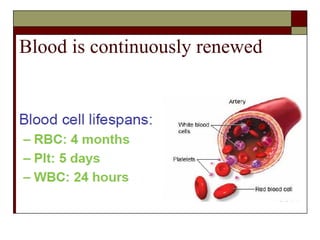
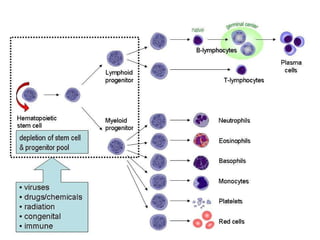
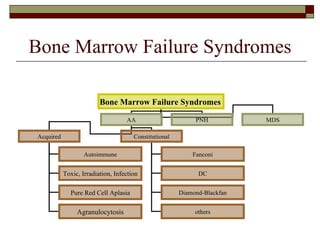
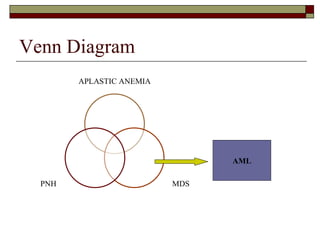
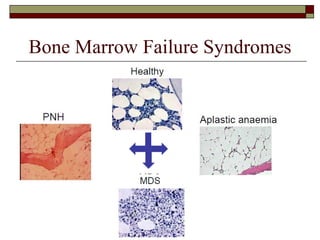
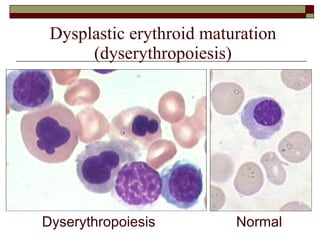
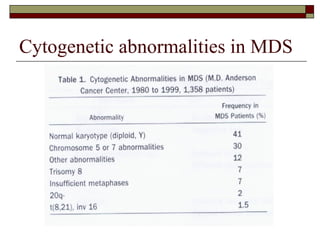
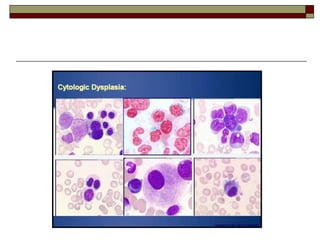
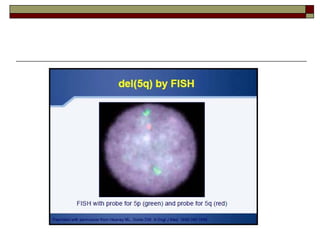
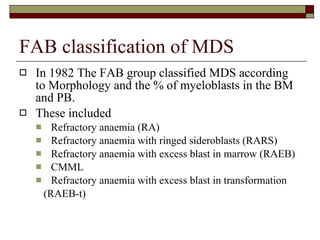
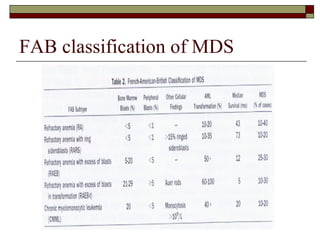
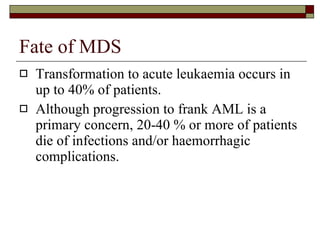
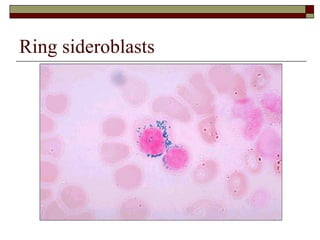
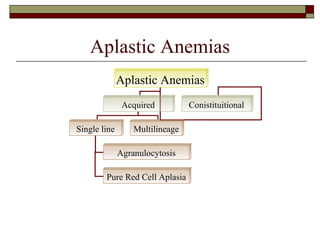
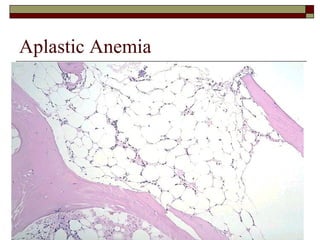
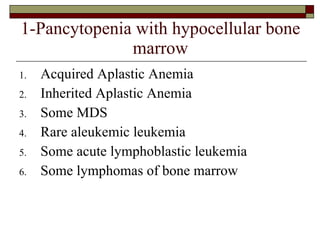
Myelodysplasia, also known as myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), is a heterogeneous group of hematopoietic stem cell disorders that results in ineffective hematopoiesis and cytopenias. MDS is primarily seen in elderly patients and has a risk of progression to acute myeloid leukemia. Characteristic features include increased marrow proliferation, failure of stem cells to differentiate, and increased marrow apoptosis. Cytogenetic abnormalities are detected in 30-70% of patients and correlate with risk of progression. Treatment may include stem cell transplant, DNA methyltransferase inhibitors, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy.