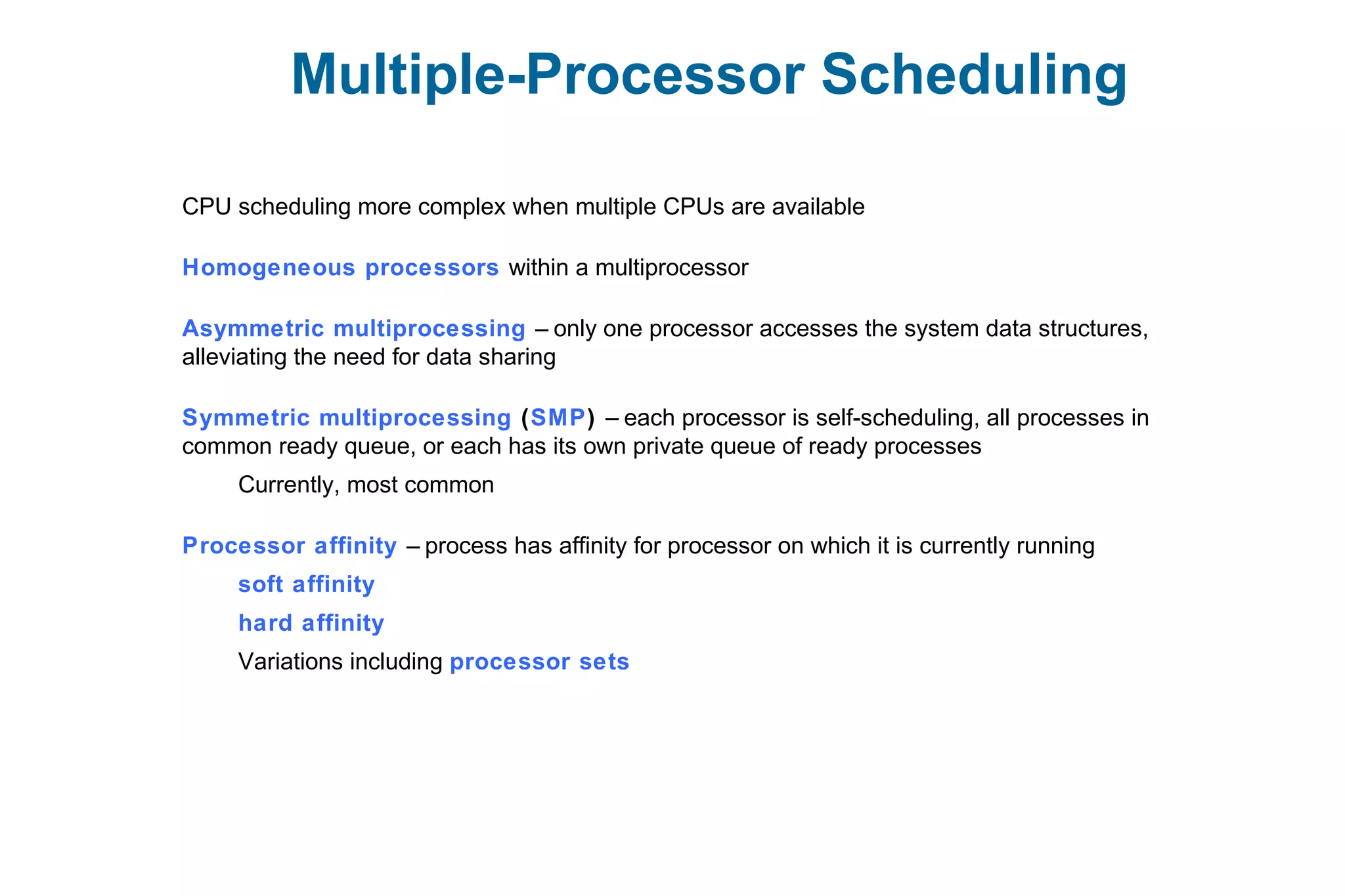
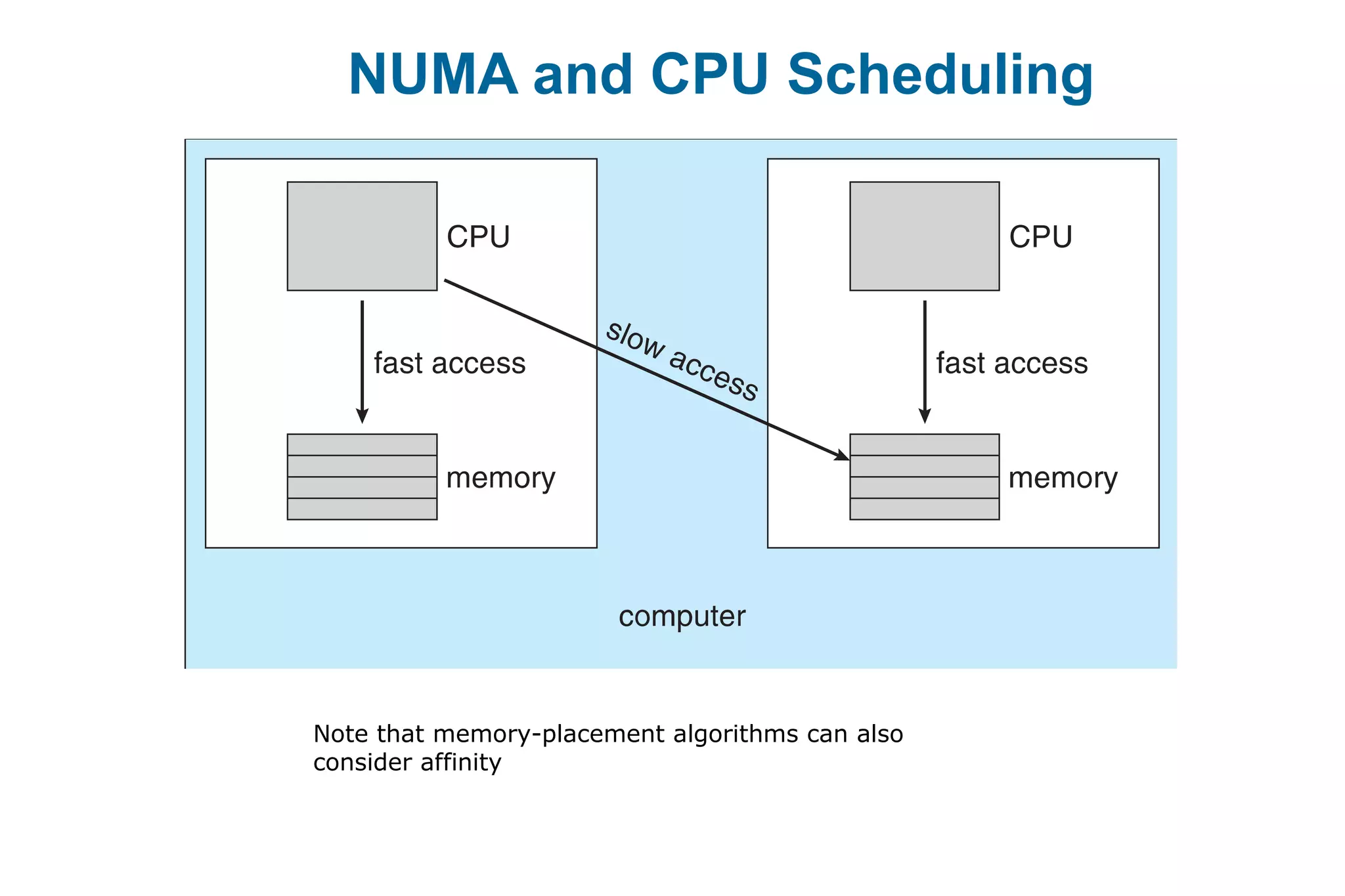
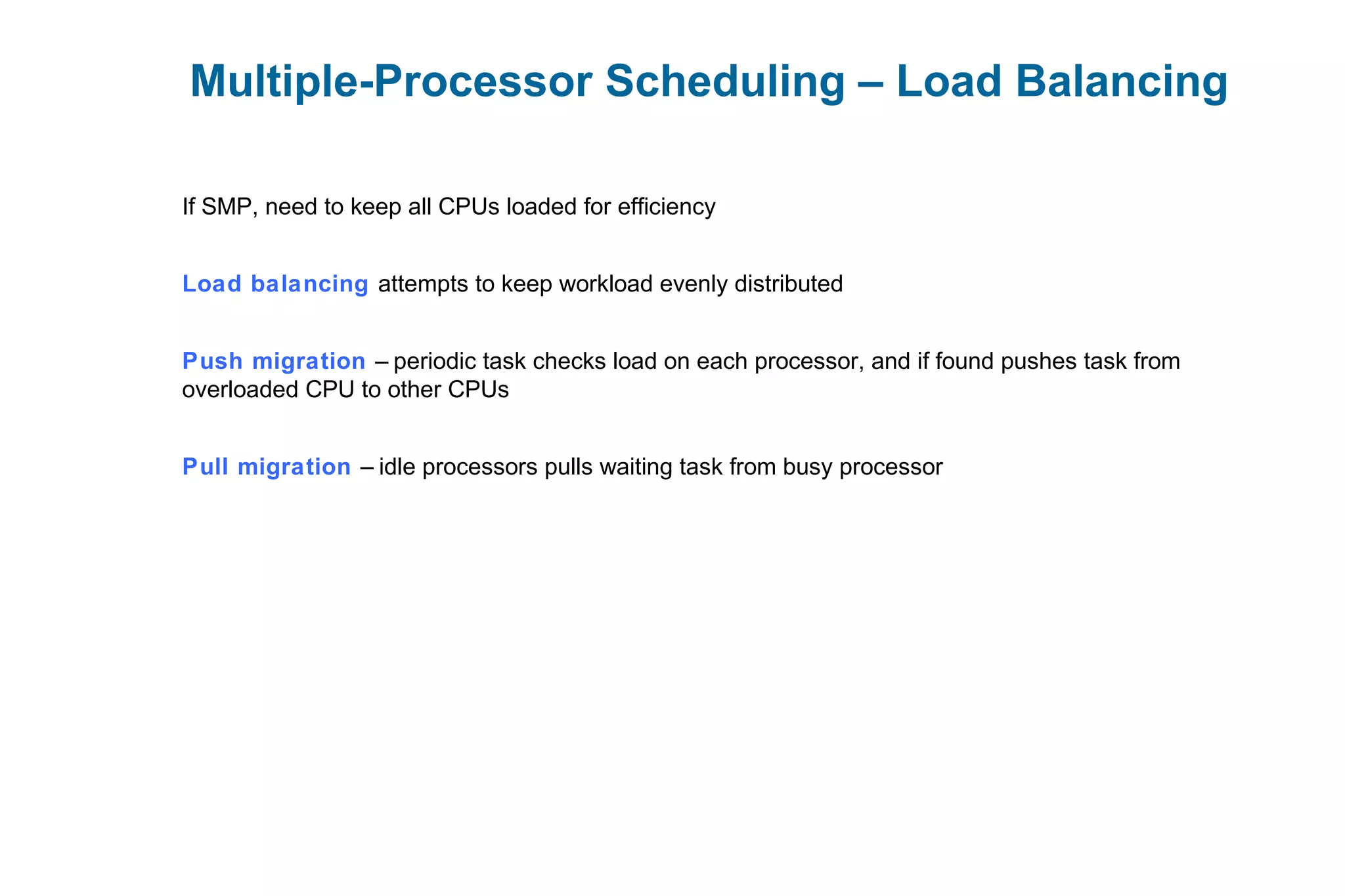
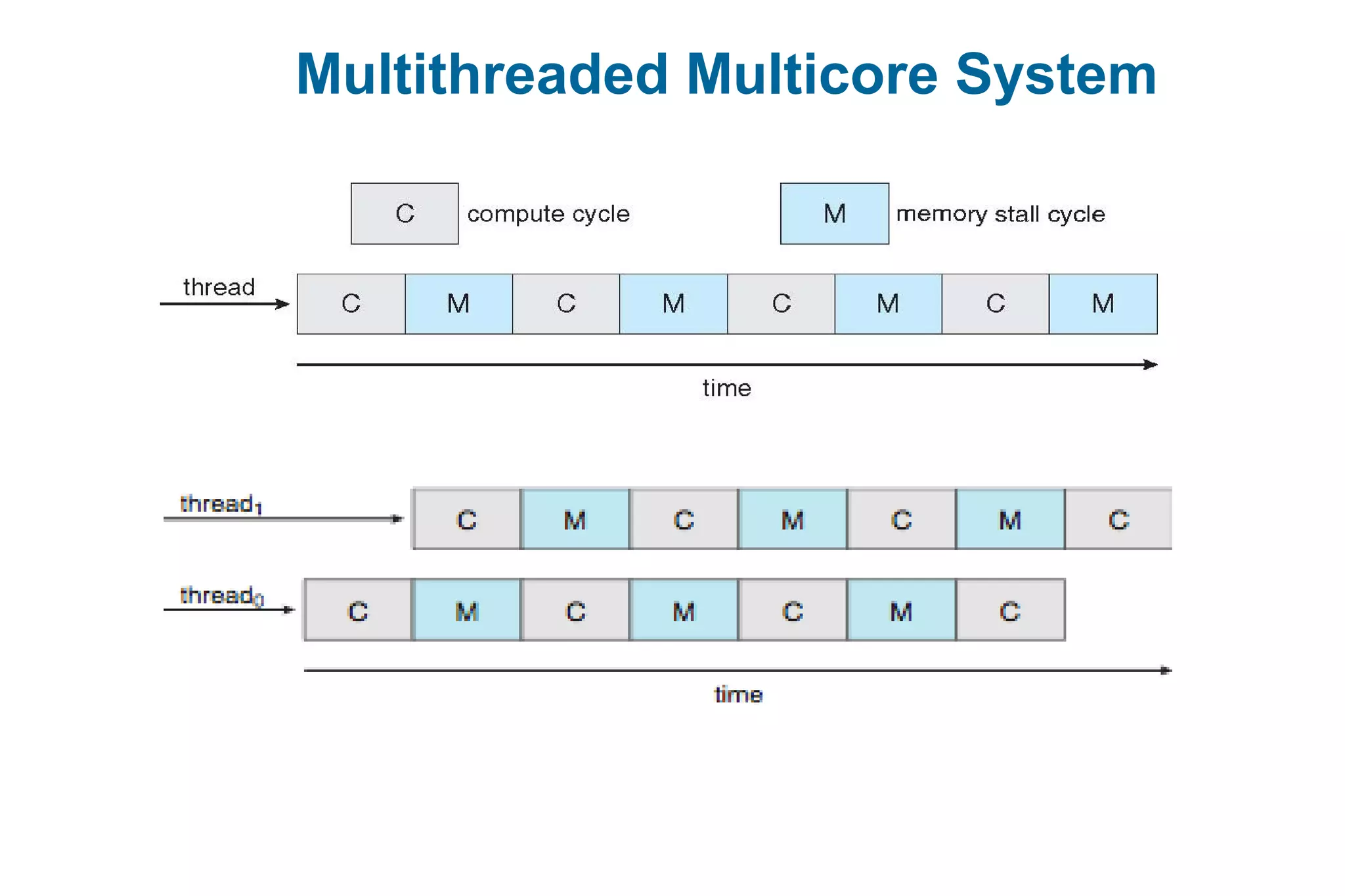
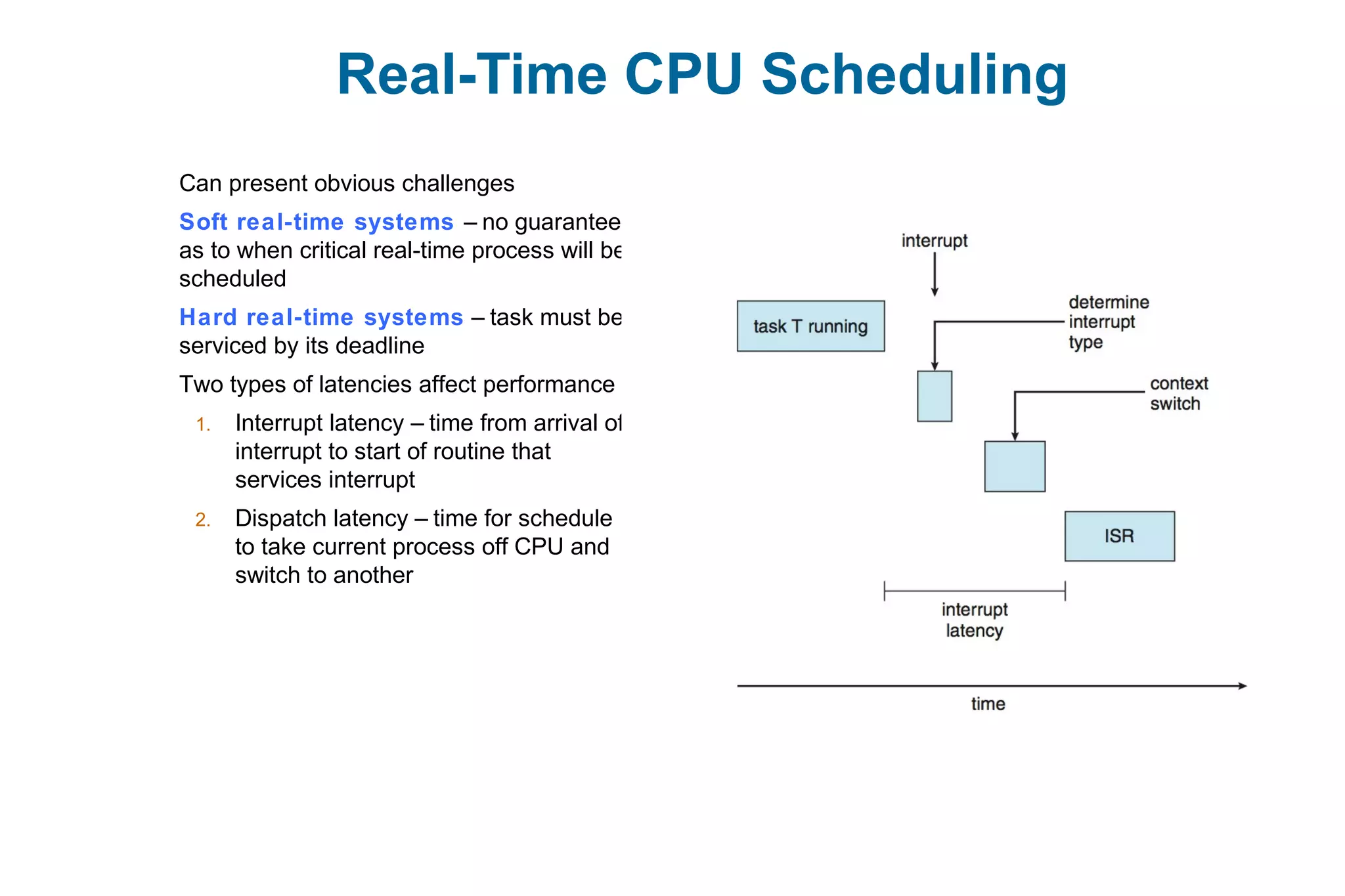
