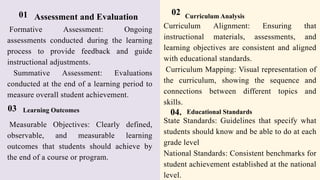
The document outlines key concepts in education analysis, examining elements such as assessment and evaluation, educational standards, data-driven decision making, and teacher effectiveness. It emphasizes the importance of curriculum alignment and stakeholder engagement in improving educational outcomes. Additionally, it discusses the role of technology, inclusion, and policy analysis in shaping effective educational practices.