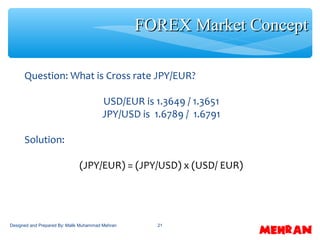
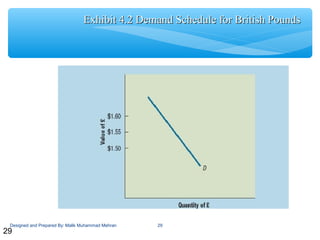
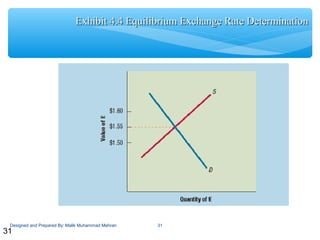
This document discusses exchange rate determination and concepts related to foreign exchange markets. It begins with objectives to explain how exchange rates are measured and determined, factors that influence exchange rates, and cross exchange rate movements. It then defines key terms related to foreign exchange markets, such as exchange rates, spot and forward rates, currency conversion, and cross rates. Subsequent sections examine how exchange rates reach equilibrium, factors that influence exchange rates like inflation and interest rates, and how movements in bilateral exchange rates impact cross exchange rates.