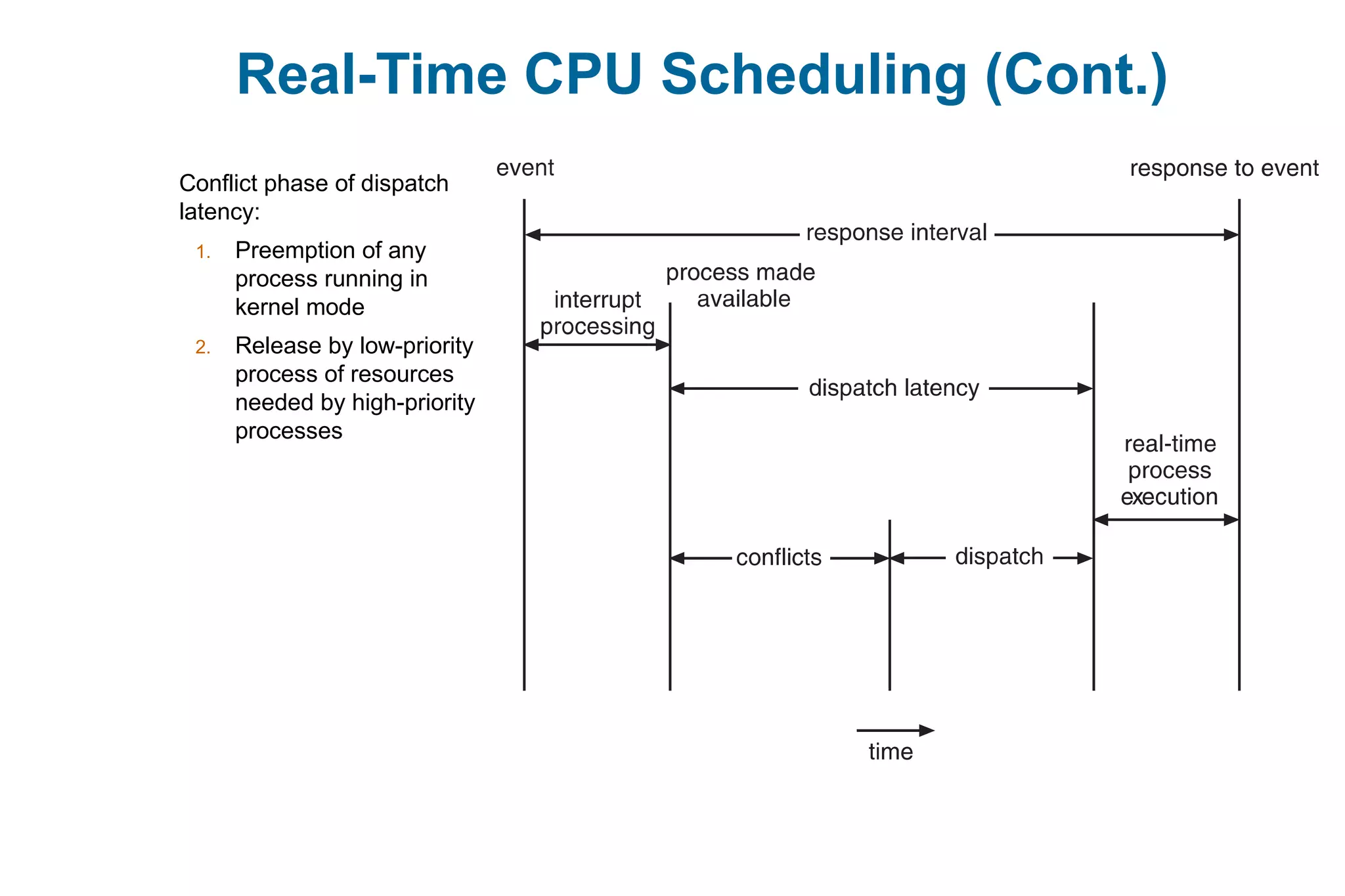
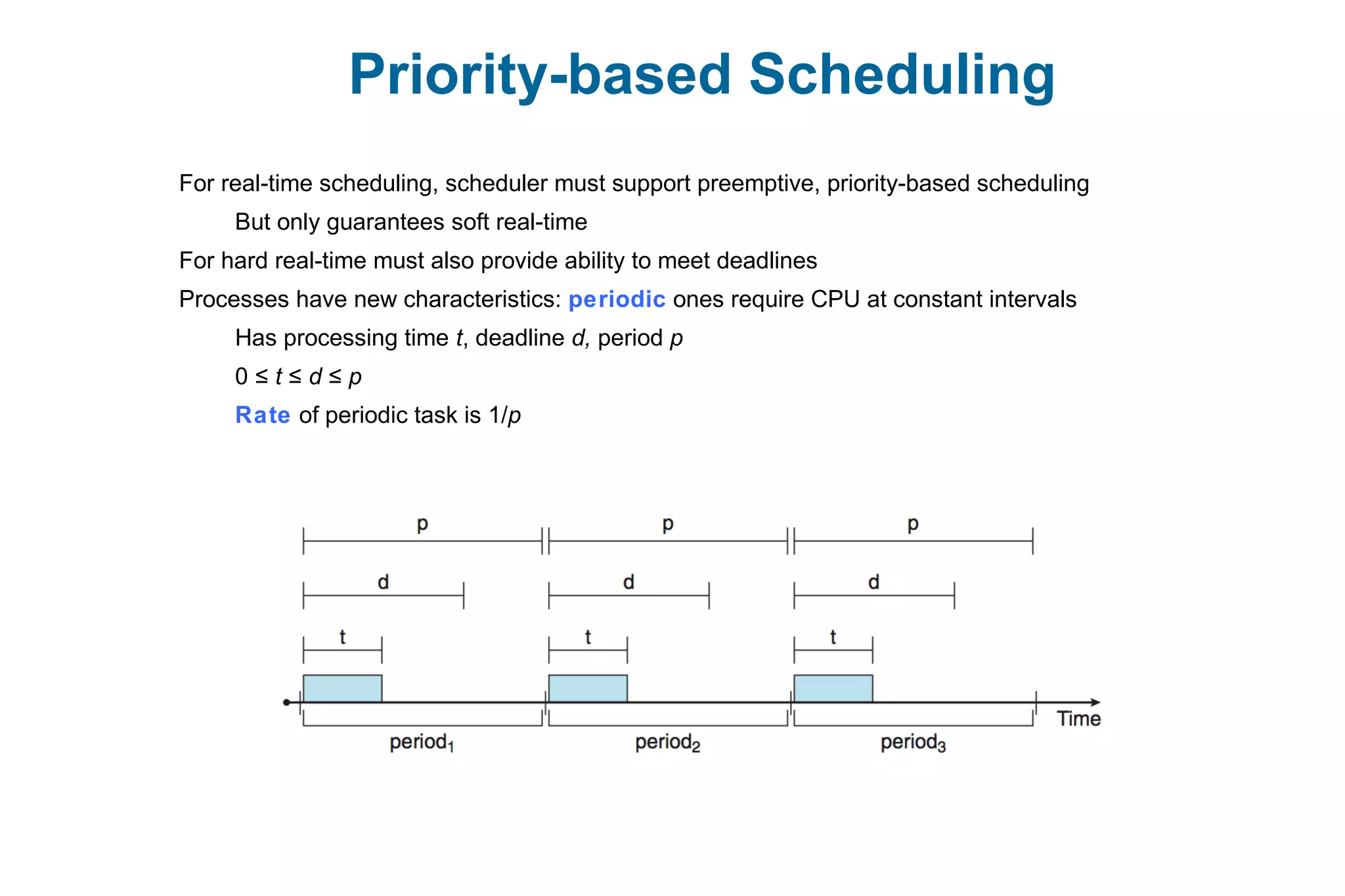
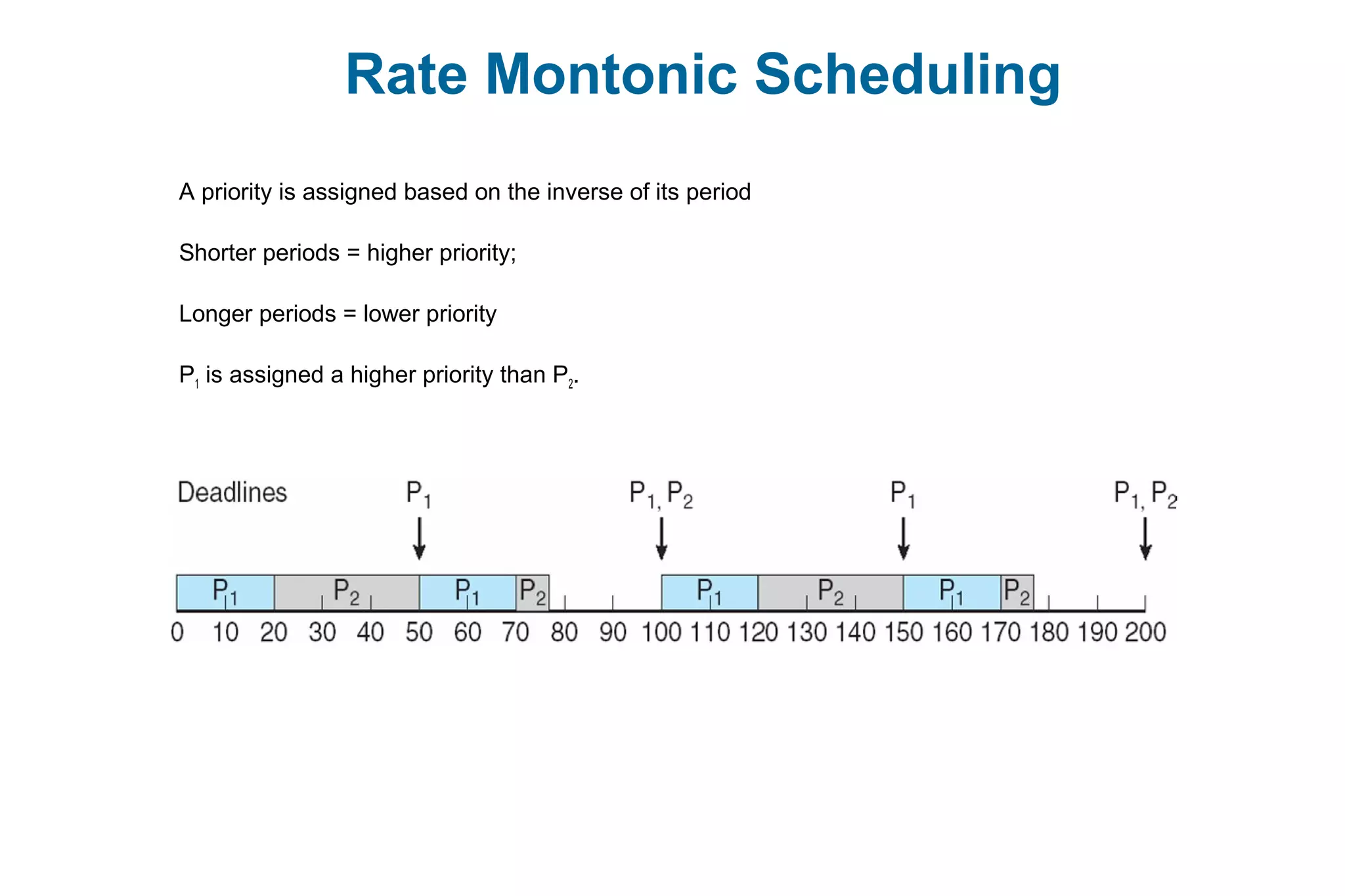
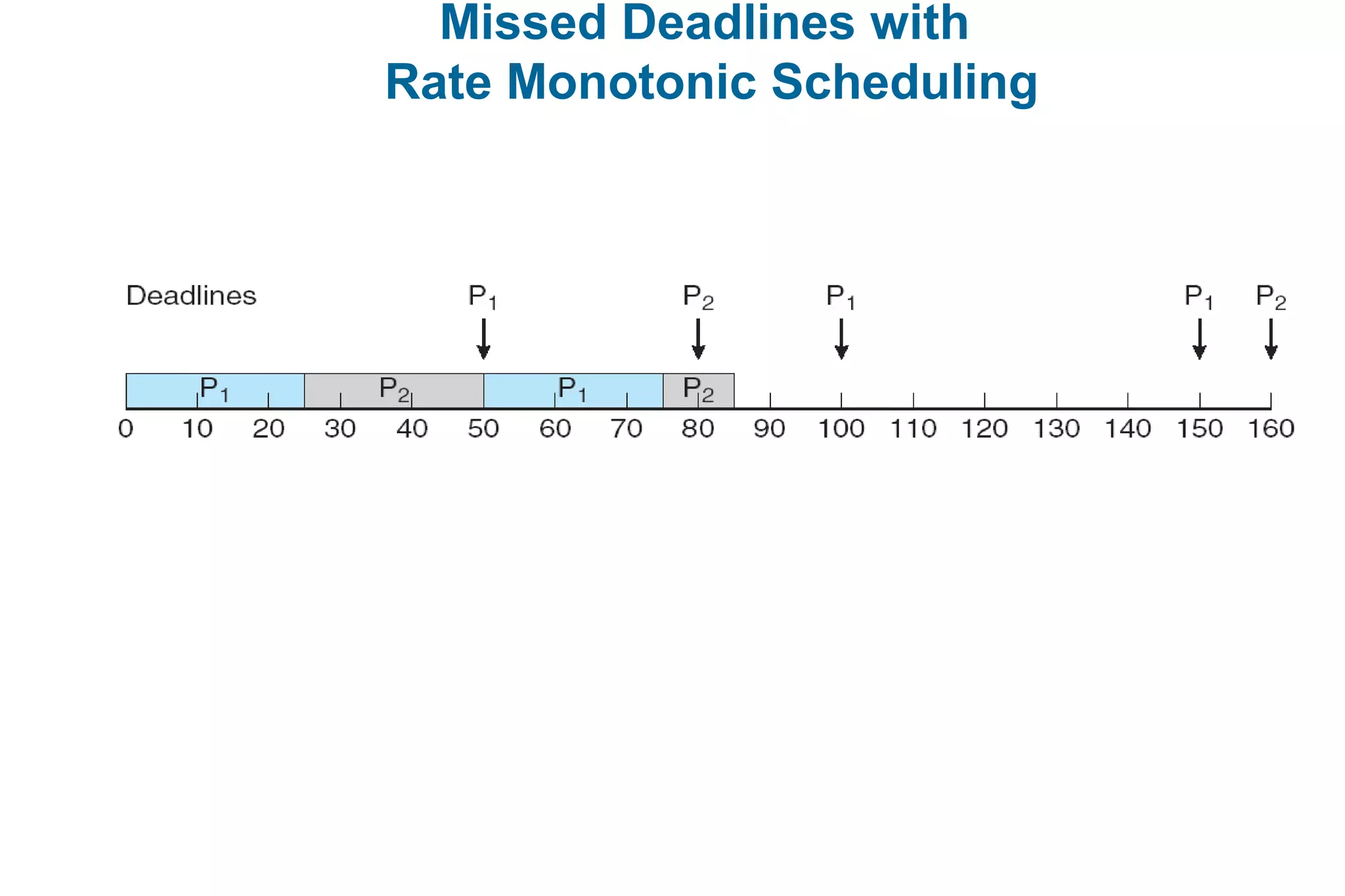
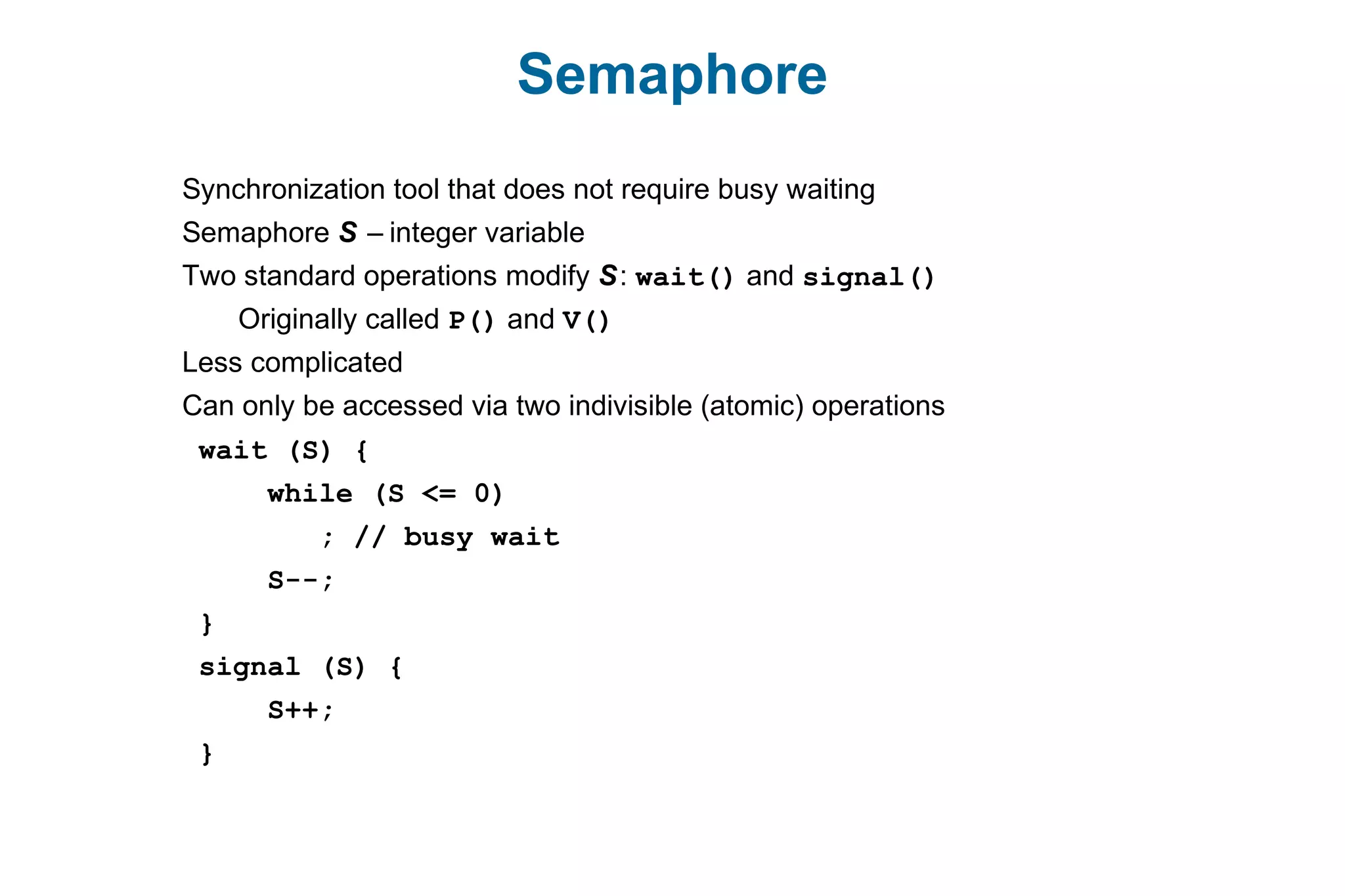
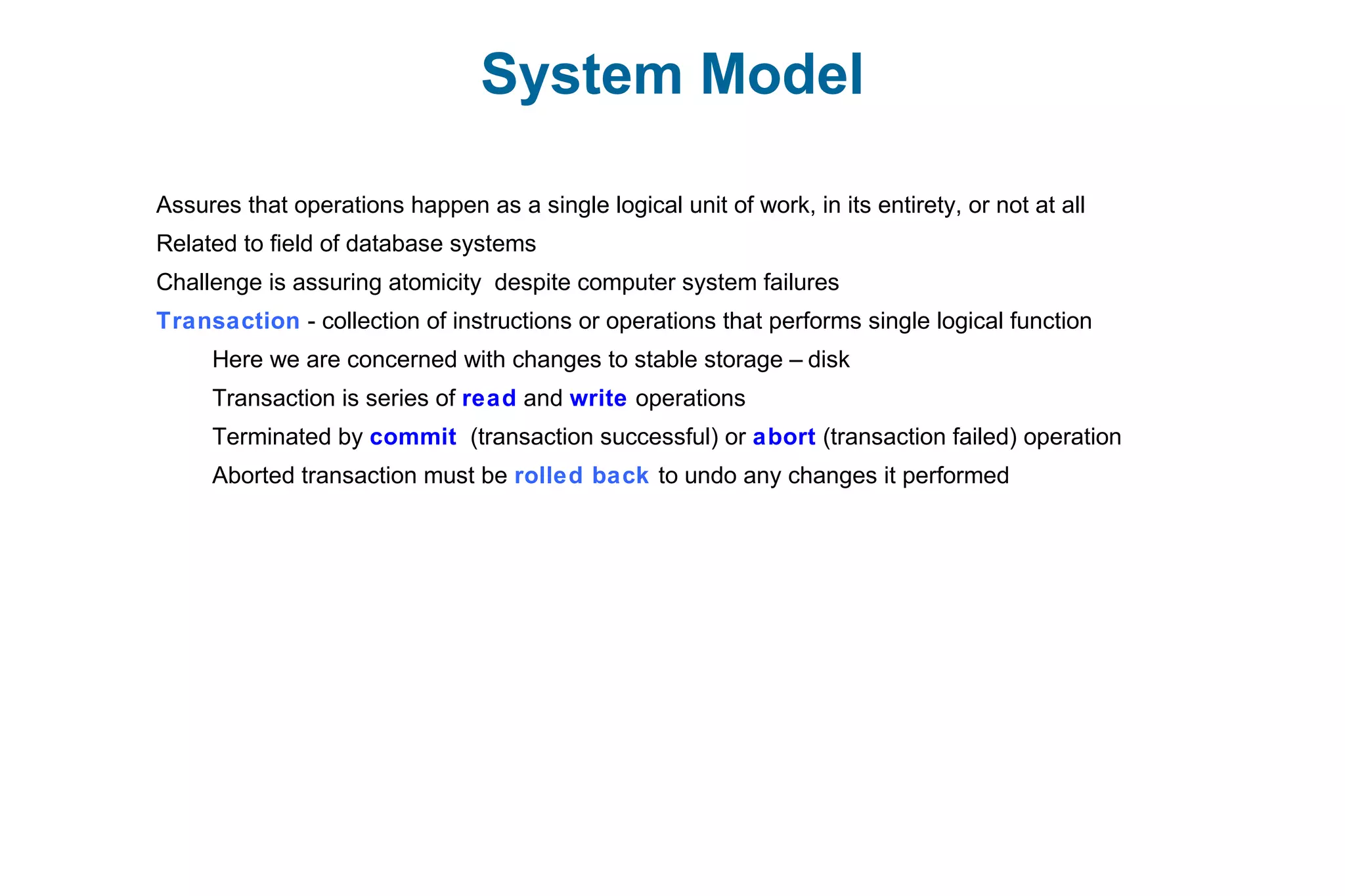
