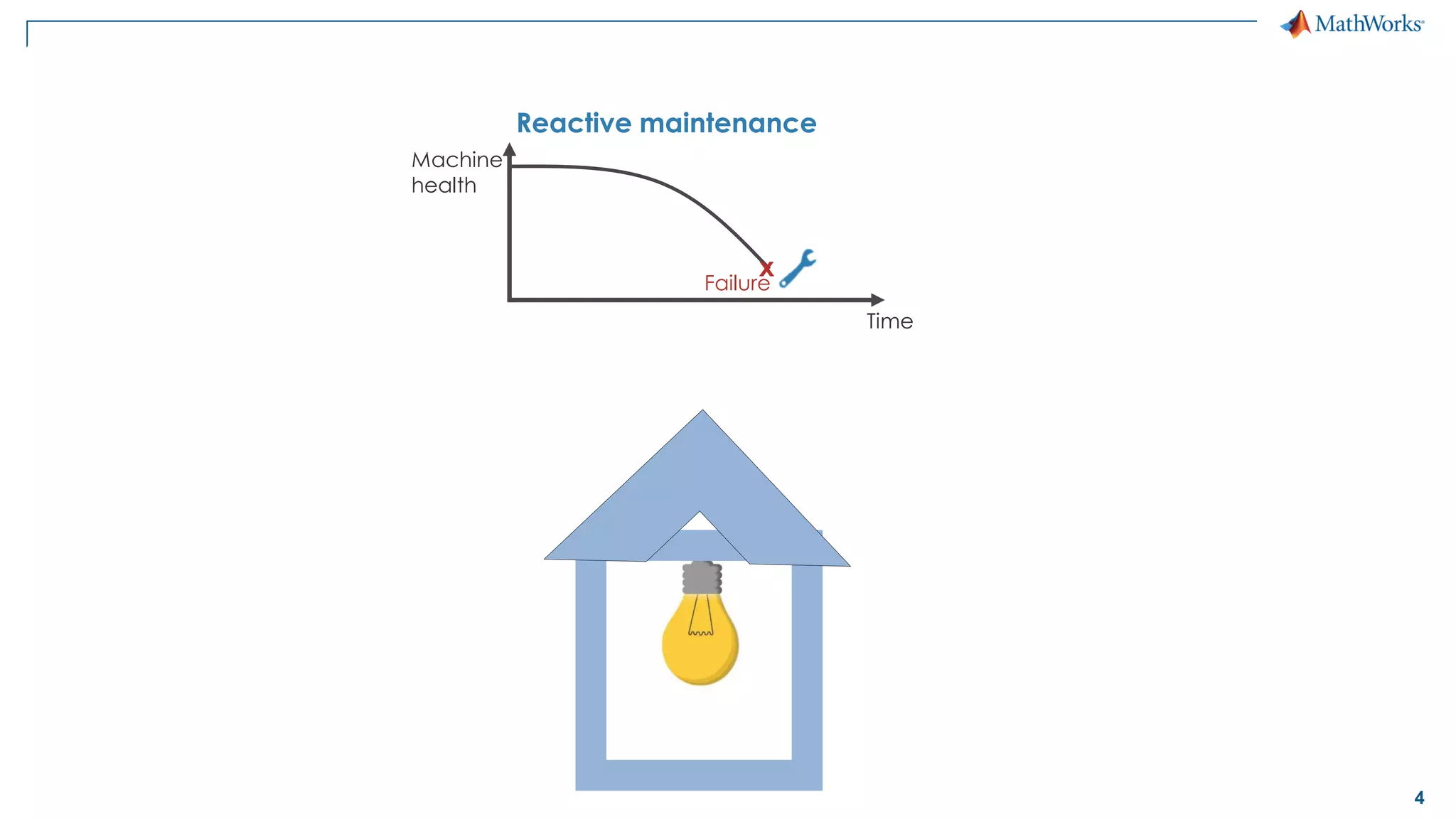
