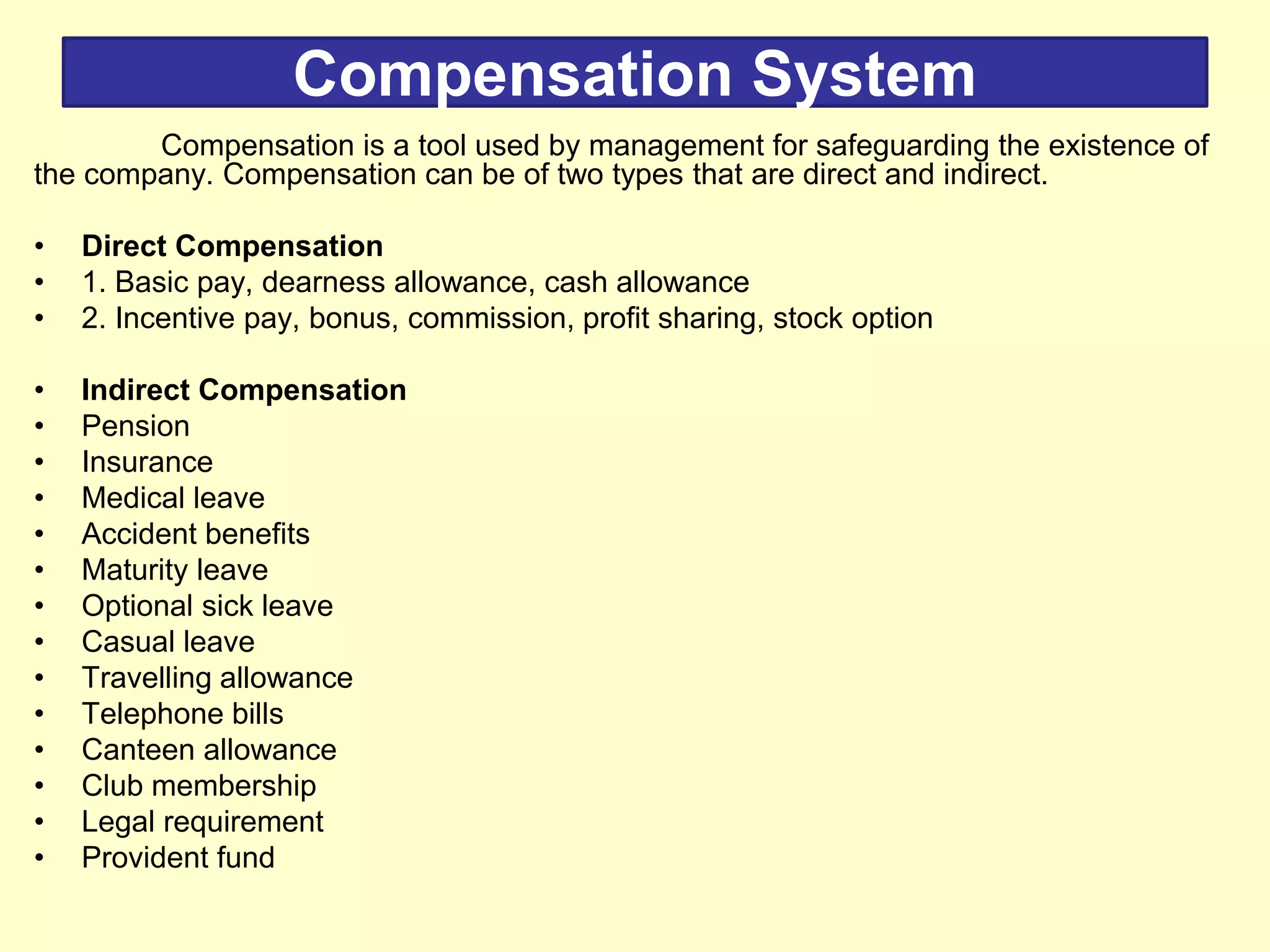
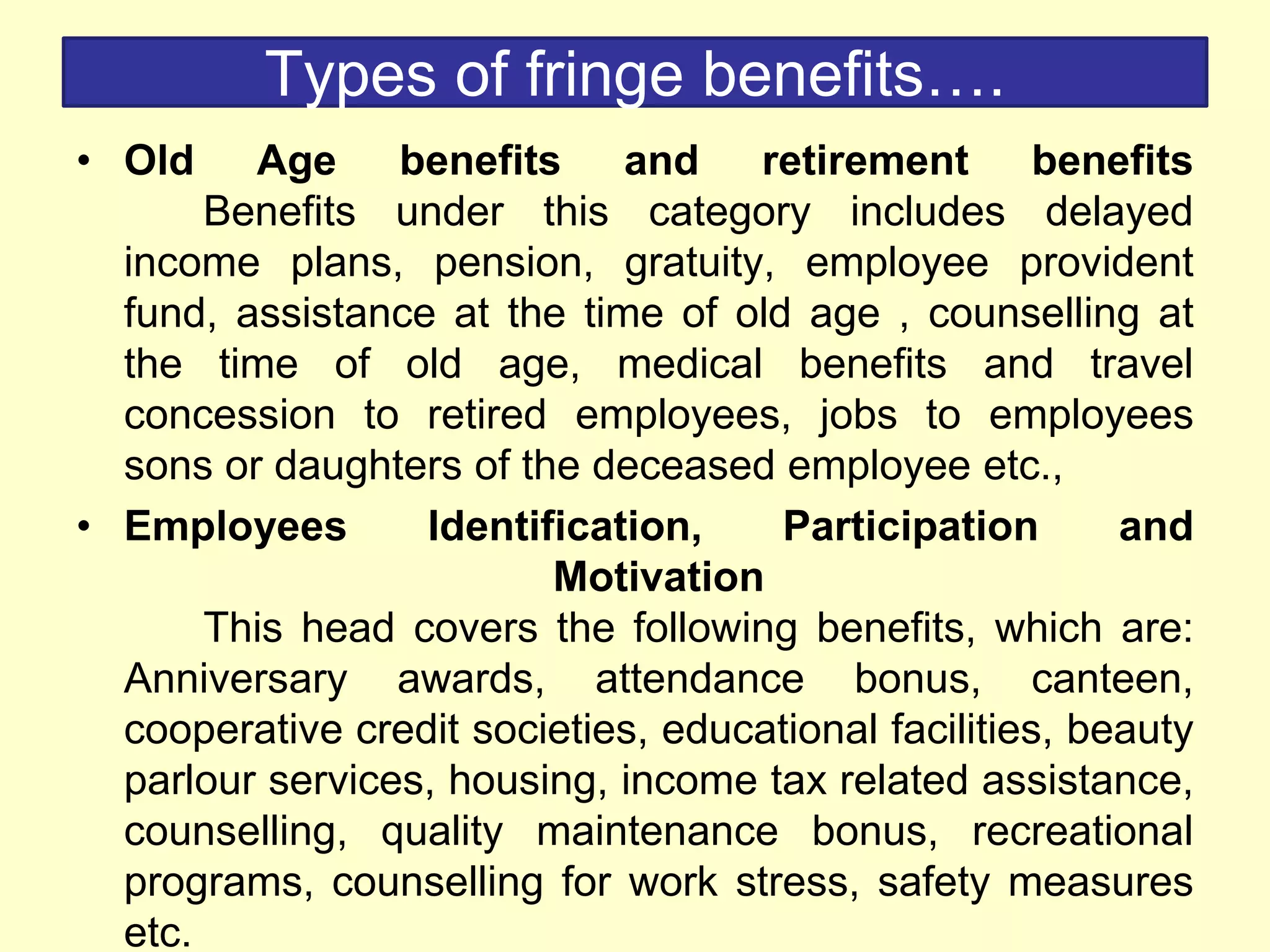
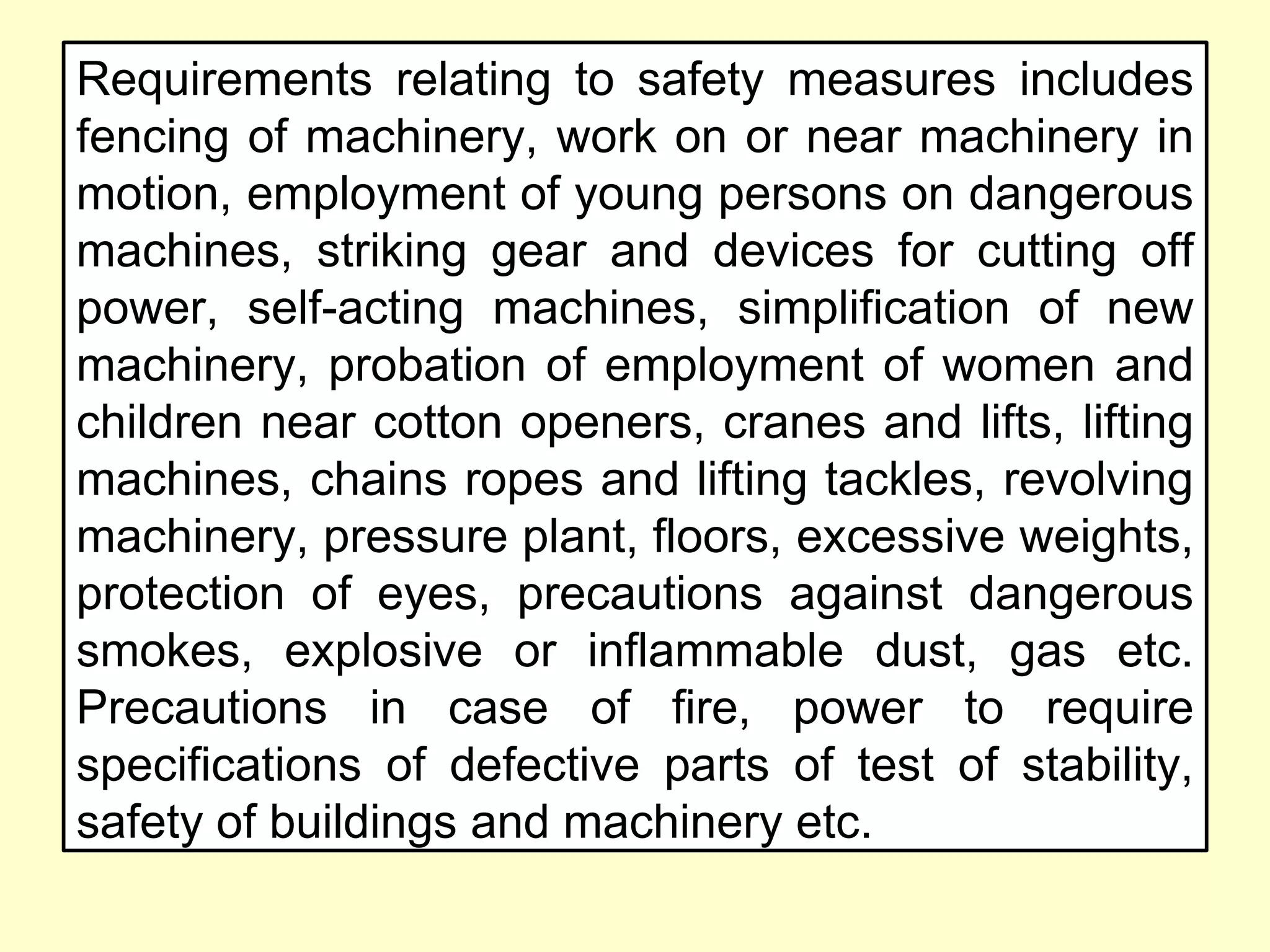
Employee compensation refers to the total rewards provided to employees in exchange for their services. It includes direct financial compensation like salary and wages, as well as indirect financial compensation or benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and legally mandated benefits. The goals of a compensation program are to attract, retain, and motivate qualified employees while achieving internal and external pay equity. Benefits can increase job satisfaction, reduce absenteeism and turnover, and provide employees with security.