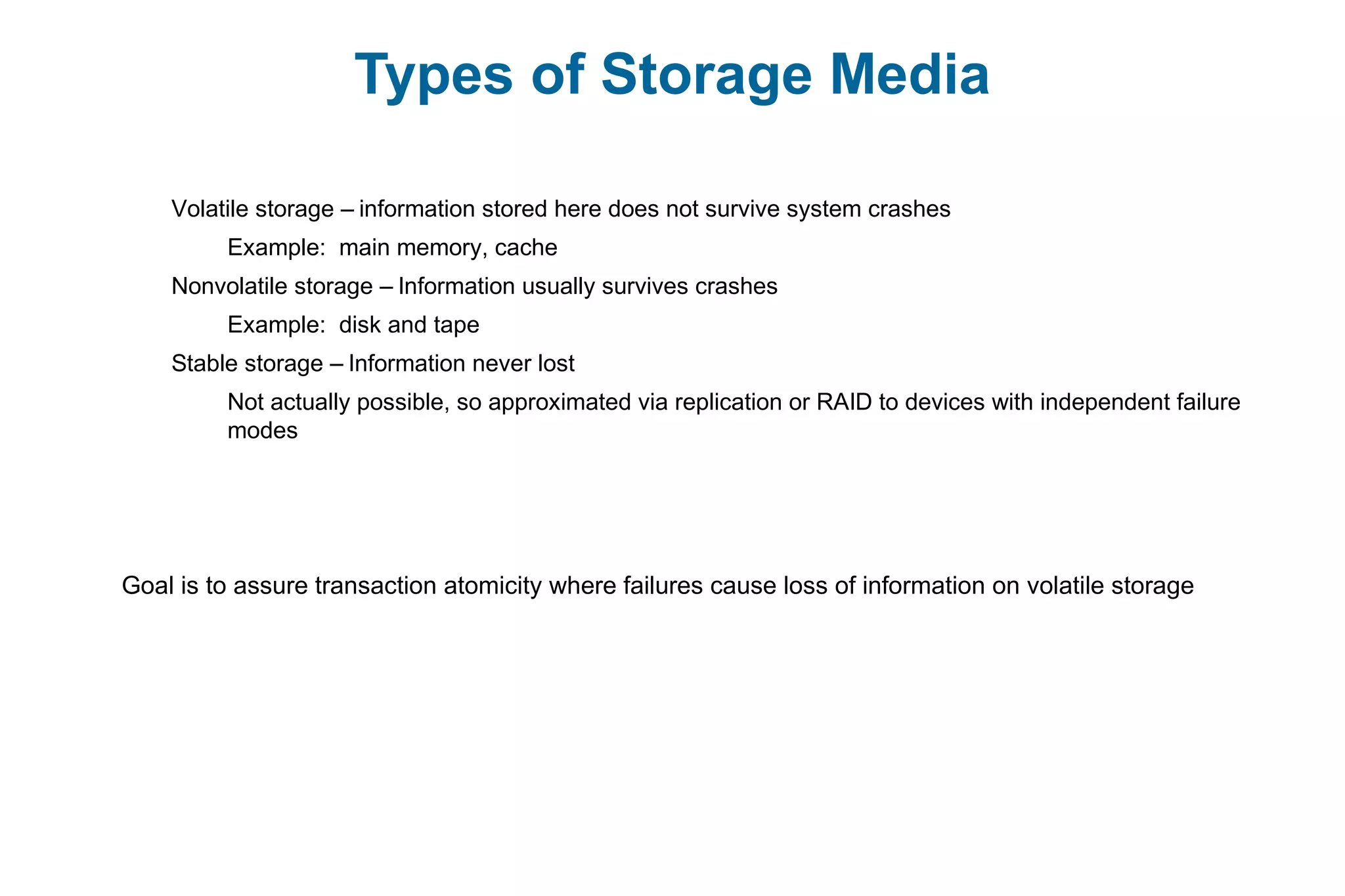
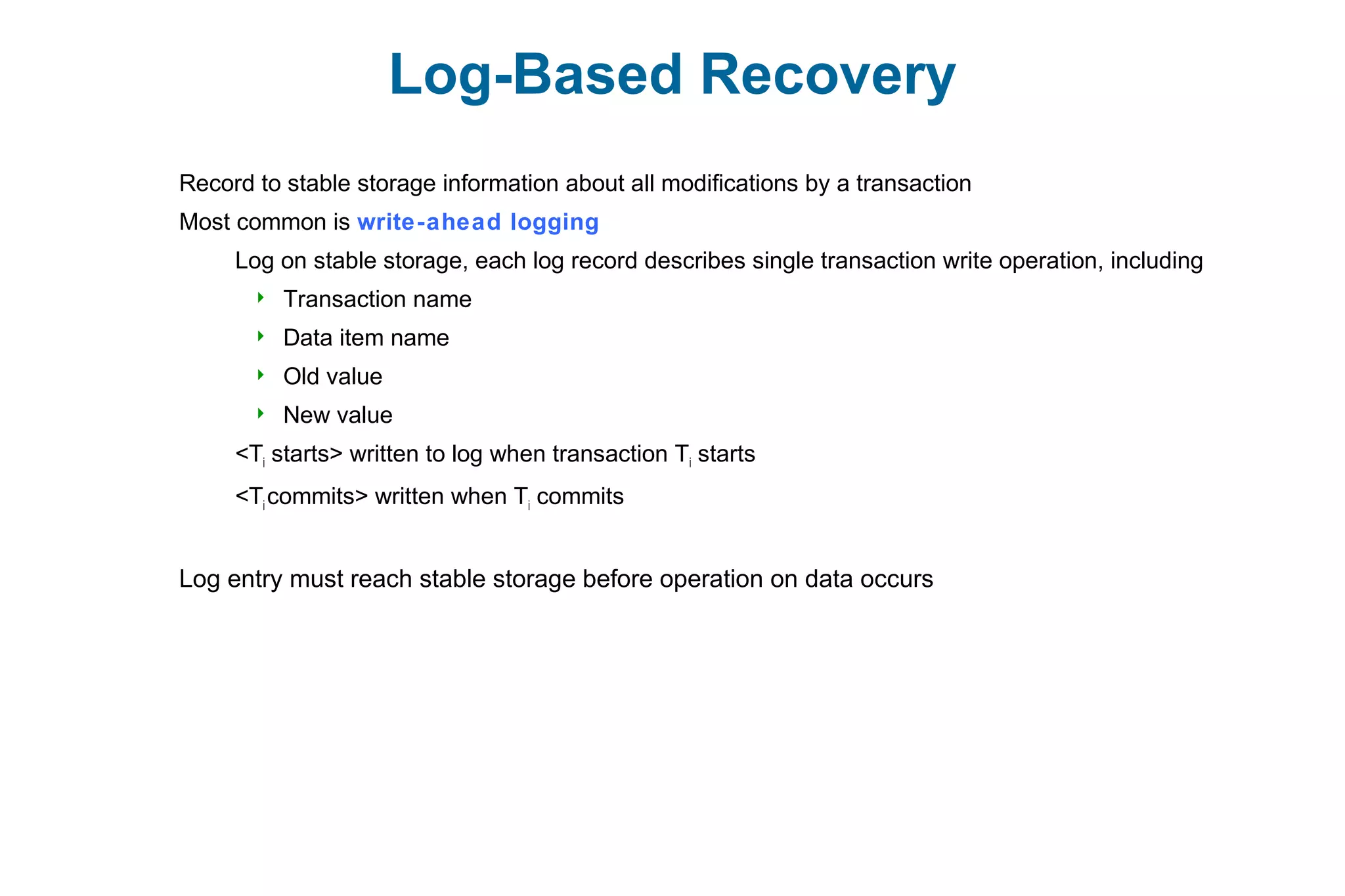
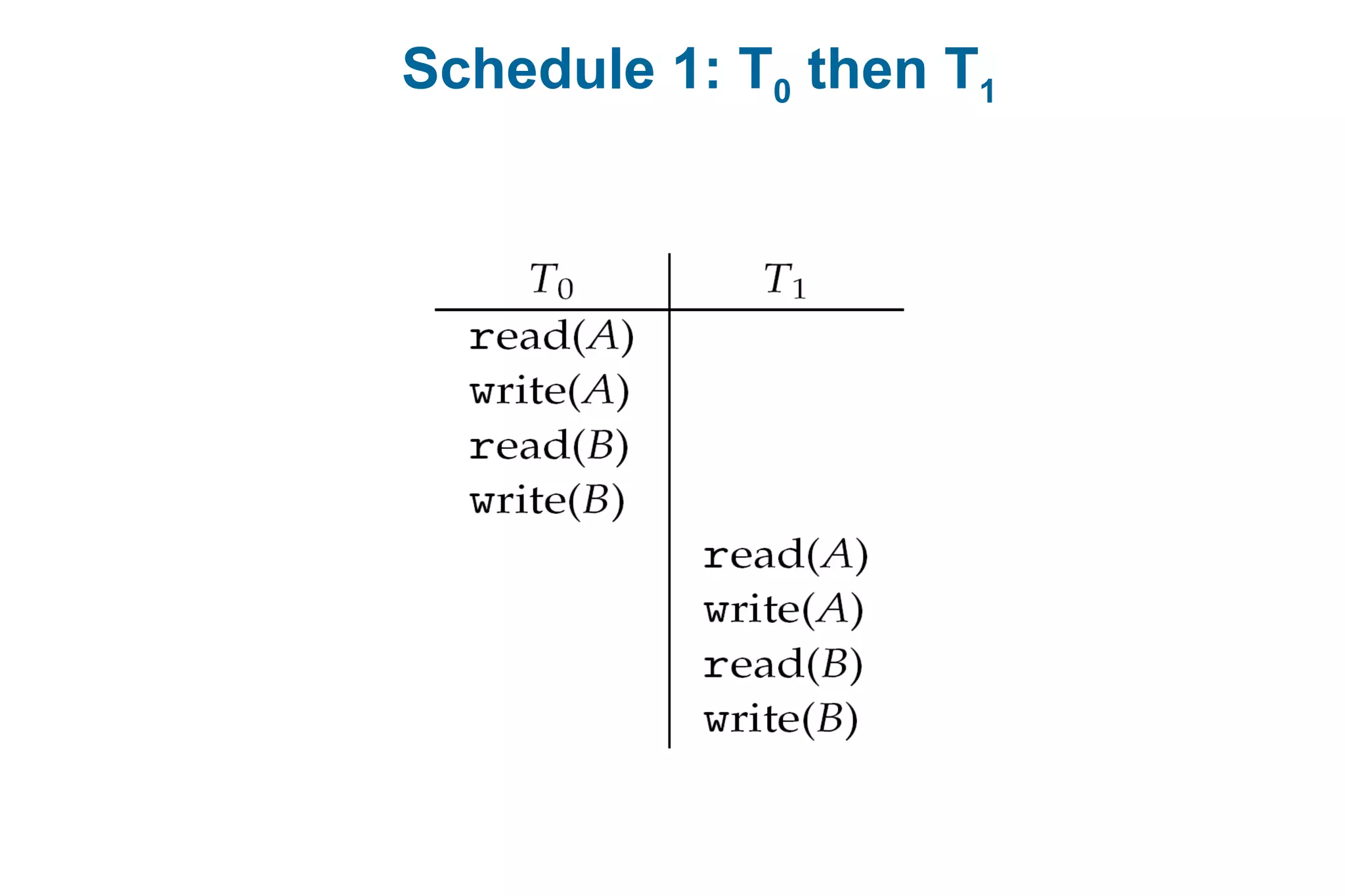
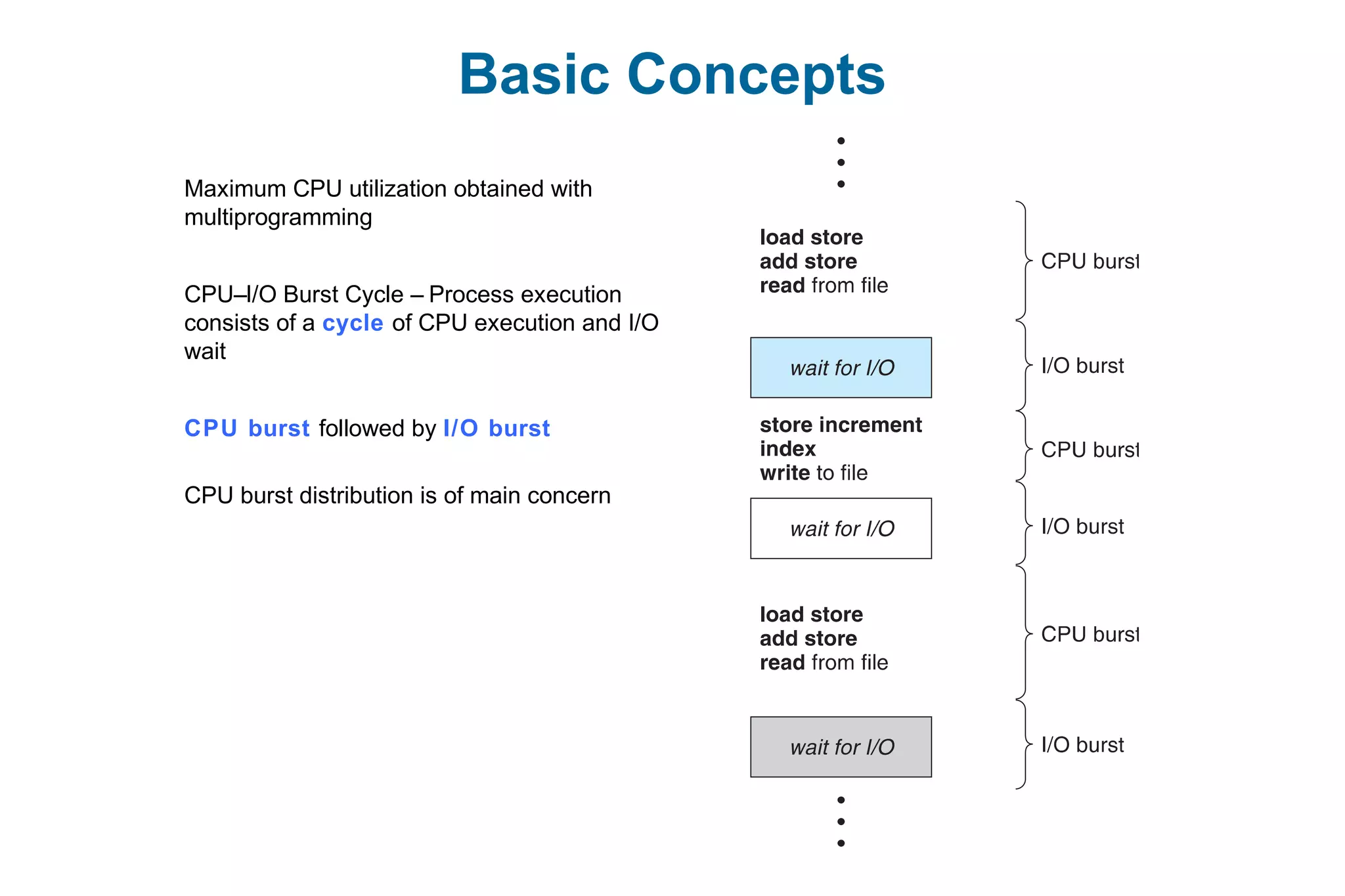
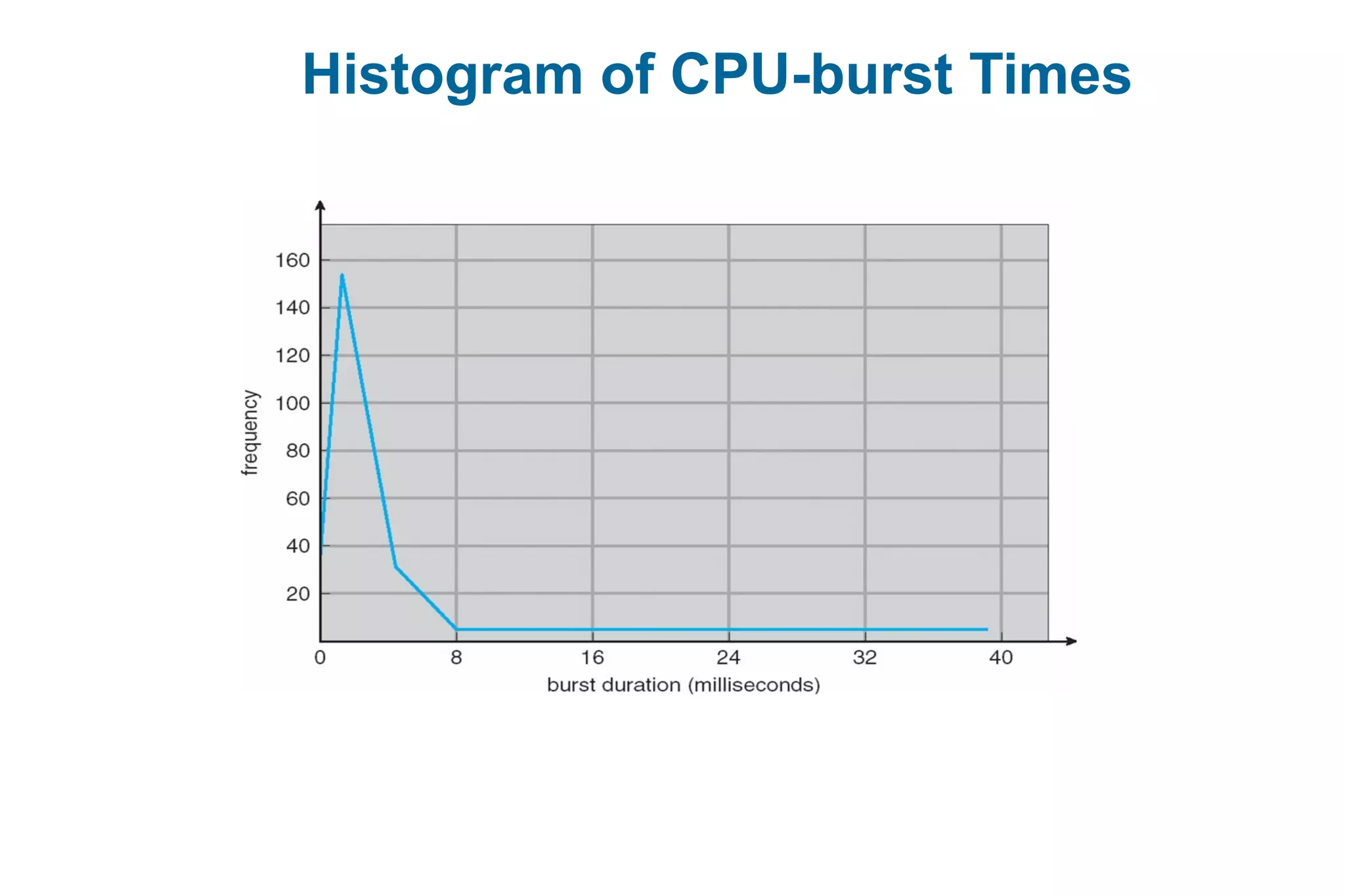
