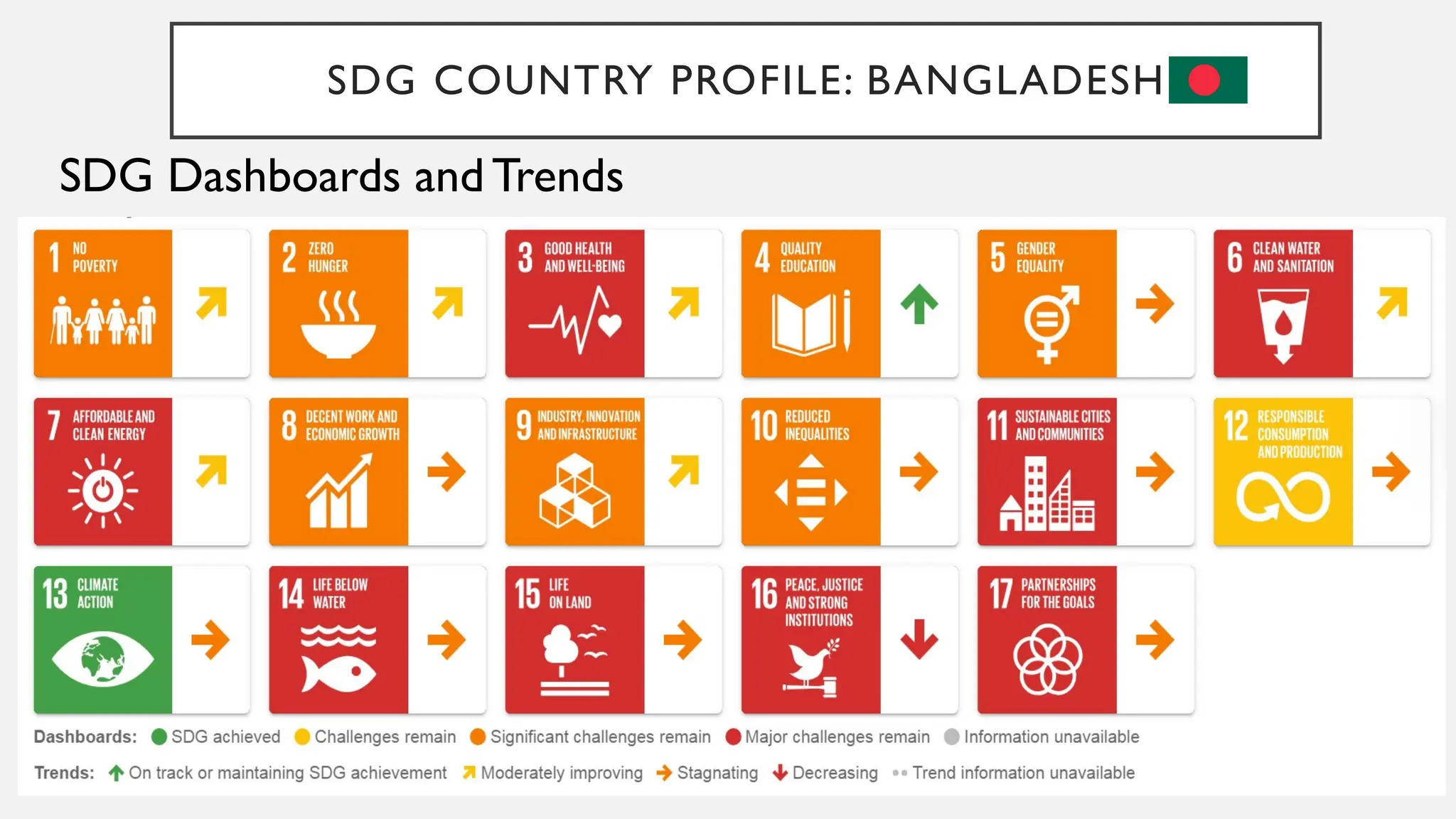
The document discusses the progress of Bangladesh regarding the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), highlighting the adoption of the SDGs in 2015 which aim to address global challenges and promote peace and prosperity. It notes improvements in areas such as maternal and child health, access to electricity, and women's representation in government, while also mentioning that Bangladesh ranked 107 in the SDG index as of 2024. Additionally, a survey indicated that global public priorities for SDGs emphasize zero hunger, no poverty, and good health and wellbeing.