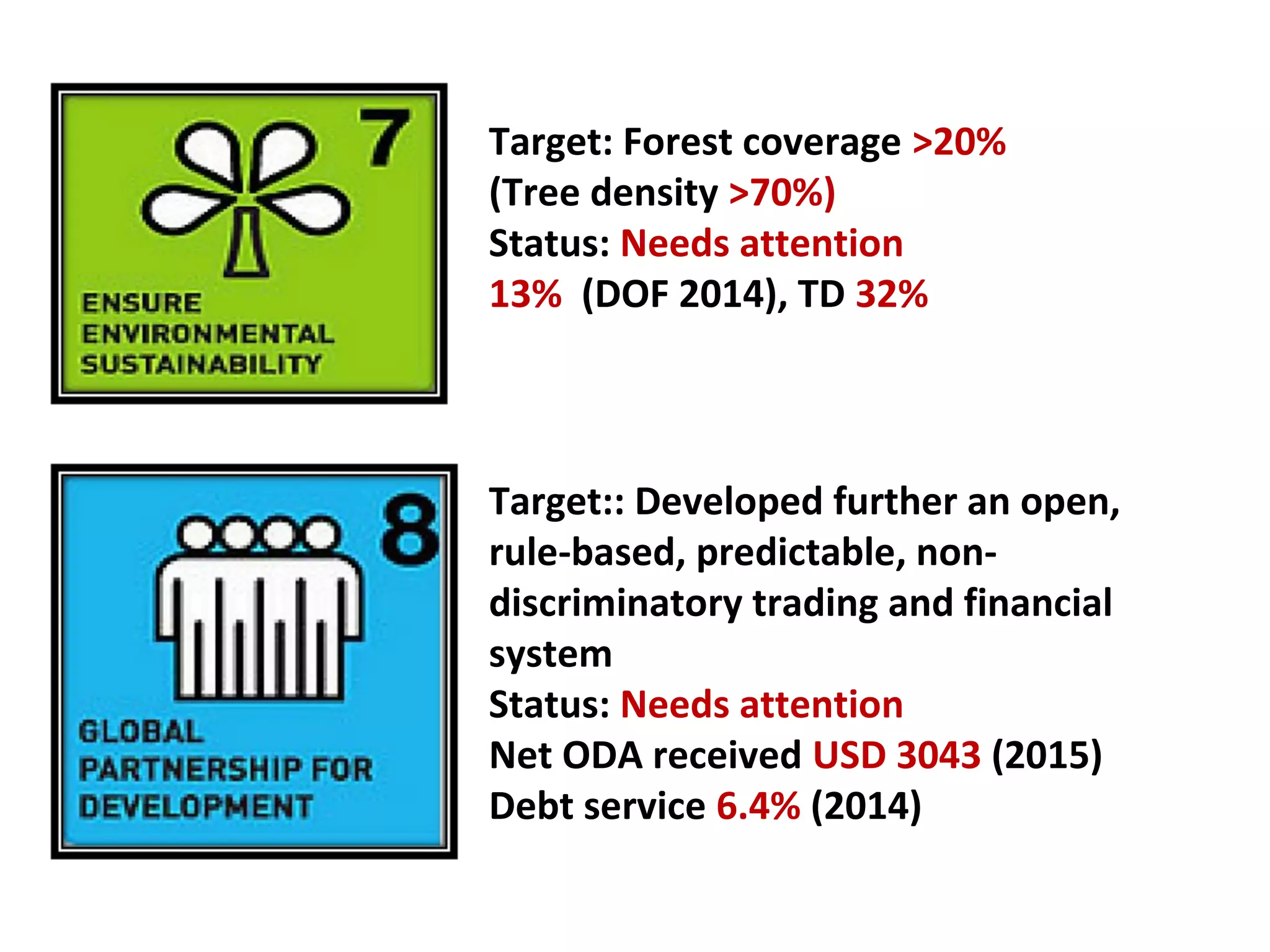
The document summarizes Bangladesh's status on achieving the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). It reports that Bangladesh is on track to meet targets for reducing poverty, increasing primary education enrollment and gender parity, and reducing maternal and child mortality. However, it needs attention on targets for reducing diseases like malaria and tuberculosis, increasing overseas development assistance, and increasing forest coverage. It discusses challenges like inadequate land for food production. It also outlines Bangladesh's plan to align its 7th Five Year Plan with the new Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) framework beginning in 2016.