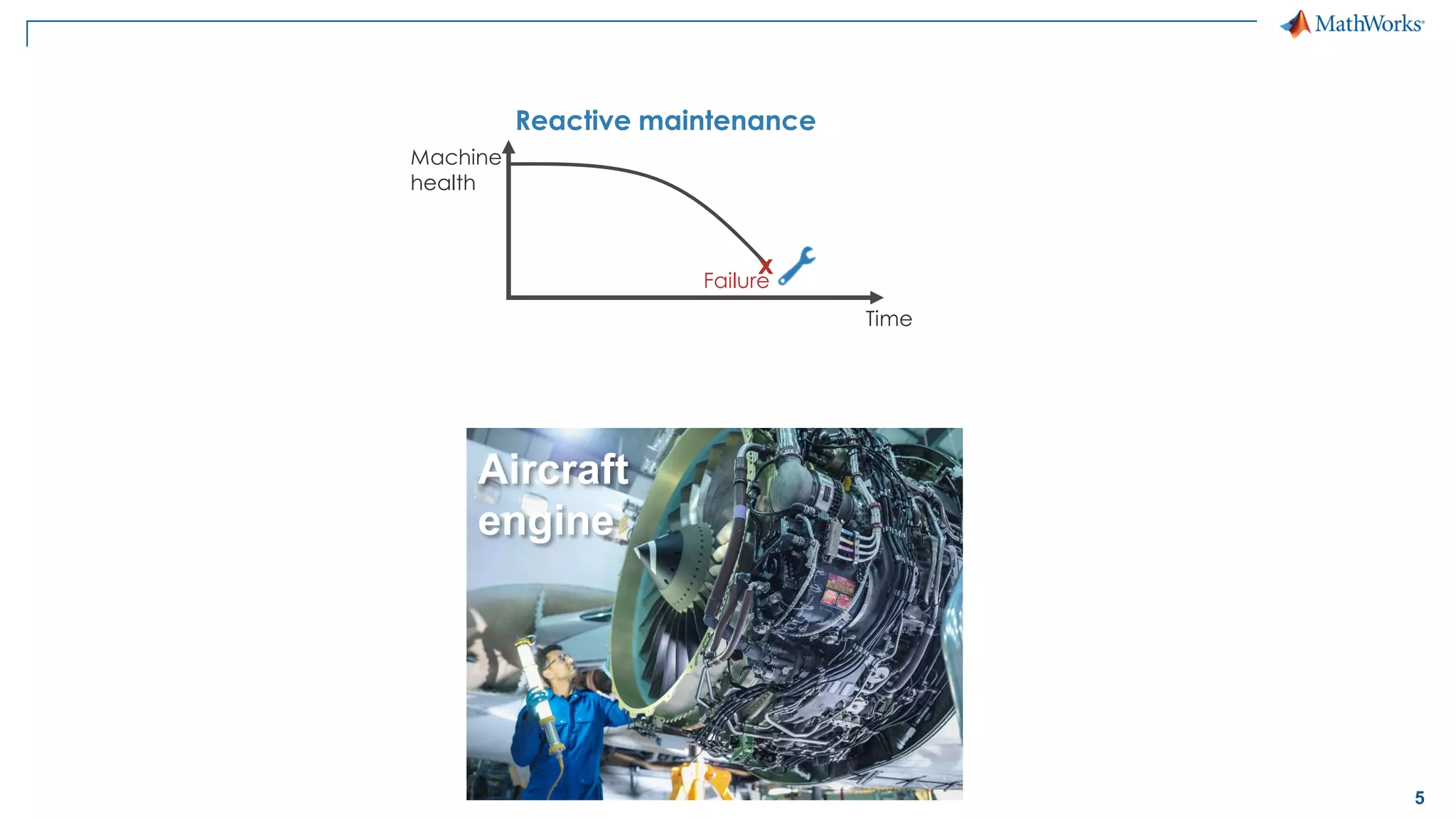
