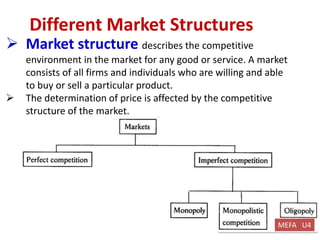
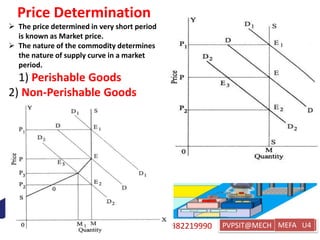
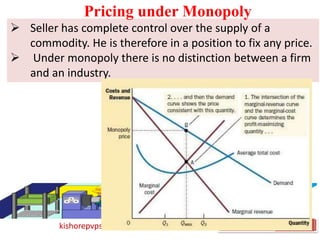
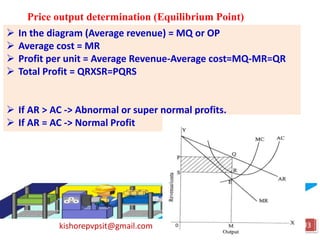
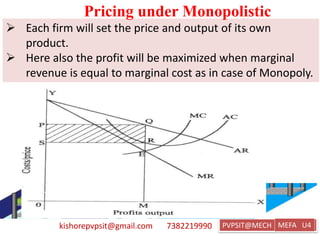
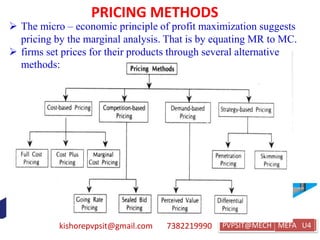
This document discusses key topics in Managerial Economics and Financial Analysis (MEFA) including market structures, pricing policies, and pricing methods. It defines different market structures like perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly. It explains how price and output are determined under each market structure. The document also discusses various pricing policies and methods that firms use to set prices like cost-based pricing, competition-based pricing, demand-based pricing, and strategy-based pricing for new products.