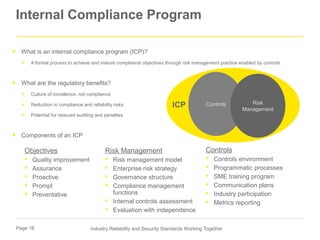
The document discusses the evolving landscape of cybersecurity and compliance standards within the power and utility industry, focusing on the integration of various frameworks like NIST and ISO. It highlights the importance of developing internal compliance programs and risk management practices tailored to organizational needs, while encouraging proactive monitoring of trends for continuous improvement. The presentation is led by experts from Ernst & Young LLP, emphasizing the need for strategic alignment with regulatory changes and effective control measures.