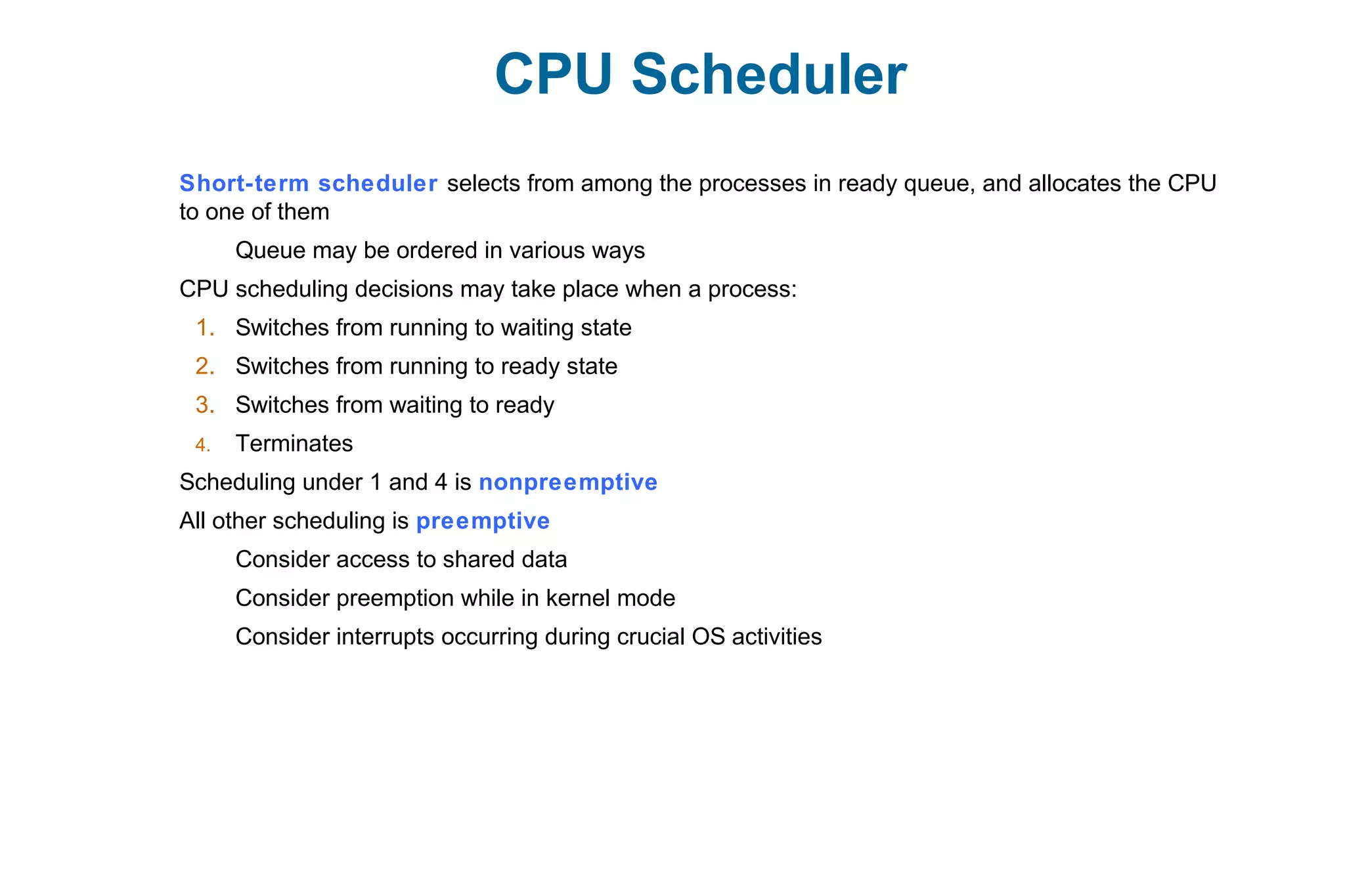
This document discusses various techniques for process synchronization and concurrency control in distributed systems. It begins by introducing classical problems like the bounded buffer problem and solutions like semaphores. It then covers monitors and condition variables as higher-level synchronization constructs. Various examples of synchronization in real systems like Solaris, Linux, and Windows are provided. The document concludes with a discussion of techniques to ensure atomic transactions in the presence of failures, including log-based recovery, checkpoints, and concurrency control protocols like two-phase locking and timestamp ordering.










