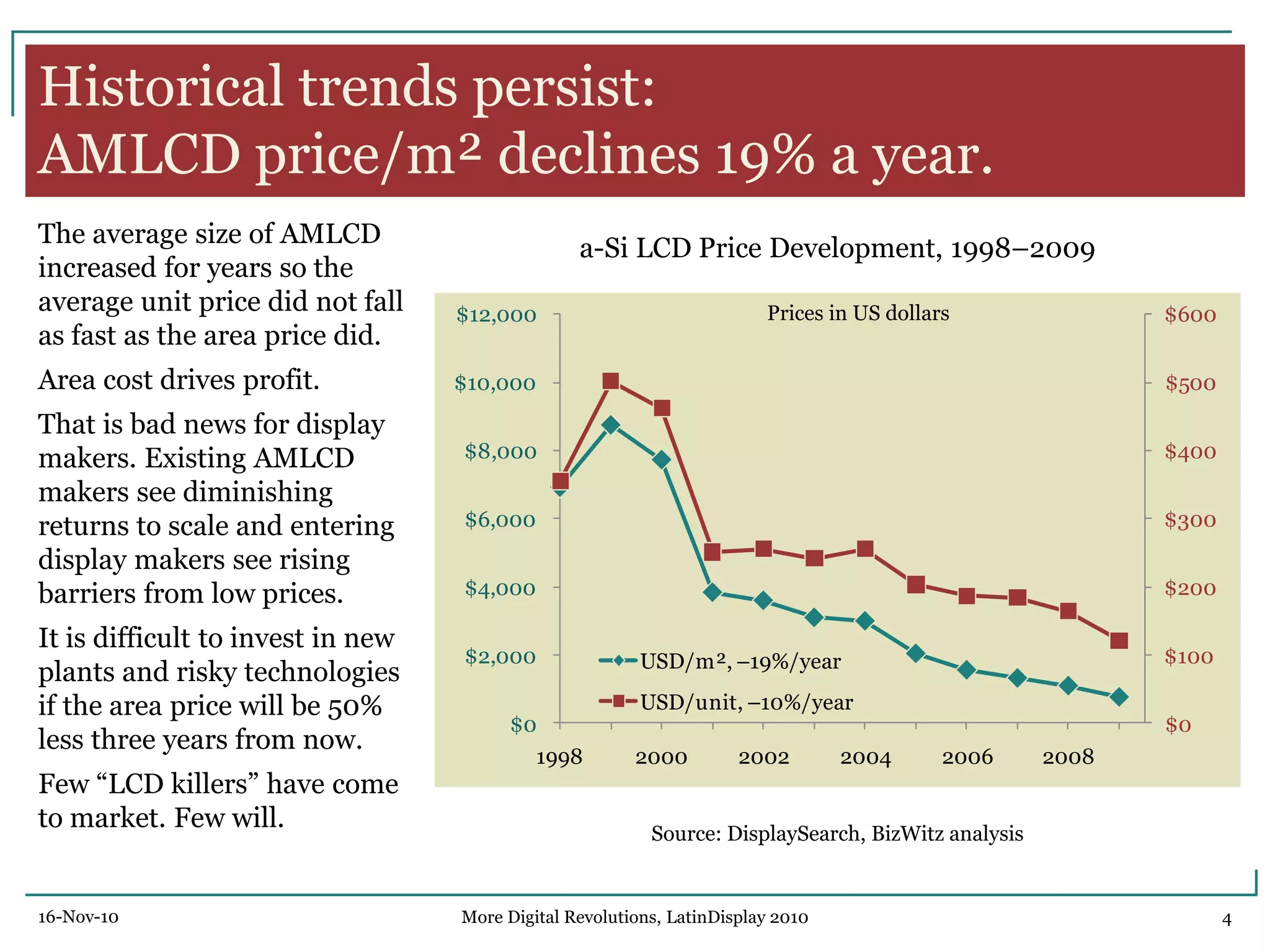
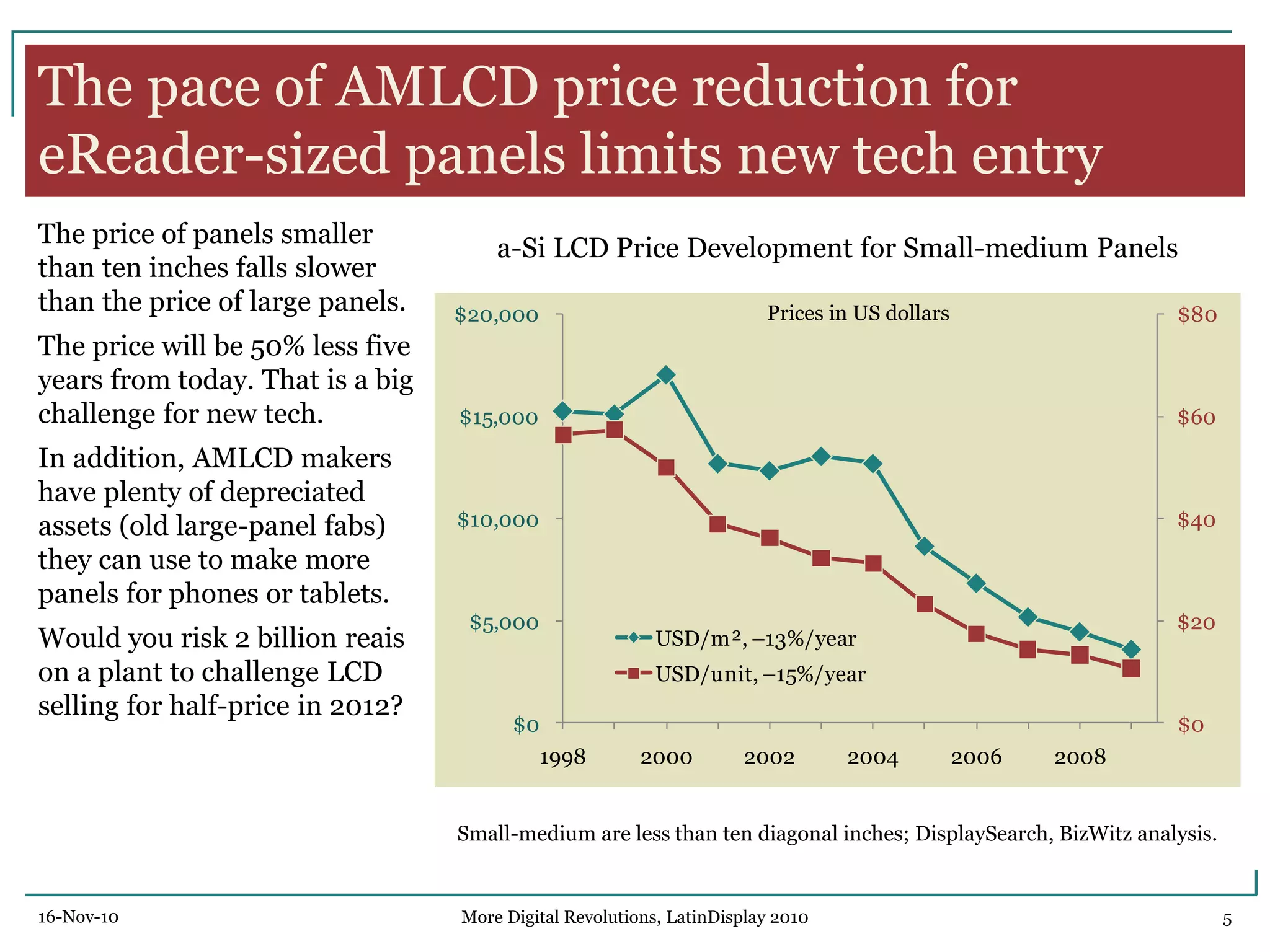
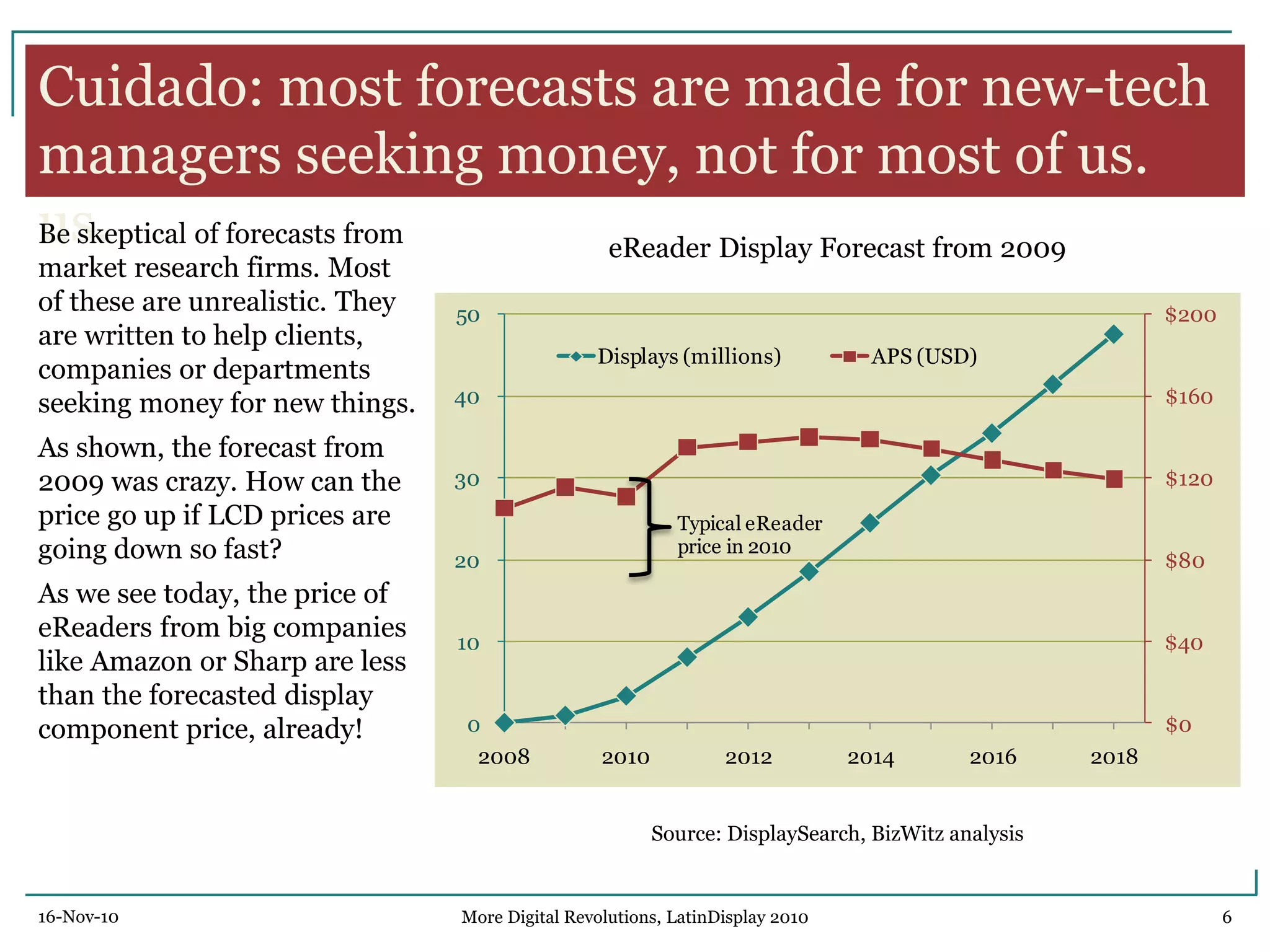
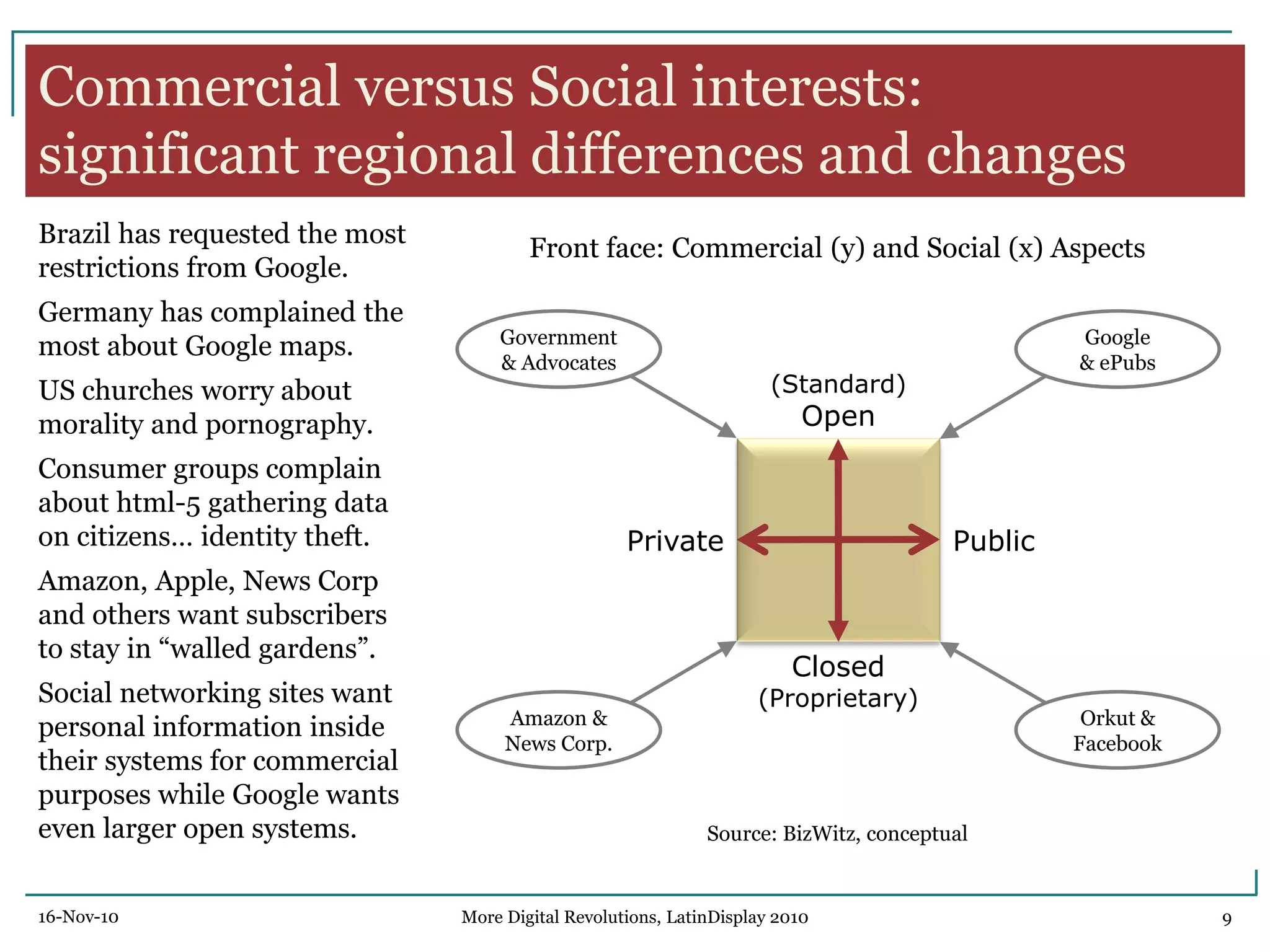