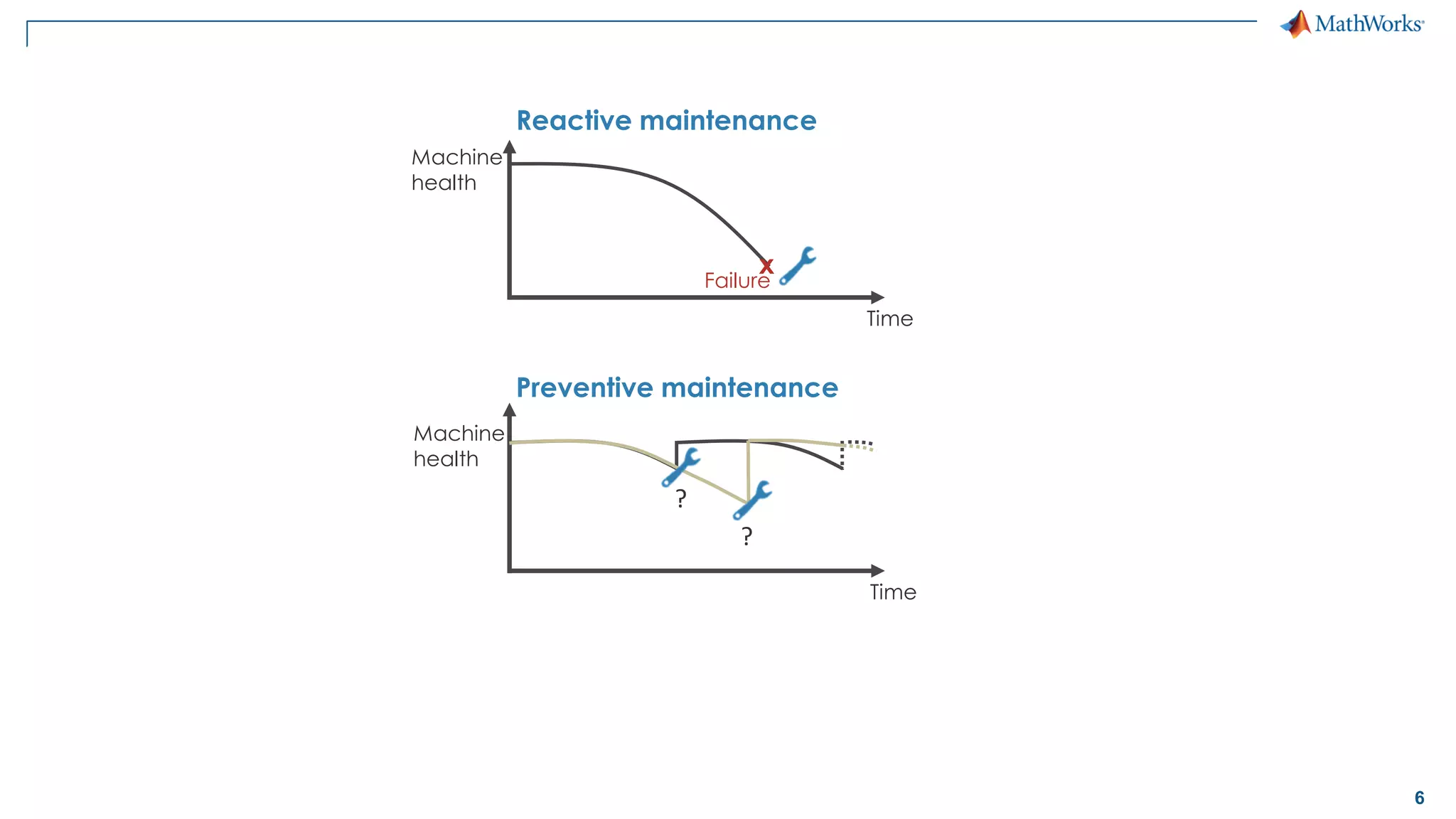
