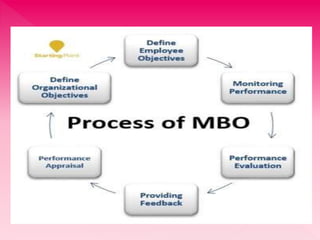
1. Management by Objectives (MBO) is a technique where managers and employees jointly set goals for a specific timeframe and work together to monitor progress.
2. The MBO process involves employees' managers informing them of organizational objectives and strategies, then employees setting their own goals for how they can contribute within a set timeframe.
3. Continuous monitoring of performance and progress against objectives is essential to the MBO process, as is regular feedback and periodic formal performance reviews between managers and employees.