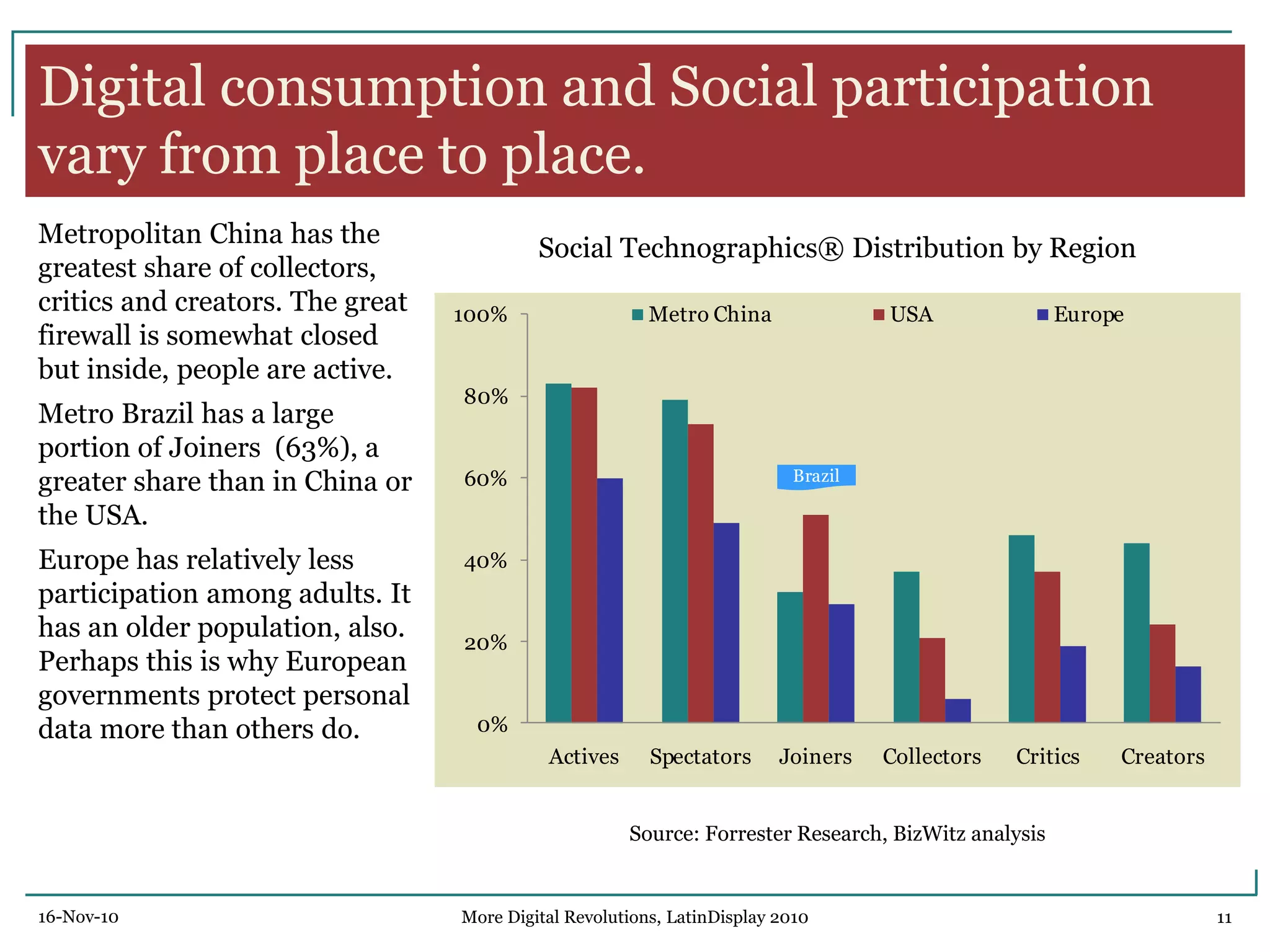
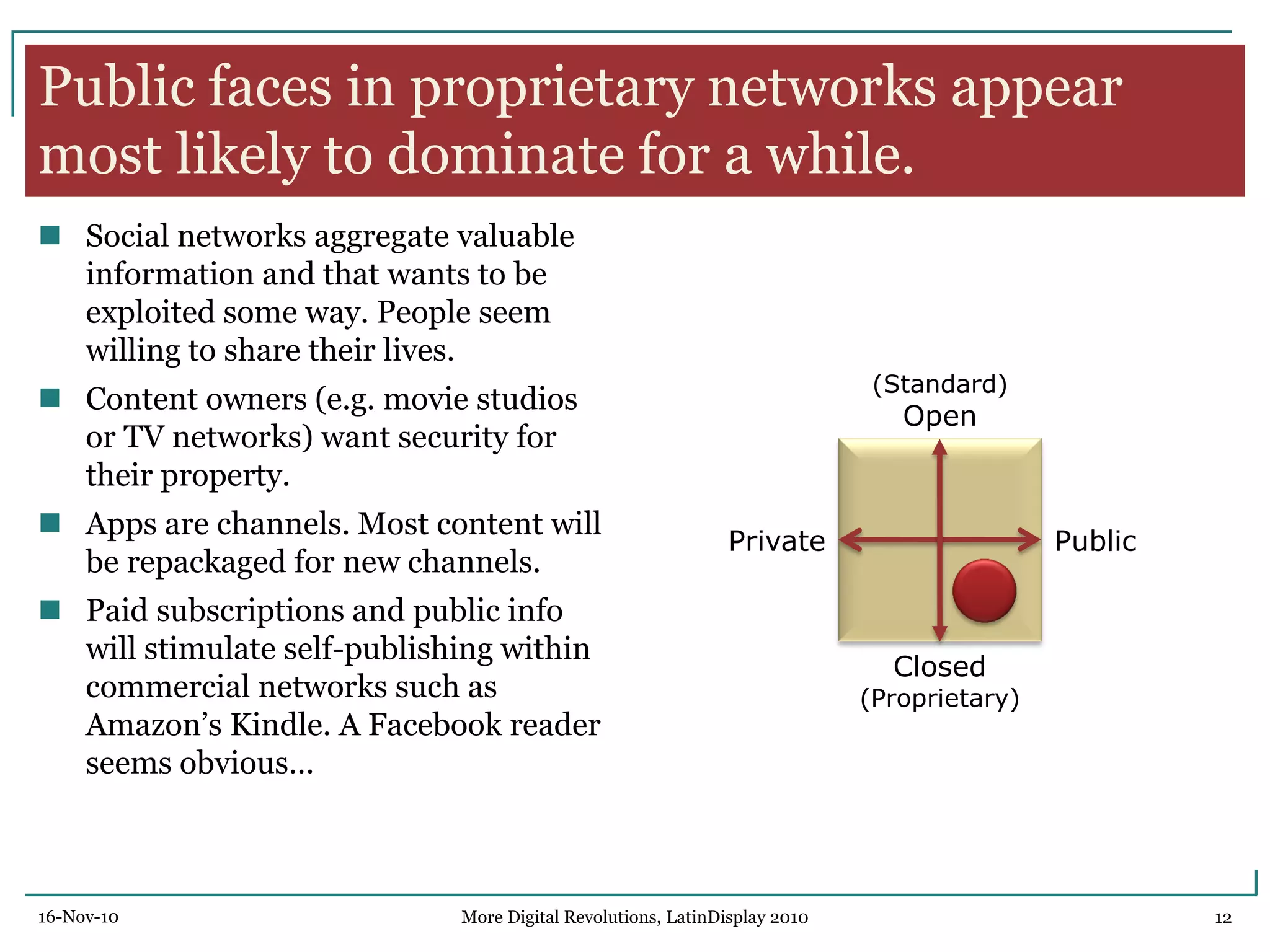
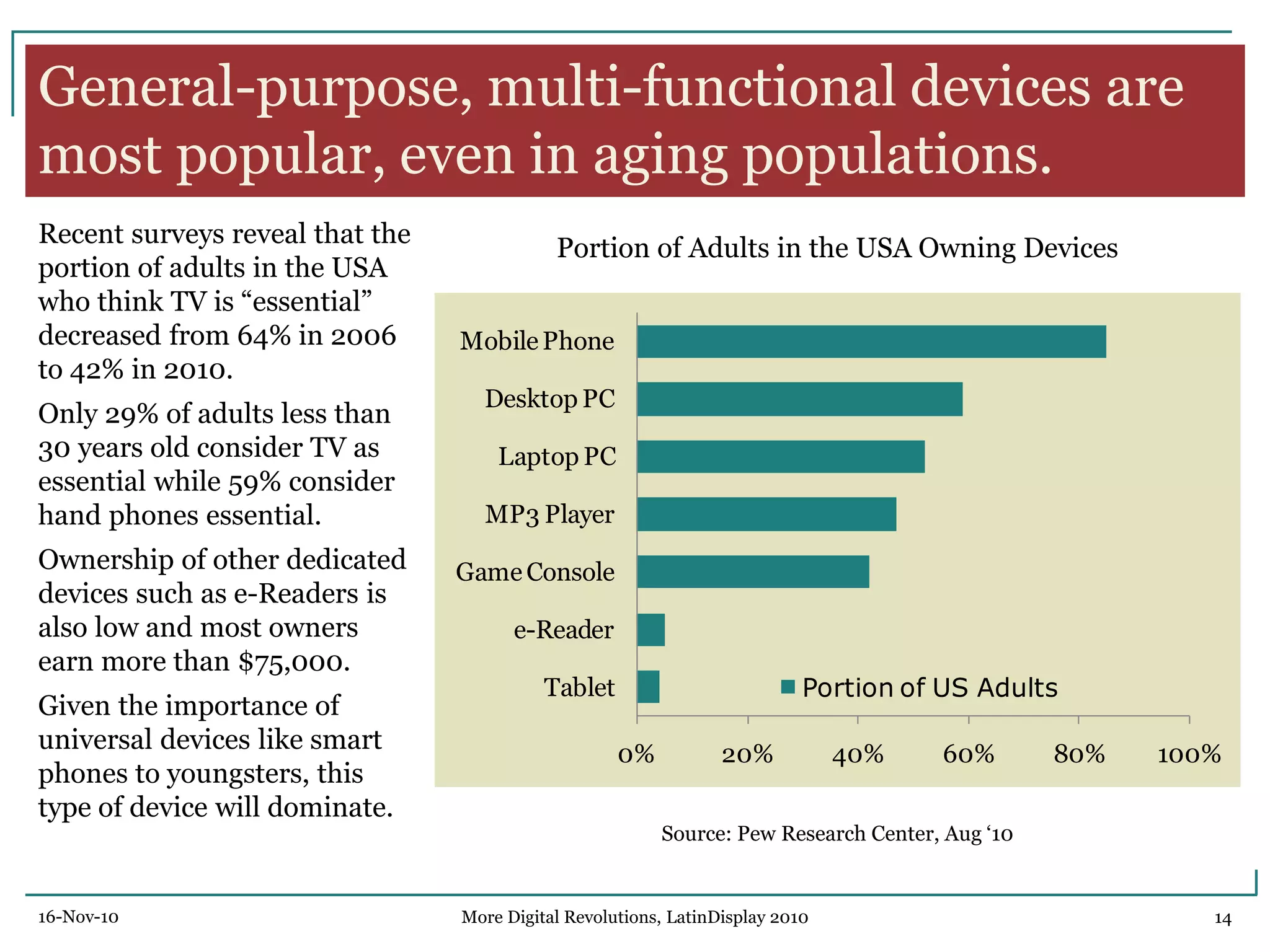
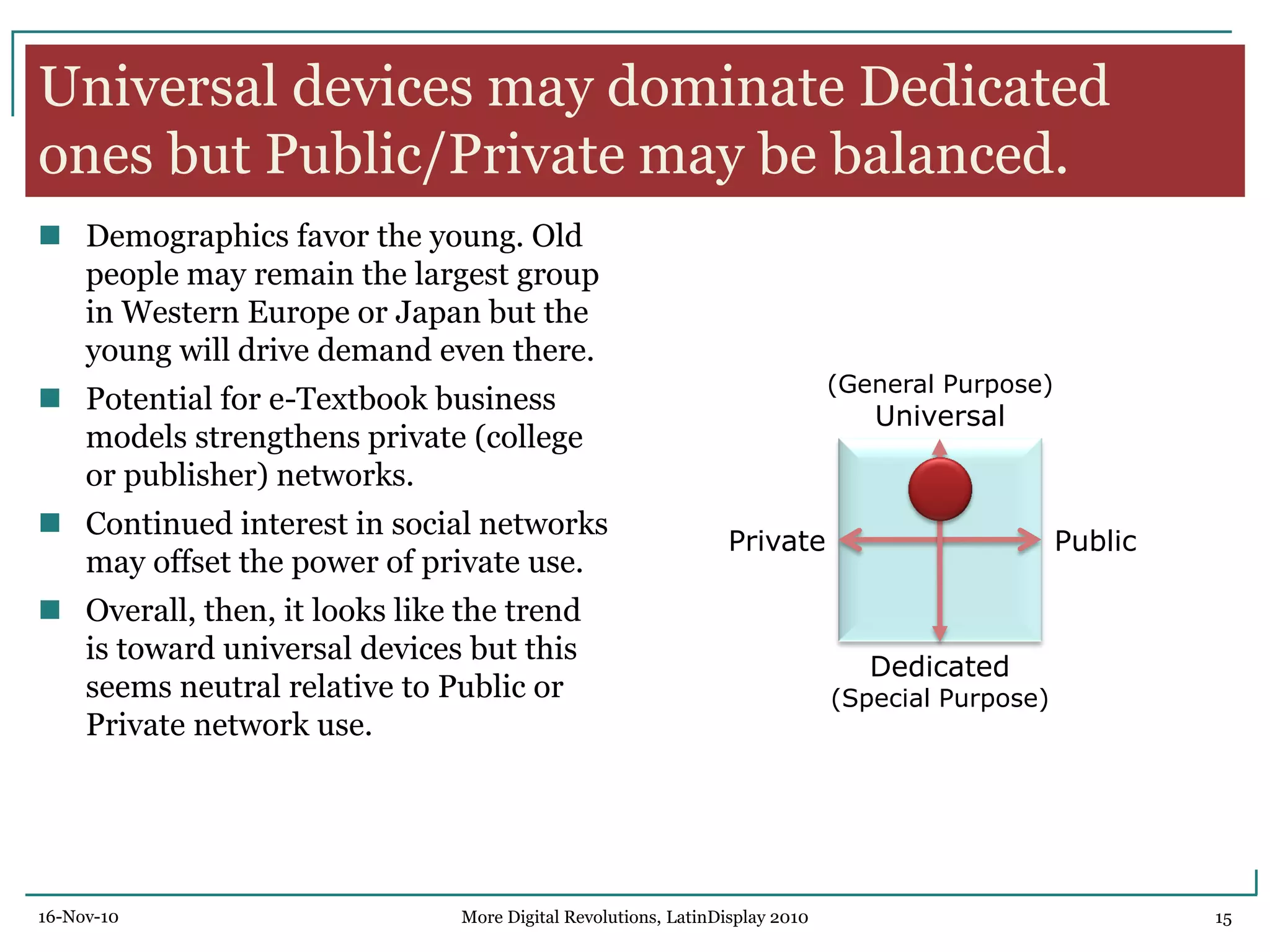