![Dining-Philosophers Problem
Philosophers spend their lives thinking and eating
Don’t interact with their neighbors, occasionally try to pick up 2 chopsticks (one at a time) to
eat from bowl
Need both to eat, then release both when done
In the case of 5 philosophers
Shared data
Bowl of rice (data set)
Semaphore chopstick [5] initialized to 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mca-iiosu-2processmanagementcommunication-150318000357-conversion-gate01/75/Mca-ii-os-u-2-process-management-communication-18-2048.jpg)
![Dining-Philosophers Problem Algorithm
The structure of Philosopher i:
do {
wait (chopstick[i] );
wait (chopStick[ (i + 1) % 5] );
// eat
signal (chopstick[i] );
signal (chopstick[ (i + 1) % 5] );
// think
} while (TRUE);
What is the problem with this algorithm?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mca-iiosu-2processmanagementcommunication-150318000357-conversion-gate01/75/Mca-ii-os-u-2-process-management-communication-19-2048.jpg)
![Solution to Dining Philosophers
monitor DiningPhilosophers
{
enum { THINKING; HUNGRY, EATING) state [5] ;
condition self [5];
void pickup (int i) {
state[i] = HUNGRY;
test(i);
if (state[i] != EATING) self [i].wait;
}
void putdown (int i) {
state[i] = THINKING;
// test left and right neighbors
test((i + 4) % 5);
test((i + 1) % 5);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mca-iiosu-2processmanagementcommunication-150318000357-conversion-gate01/75/Mca-ii-os-u-2-process-management-communication-26-2048.jpg)
![Solution to Dining Philosophers (Cont.)
void test (int i) {
if ( (state[(i + 4) % 5] != EATING) &&
(state[i] == HUNGRY) &&
(state[(i + 1) % 5] != EATING) ) {
state[i] = EATING ;
self[i].signal () ;
}
}
initialization_code() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
state[i] = THINKING;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mca-iiosu-2processmanagementcommunication-150318000357-conversion-gate01/75/Mca-ii-os-u-2-process-management-communication-27-2048.jpg)















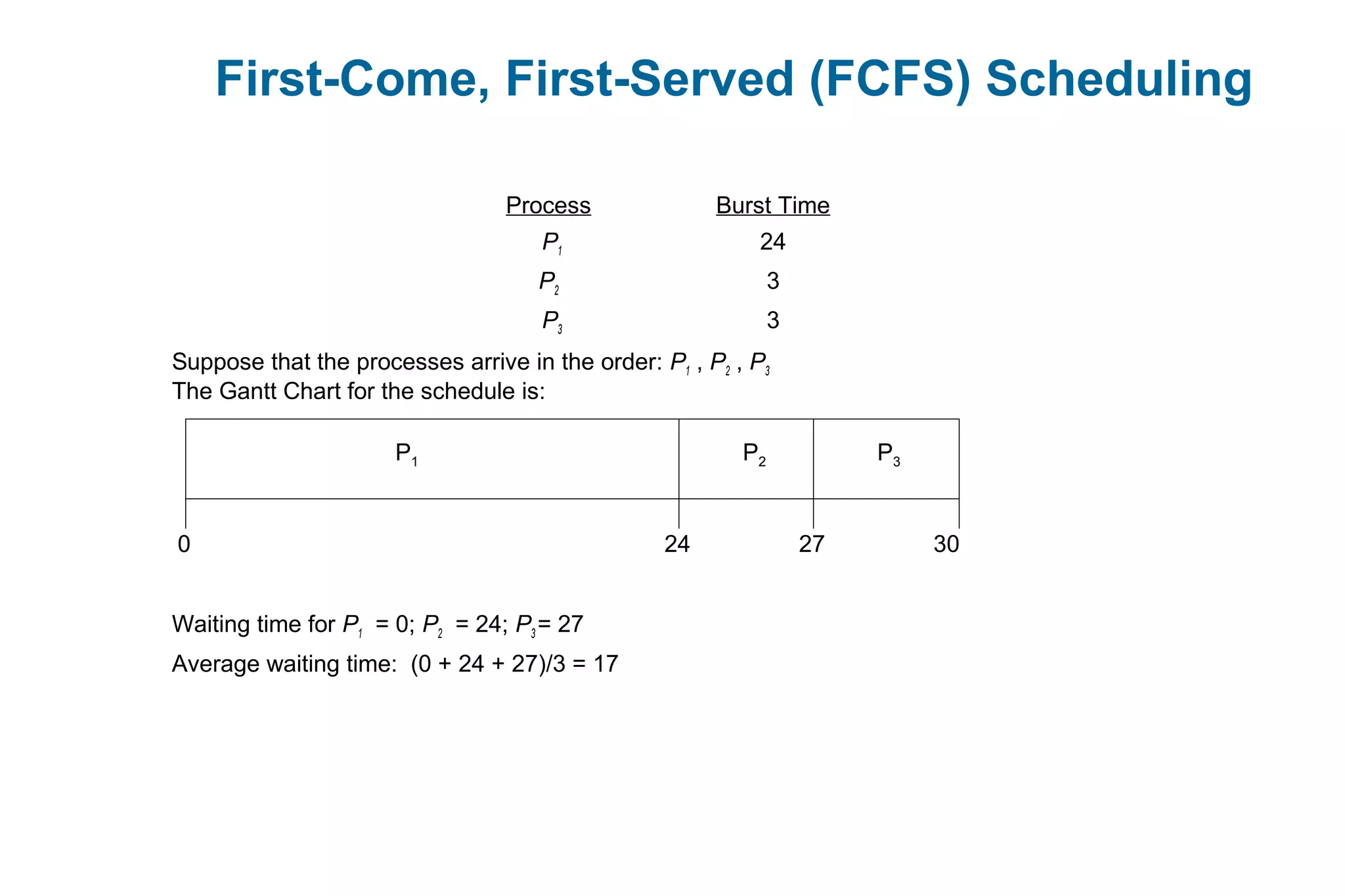
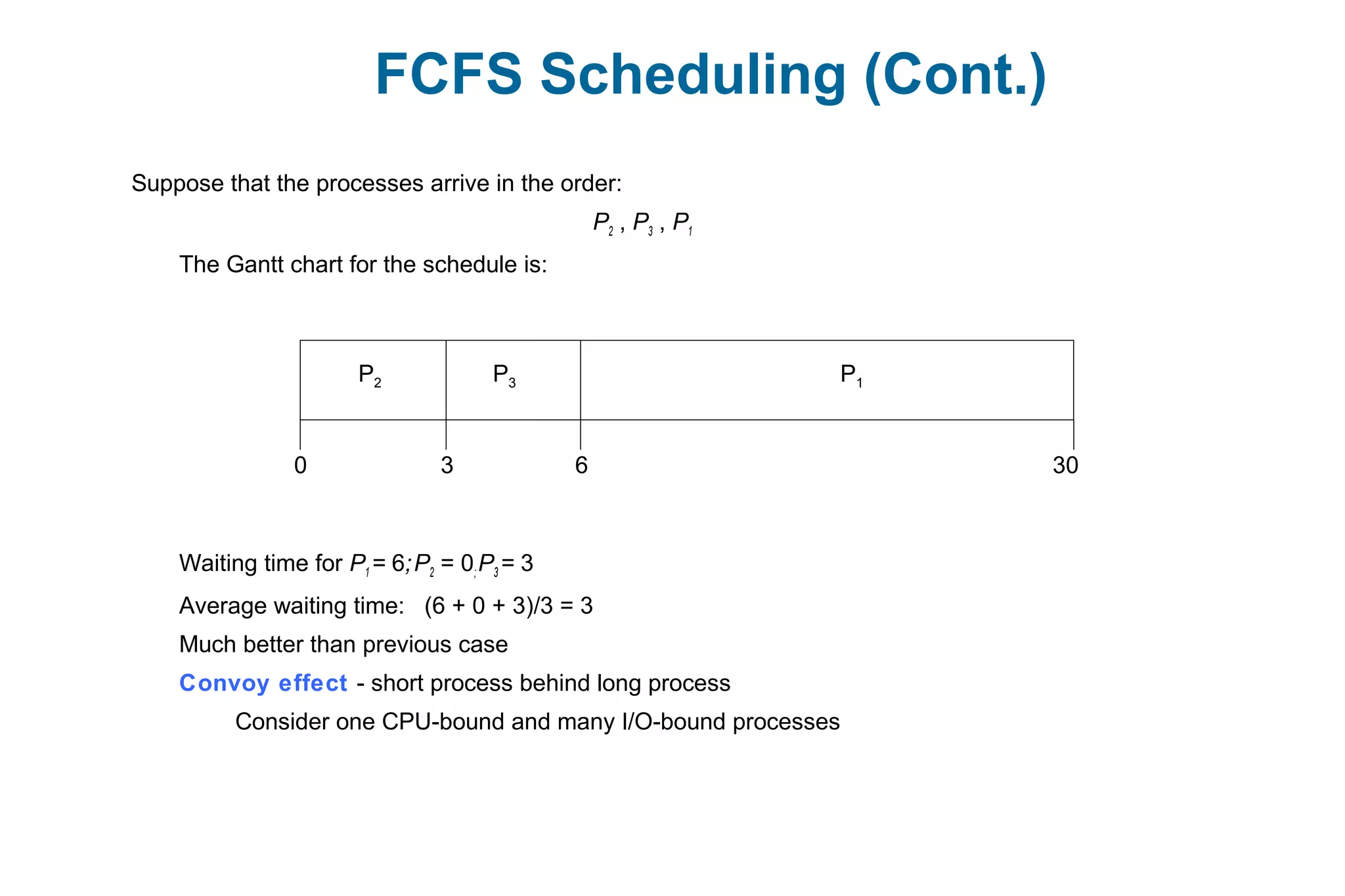

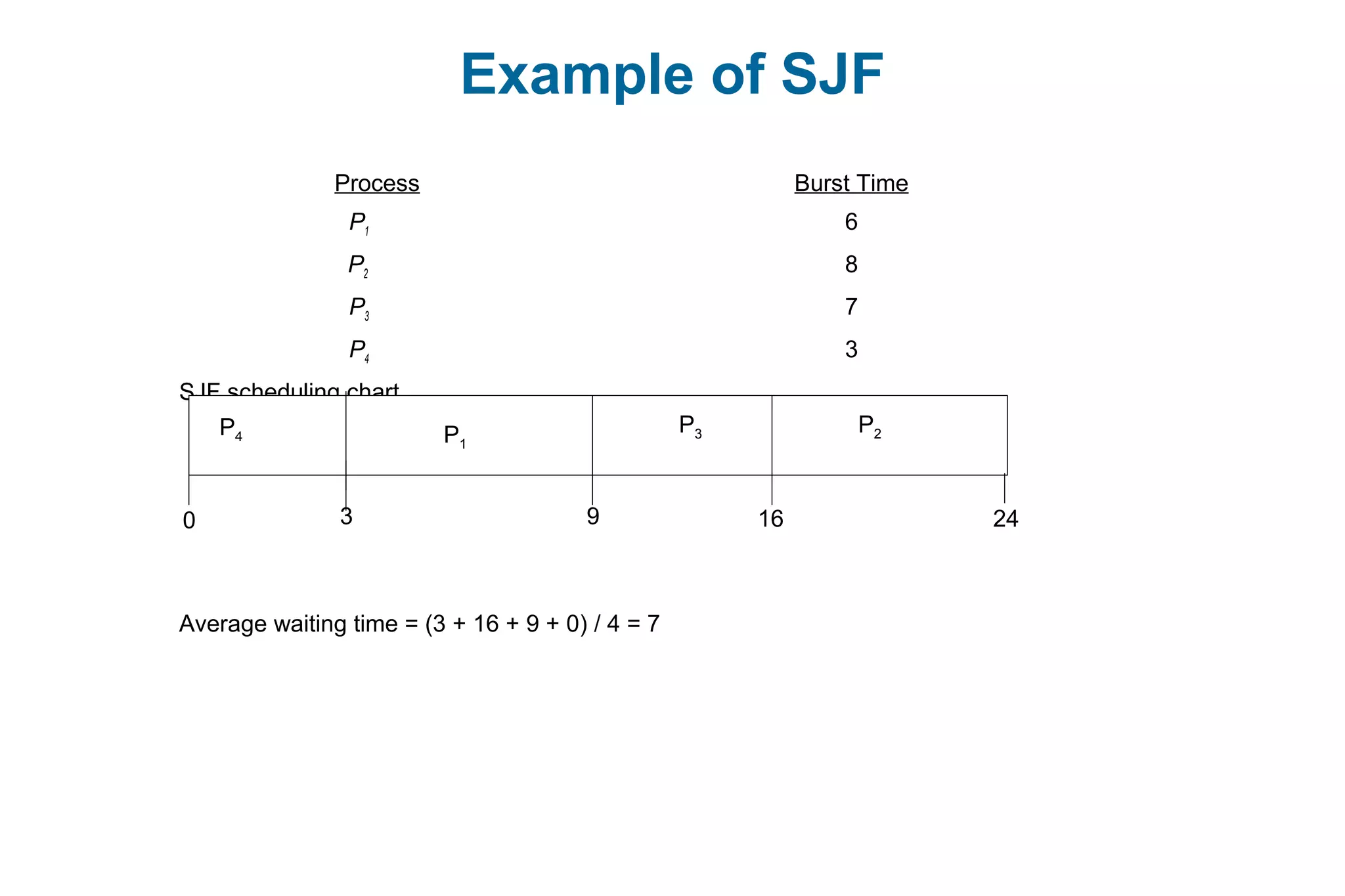
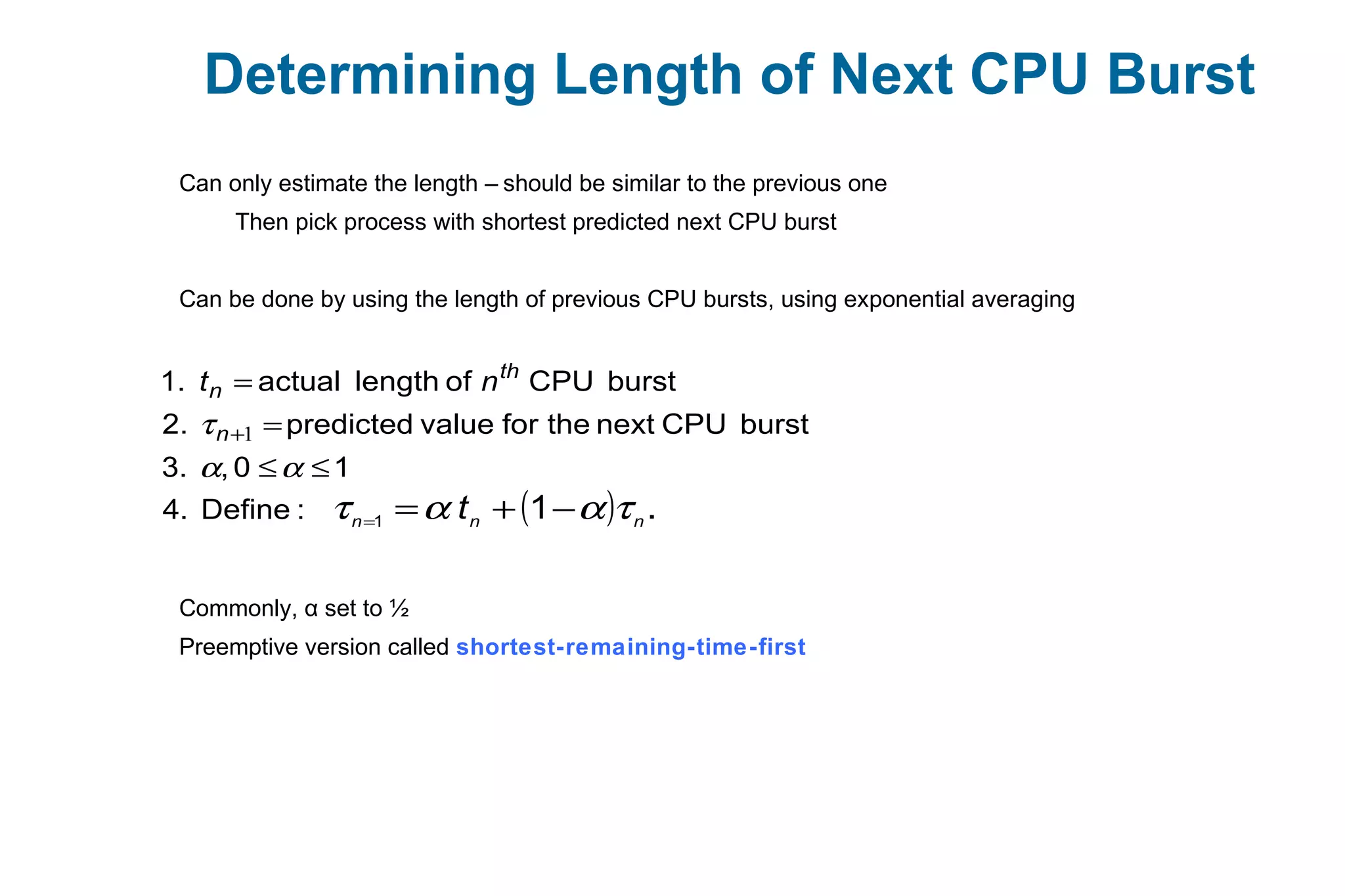