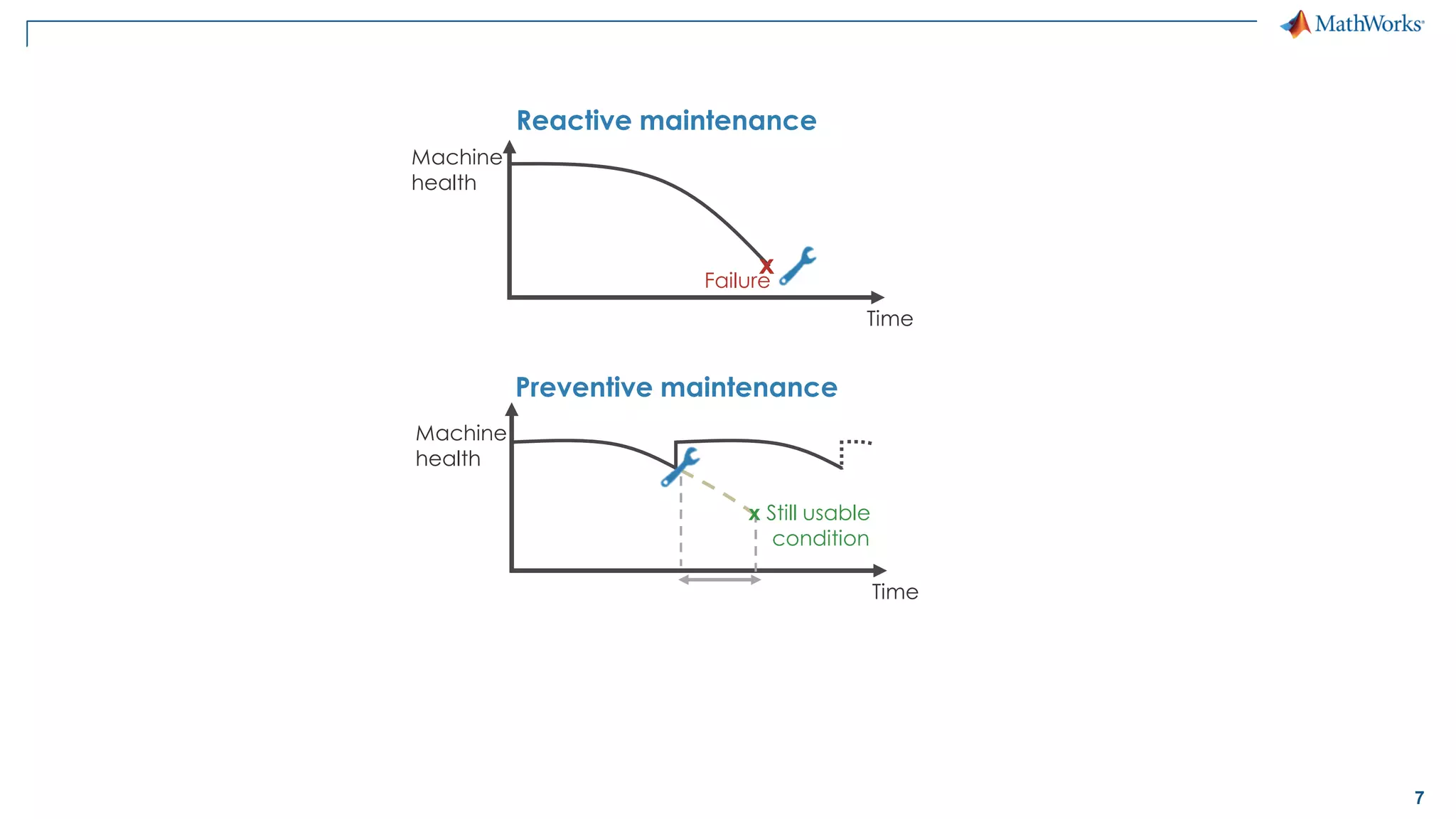
