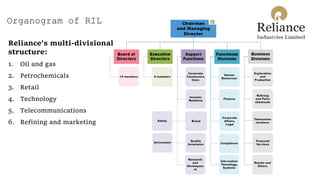
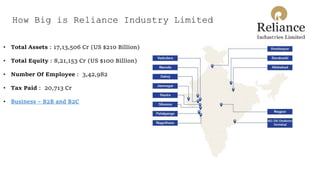
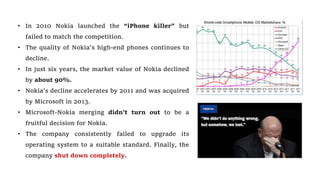
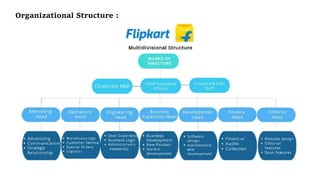
The document presents case studies on Nifty Fifty companies, focusing on their organizational structures, strategies, and challenges. Key companies include Hero MotoCorp, Reliance Industries, Nokia, Flipkart, Myntra, Jindal Saw, and Rajwant Engineering, illustrating various aspects of decision-making, market competition, and ethical dilemmas faced by these firms. Through these examples, the document explores organizational theory in practice, highlighting the importance of adaptability and ethical considerations in business operations.