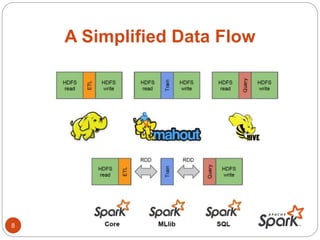
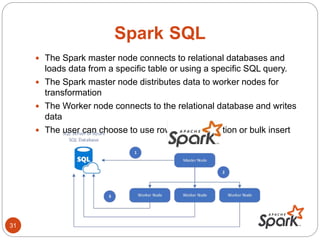
This document provides an overview of Apache Spark, including:
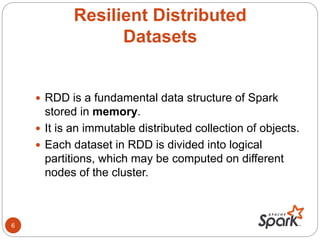
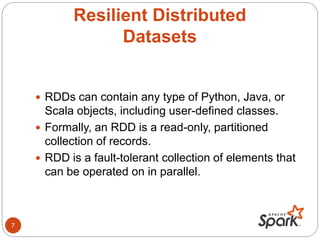
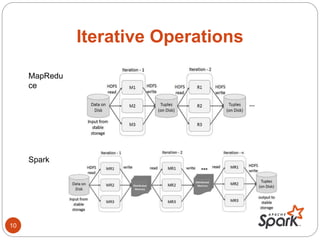
- Spark is an open-source cluster computing framework that supports in-memory processing of large datasets across clusters of computers using a concept called resilient distributed datasets (RDDs).
- RDDs allow data to be partitioned across nodes in a fault-tolerant way, and support operations like map, filter, and reduce.
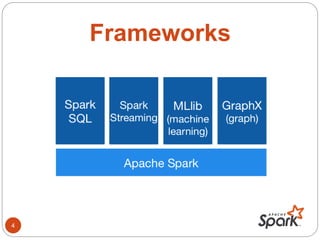
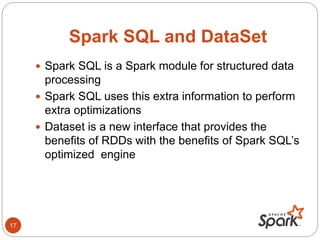
- Spark SQL, DataFrames, and Datasets provide interfaces for structured and semi-structured data processing.
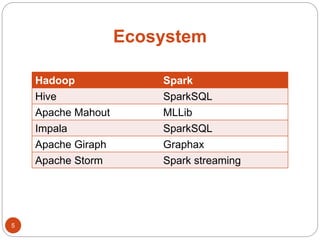
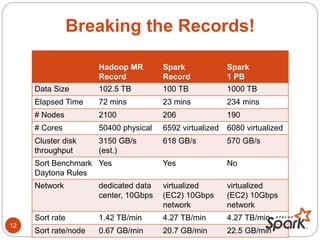
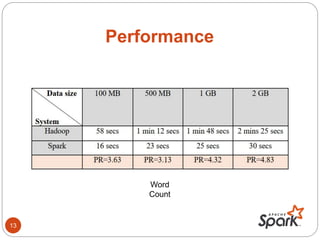
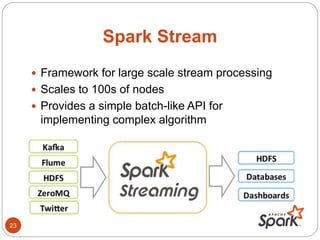
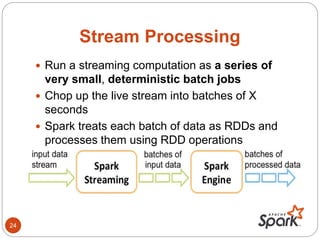
- The document discusses Spark's performance advantages over Hadoop MapReduce and provides examples of common Spark applications like word count, Pi estimation, and stream processing.


















![References
[1]: Apache Spark officially sets a new record in
large-scale sorting
[2]: 2014 Data Science Salary Survey
[3]: The Performance Comparison of Hadoop and
Spark
[4] Apache Maven Project
[5] The Scala Programming Language
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-201222231123/85/Spark-32-320.jpg)