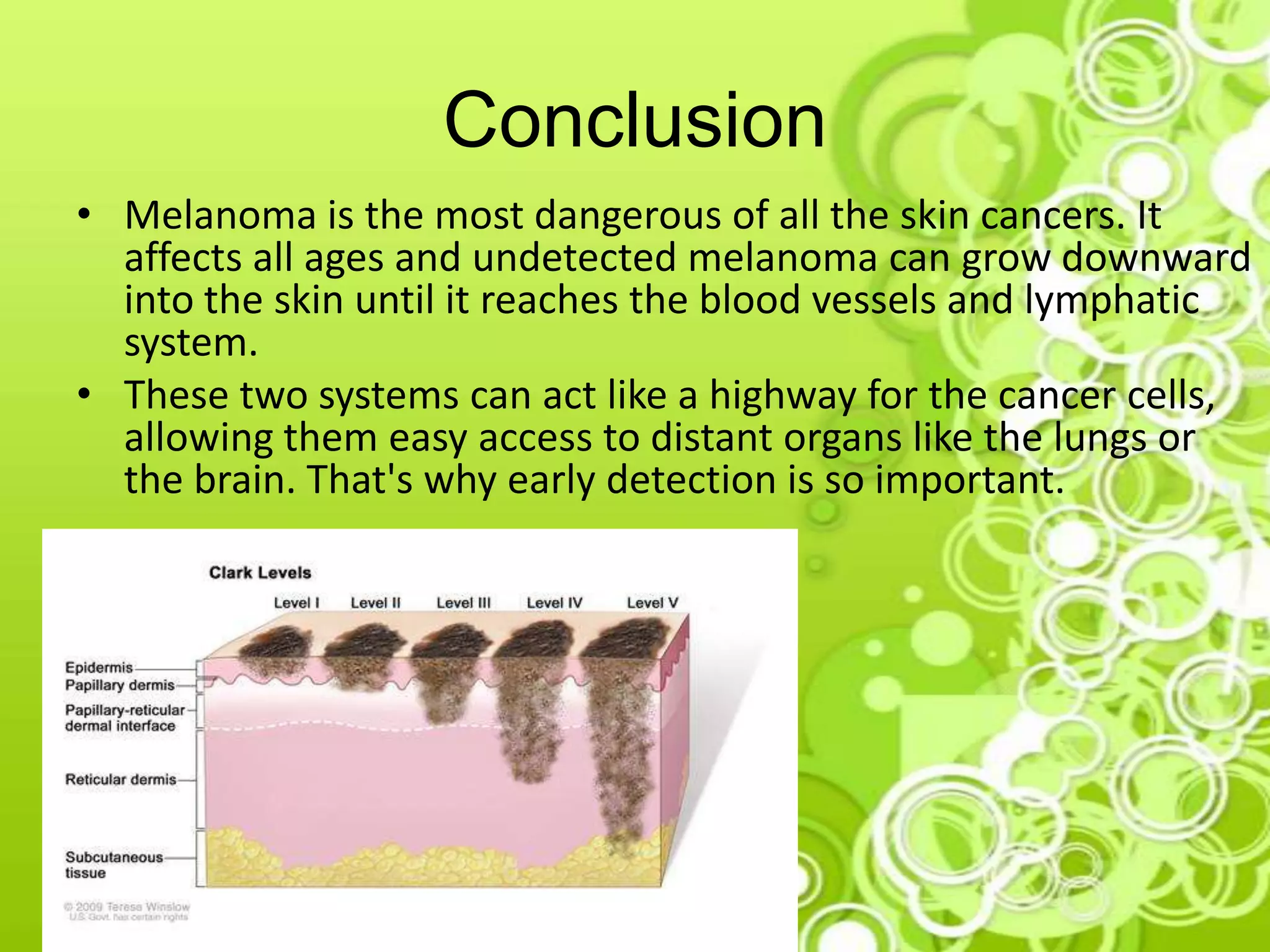
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops from melanocytes, which are the cells that produce melanin and give skin its color. It is the deadliest form of skin cancer and is no longer considered only an "old person's disease" as cases are increasing in younger people due to childhood sun exposure. The document discusses causes like UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds, risk factors like fair skin and sunburns, signs like an evolving mole, and prevention through sun protection and skin self-exams. Judy, a fair-skinned young woman concerned about a changing mole, may be at risk of melanoma due to her skin type and sun exposure habits. Early detection through screening is important for treatment