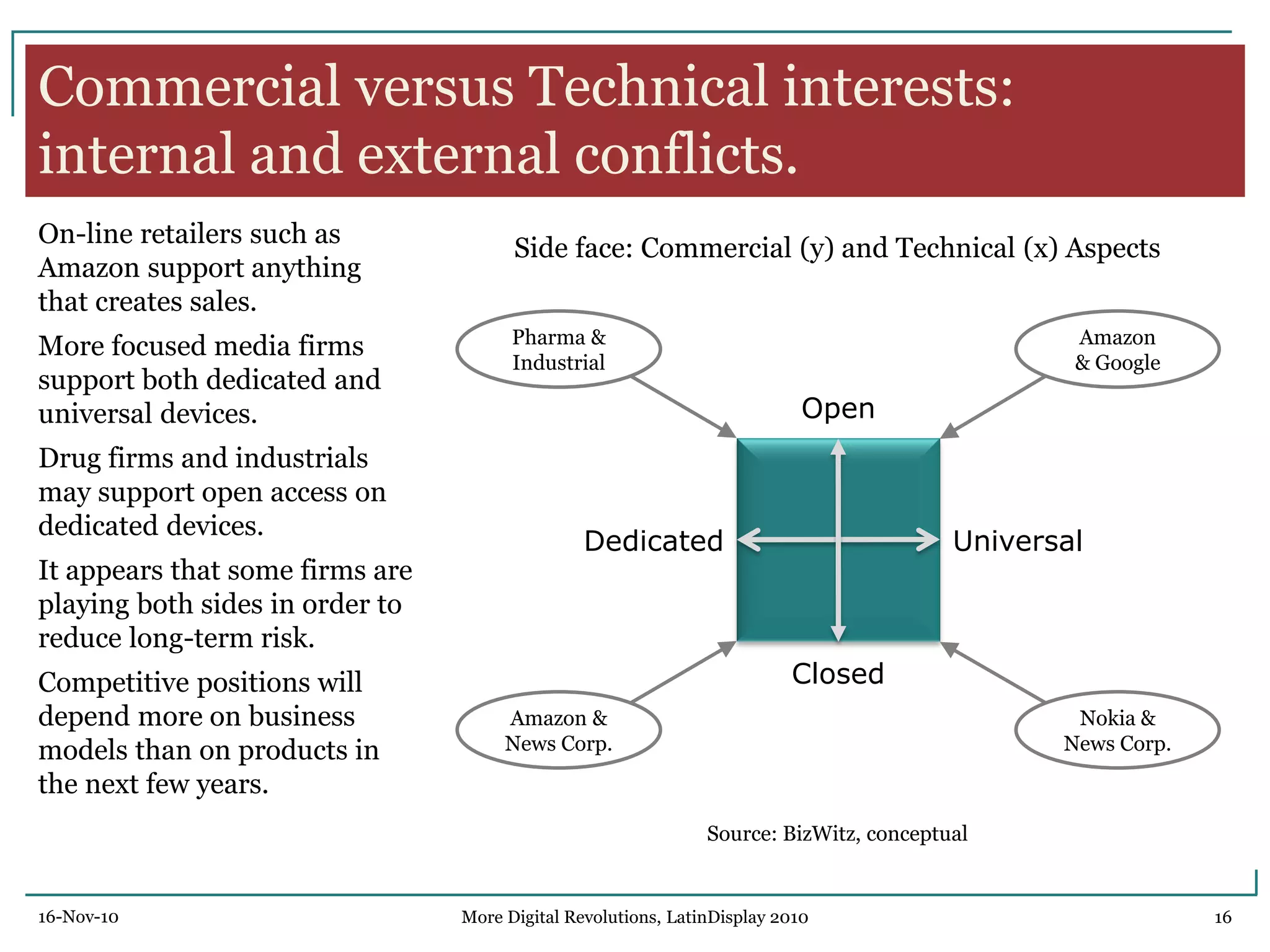
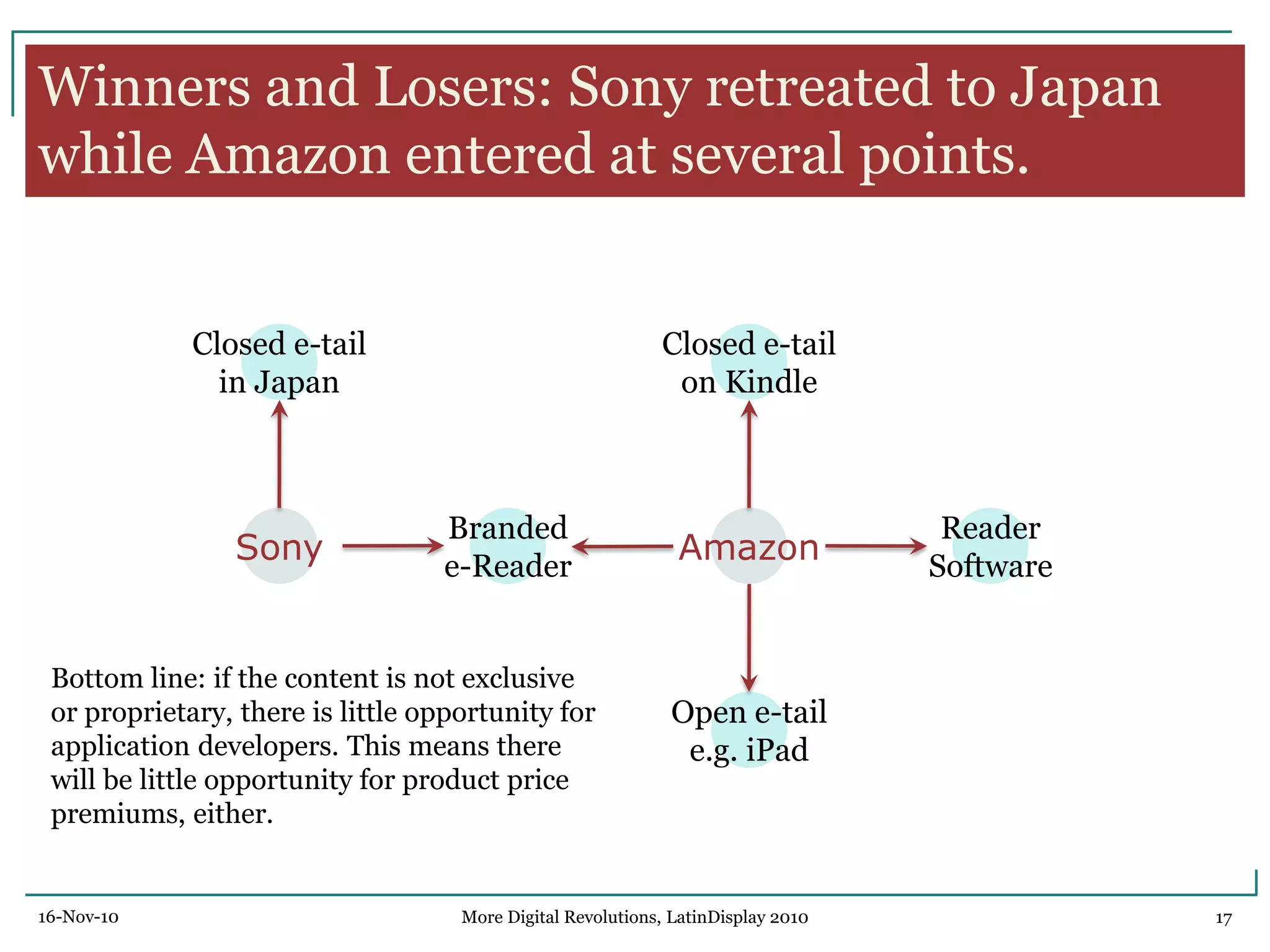
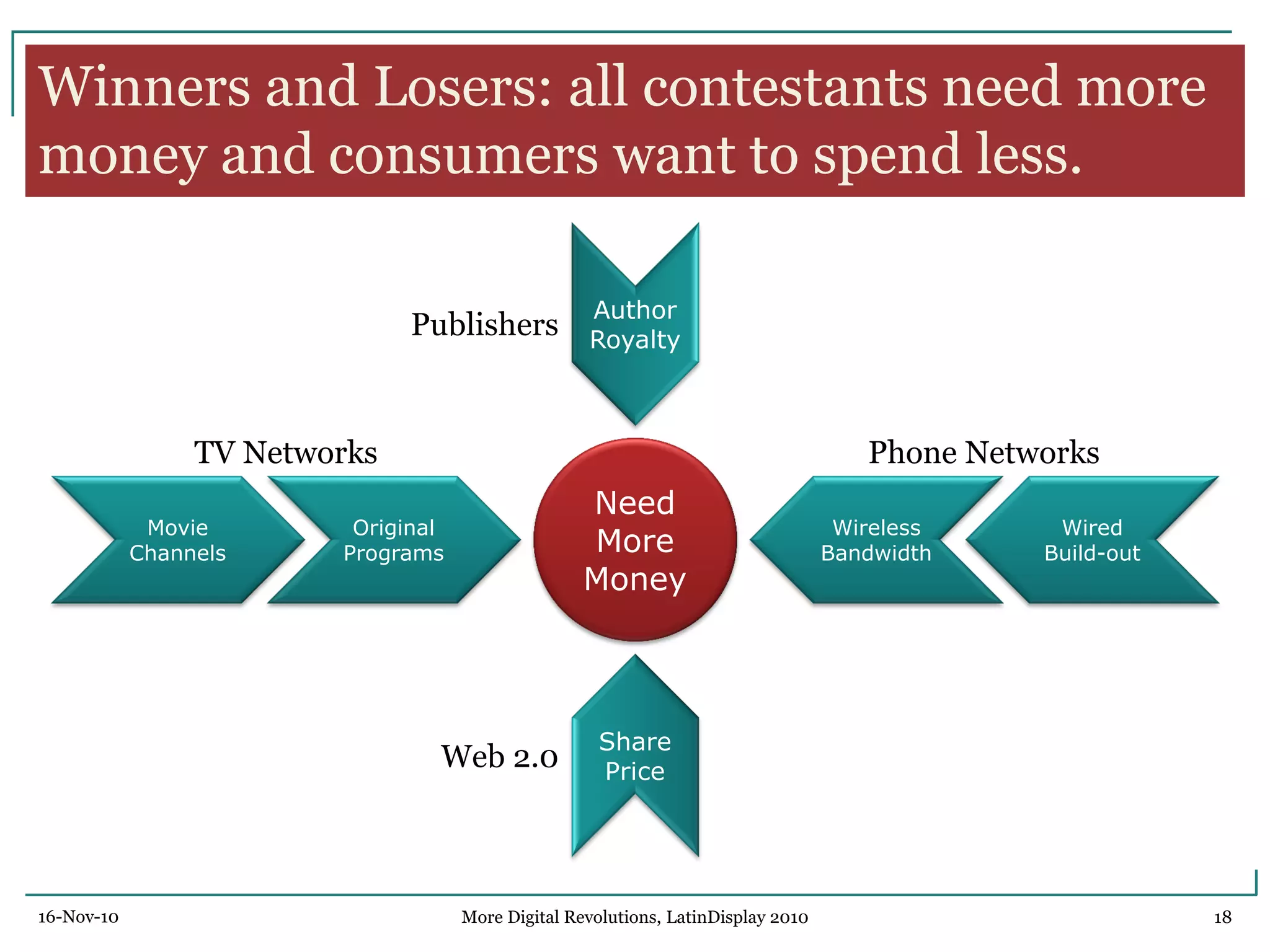
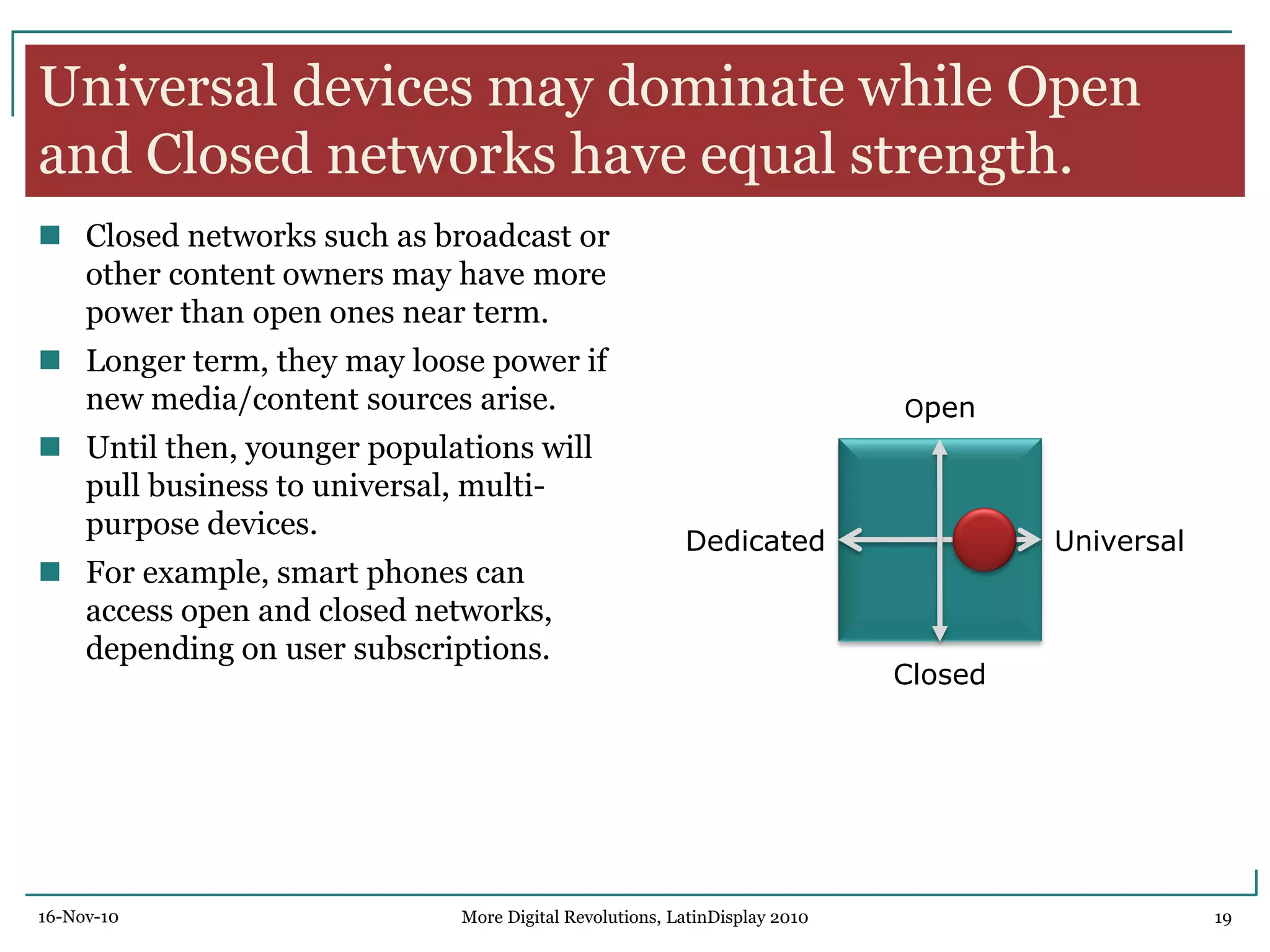
