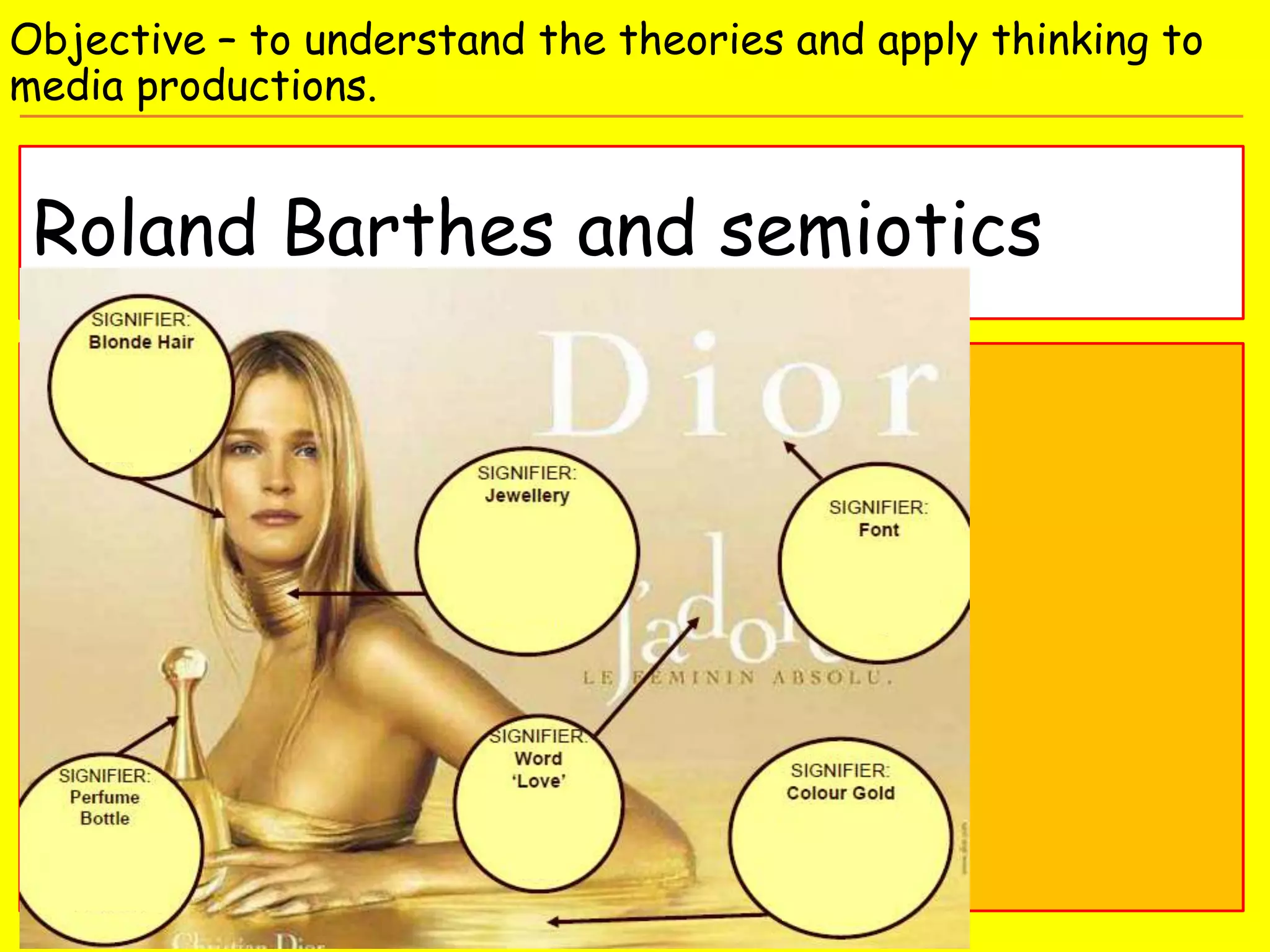
This document discusses media language and semiotics theories that can be applied to media productions. It defines key terms like media language, semiotics, denotation and connotation. It discusses theorists like Saussure who see signs as composed of a signifier and signified, and Barthes who saw how signs in media construct cultural myths and realities. It provides examples of how these concepts could be applied to analyze students' thriller openings by examining the signs, codes, realities constructed, and whose interests are privileged or suppressed through the media language.