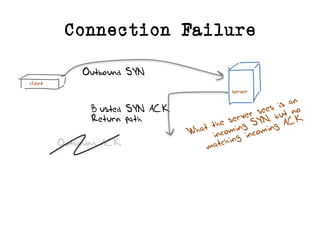
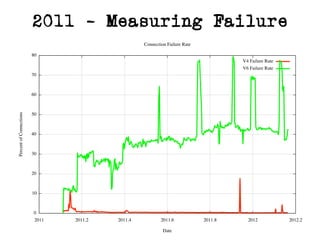
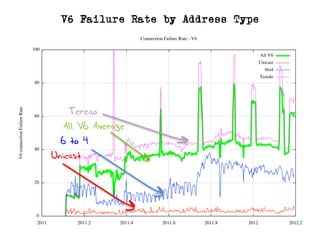
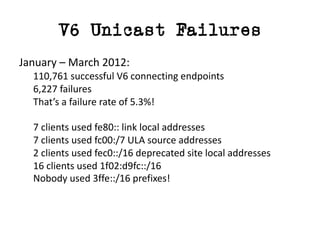
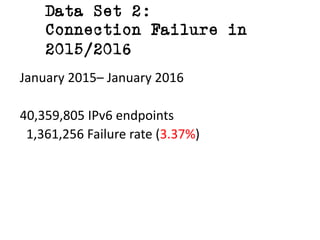
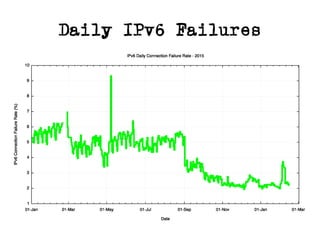
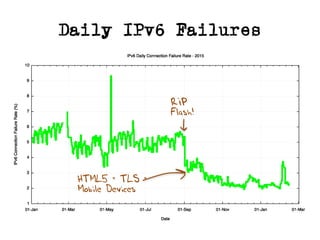
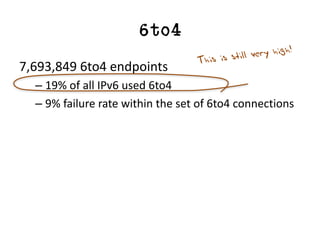
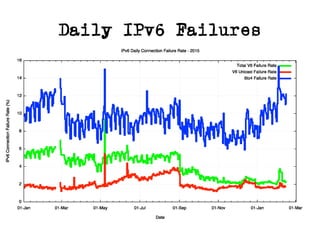
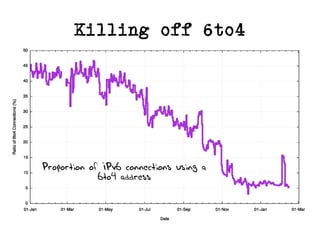
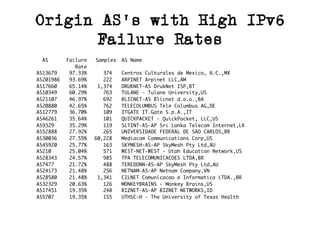
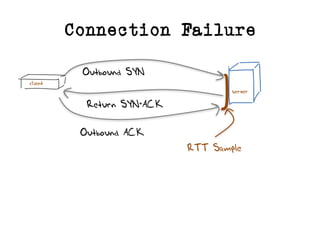
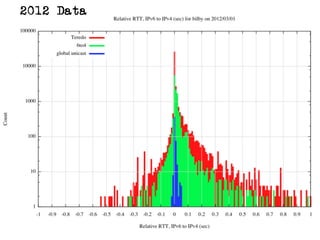
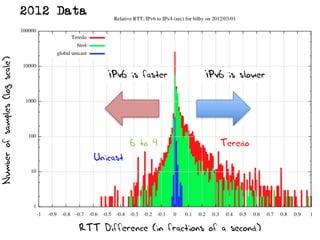
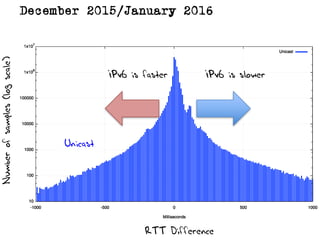
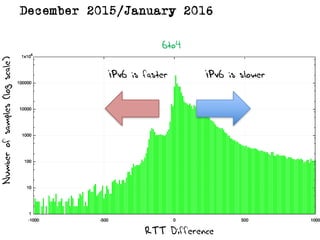
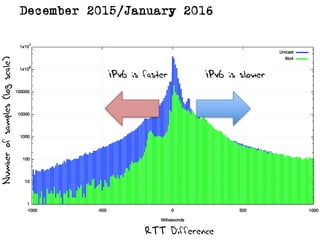
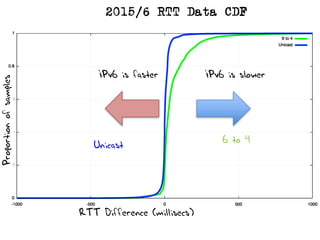
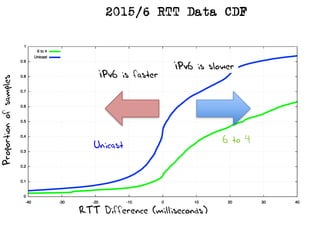
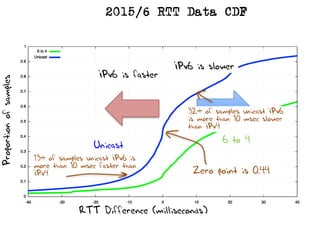
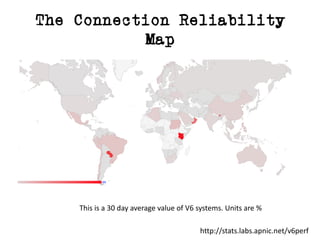
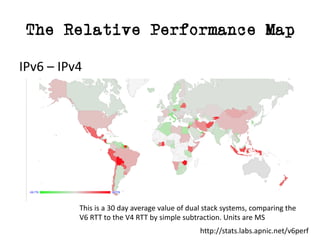
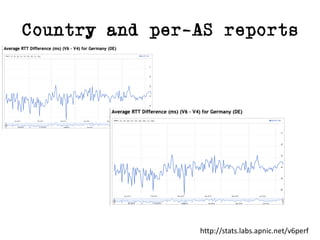
The document discusses measuring the performance and reliability of IPv6 connections compared to IPv4. It analyzes data from 2011 and 2015-2016 on connection failure rates and round-trip times. In 2011, IPv6 connections using 6to4 and Teredo tunnels had high failure rates of 10-20% and 5.3% respectively, while unicast was lower at 5.3%. By 2015, 6to4 failure dropped to 9% while unicast was between 1.5-4%. Round-trip time analyses found 13% of unicast IPv6 connections were over 10ms faster than IPv4 in 2015-2016, while 32% were over 10ms slower. The document provides online maps showing average connection reliability and