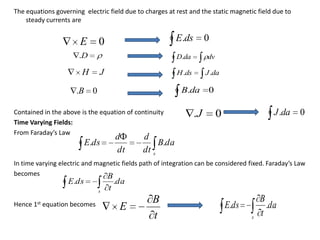
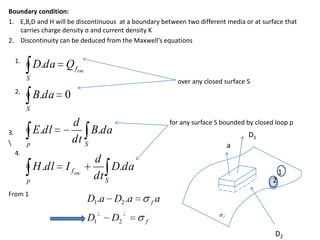
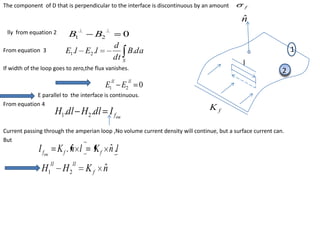
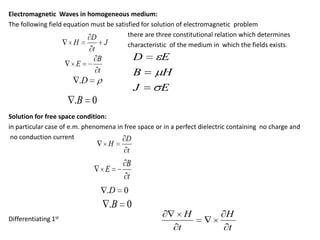
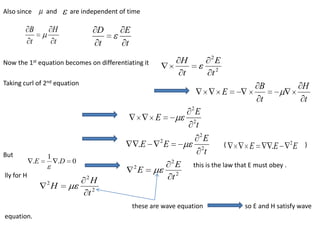
Maxwell's equations govern electric and magnetic fields and describe how they change over time. The equations relate the electric field, magnetic field, electric displacement field, magnetic induction, electric charge density, and electric current density. Maxwell showed that changing electric fields produce magnetic fields and changing magnetic fields produce electric fields. This led to the prediction and understanding of electromagnetic waves, including light. The equations also describe conditions at boundaries between different media, where some field components are continuous while others experience a discontinuity.