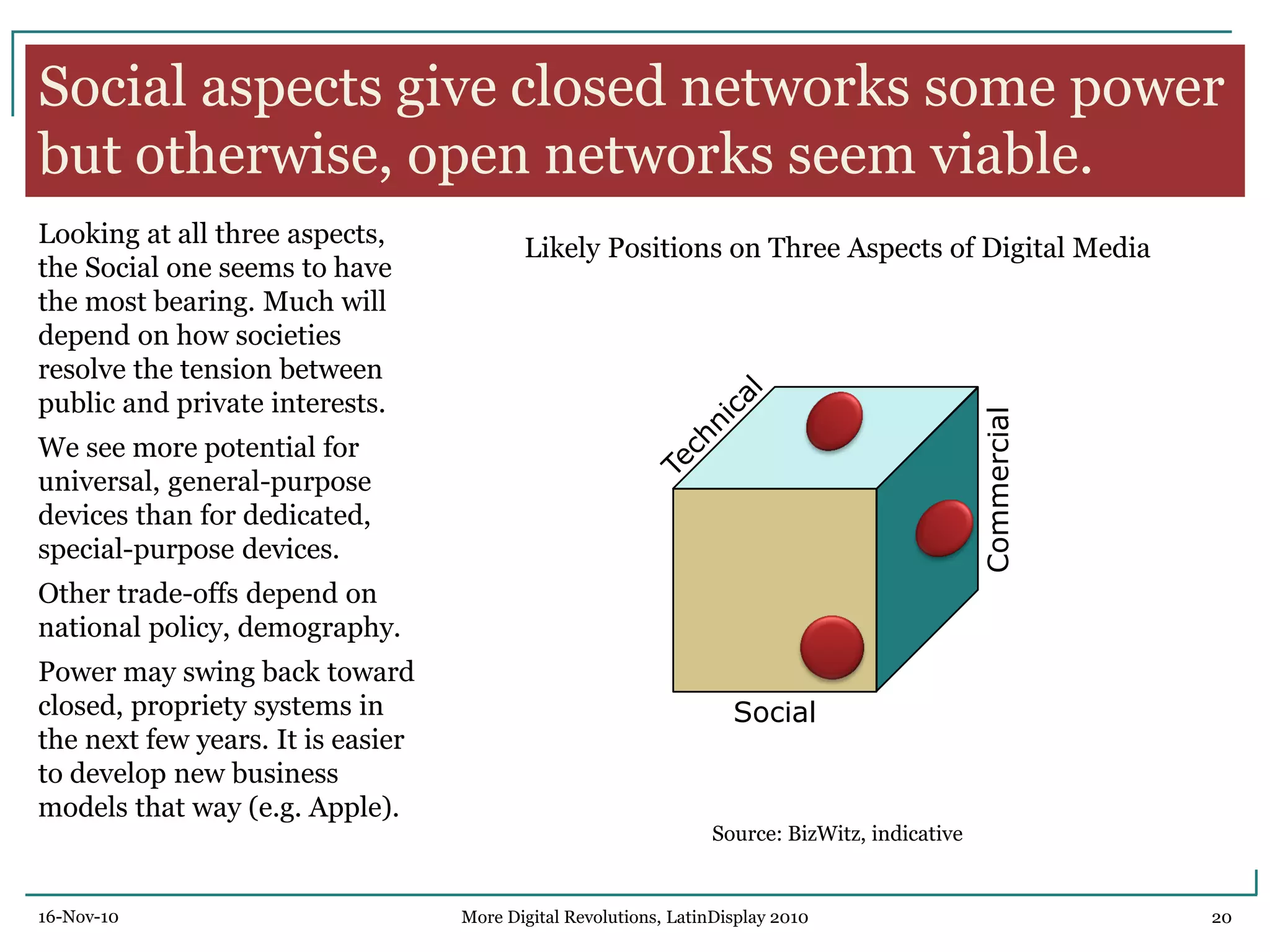
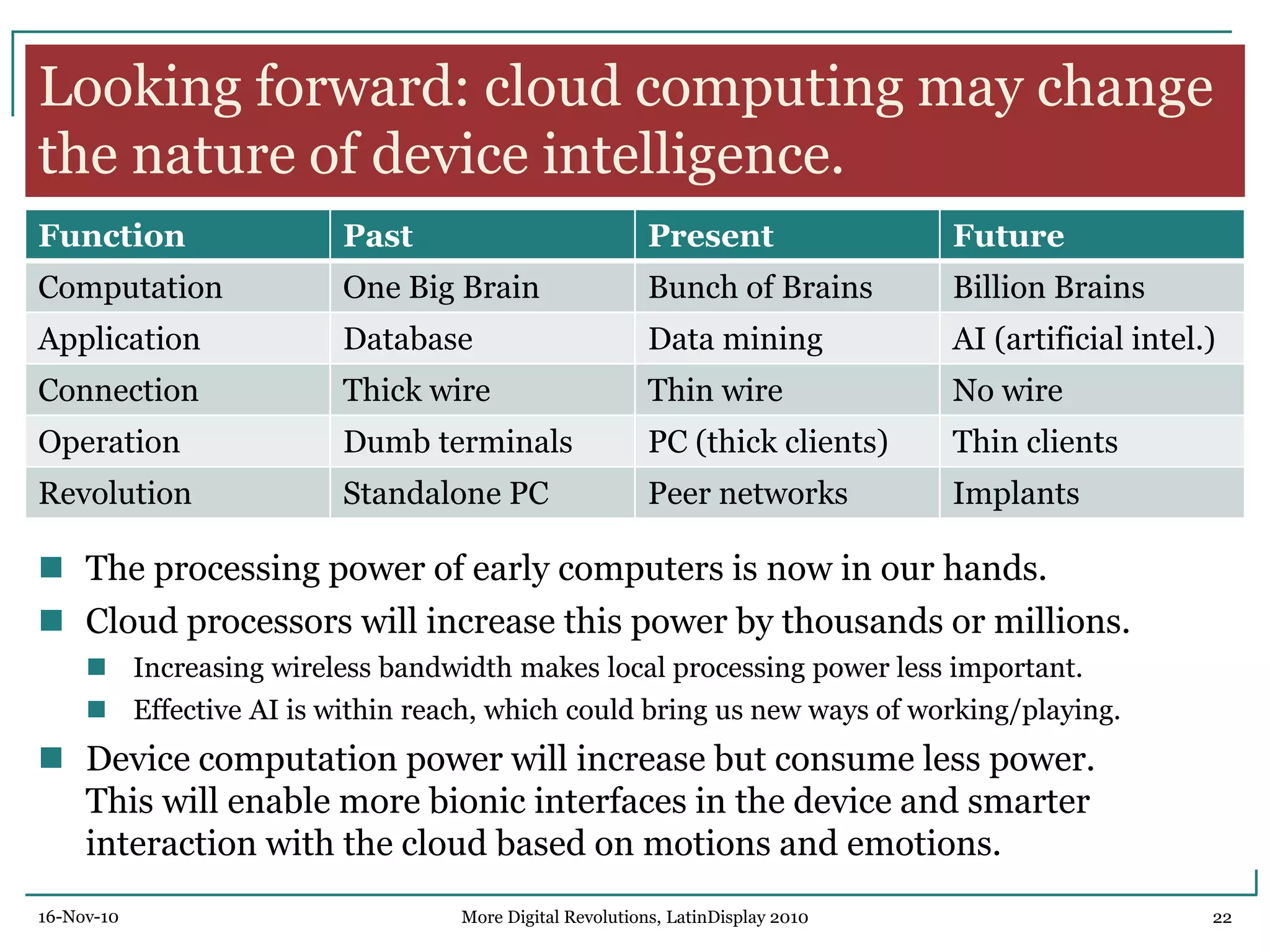
The document discusses trends in digital displays and media from 2000 to the present. It covers three parts: how displays have influenced digital media, a 3D view of digital media trends, and how digital media will influence future displays. Key points discussed include how lower display prices have enabled new devices, the rise of universal devices over dedicated ones, and how social, commercial, and technical aspects will impact whether open or closed networks dominate digital media. The document predicts displays will continue getting cheaper, higher resolution, and more integrated with cloud computing, but questions whether new technologies can compete with falling LCD prices.