![Example of Shortest-remaining-time-first
Now we add the concepts of varying arrival times and preemption to the analysis
ProcessA arri Arrival TimeT Burst Time
P1 0 8
P2 1 4
P3 2 9
P4 3 5
Preemptive SJF Gantt Chart
Average waiting time = [(10-1)+(1-1)+(17-2)+5-3)]/4 = 26/4 = 6.5 msec
P1
P1P2
1 170 10
P3
265
P4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mca-iiosu-2processmanagementcommunication-150318000357-conversion-gate01/75/Mca-ii-os-u-2-process-management-communication-71-2048.jpg)





![Pthread Scheduling API
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define NUM_THREADS 5
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int i, scope;
pthread_t tid[NUM THREADS];
pthread_attr_t attr;
/* get the default attributes */
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
/* first inquire on the current scope */
if (pthread_attr_getscope(&attr, &scope) != 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to get scheduling scopen");
else {
if (scope == PTHREAD_SCOPE_PROCESS)
printf("PTHREAD_SCOPE_PROCESS");
else if (scope == PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM)
printf("PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM");
else
fprintf(stderr, "Illegal scope value.n");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mca-iiosu-2processmanagementcommunication-150318000357-conversion-gate01/75/Mca-ii-os-u-2-process-management-communication-84-2048.jpg)
![Pthread Scheduling API
/* set the scheduling algorithm to PCS or SCS */
pthread_attr_setscope(&attr, PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM);
/* create the threads */
for (i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++)
pthread_create(&tid[i],&attr,runner,NULL);
/* now join on each thread */
for (i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++)
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
/* Each thread will begin control in this function */
void *runner(void *param)
{
/* do some work ... */
pthread_exit(0);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mca-iiosu-2processmanagementcommunication-150318000357-conversion-gate01/75/Mca-ii-os-u-2-process-management-communication-85-2048.jpg)