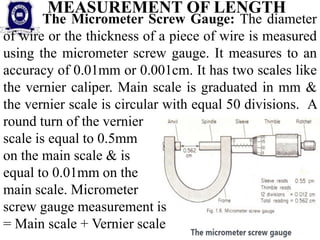
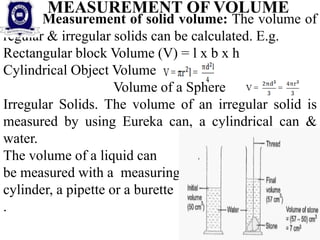
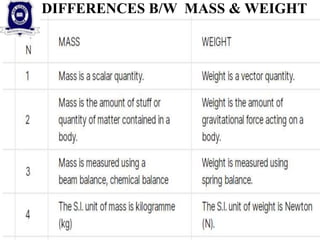
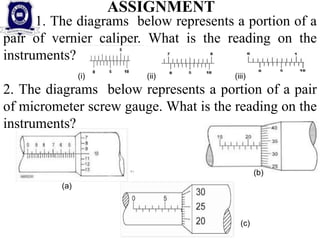
This document provides information on measuring instruments and units used to measure various physical quantities. It discusses tools used to measure time like clocks, stopwatches, and heart rate. Instruments for measuring length such as meter sticks, measuring tapes, calipers, and micrometers are also outlined. The document also covers volume measurement of solids and liquids using containers. Mass is defined as the amount of matter in an object, with kilograms as the SI unit, while weight varies by location and is measured using balances. Examples of using measuring instruments to find readings are provided at the end.