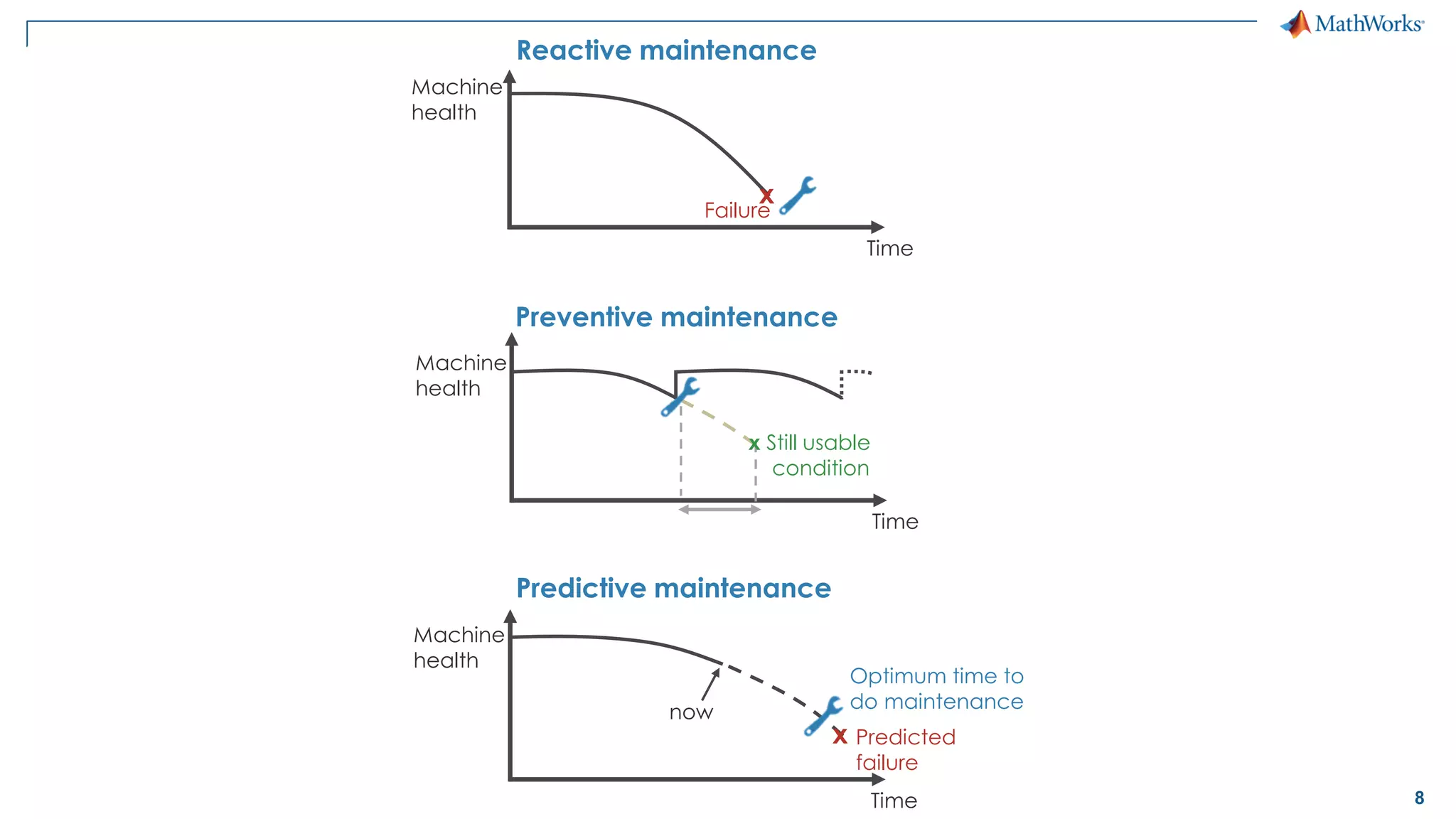
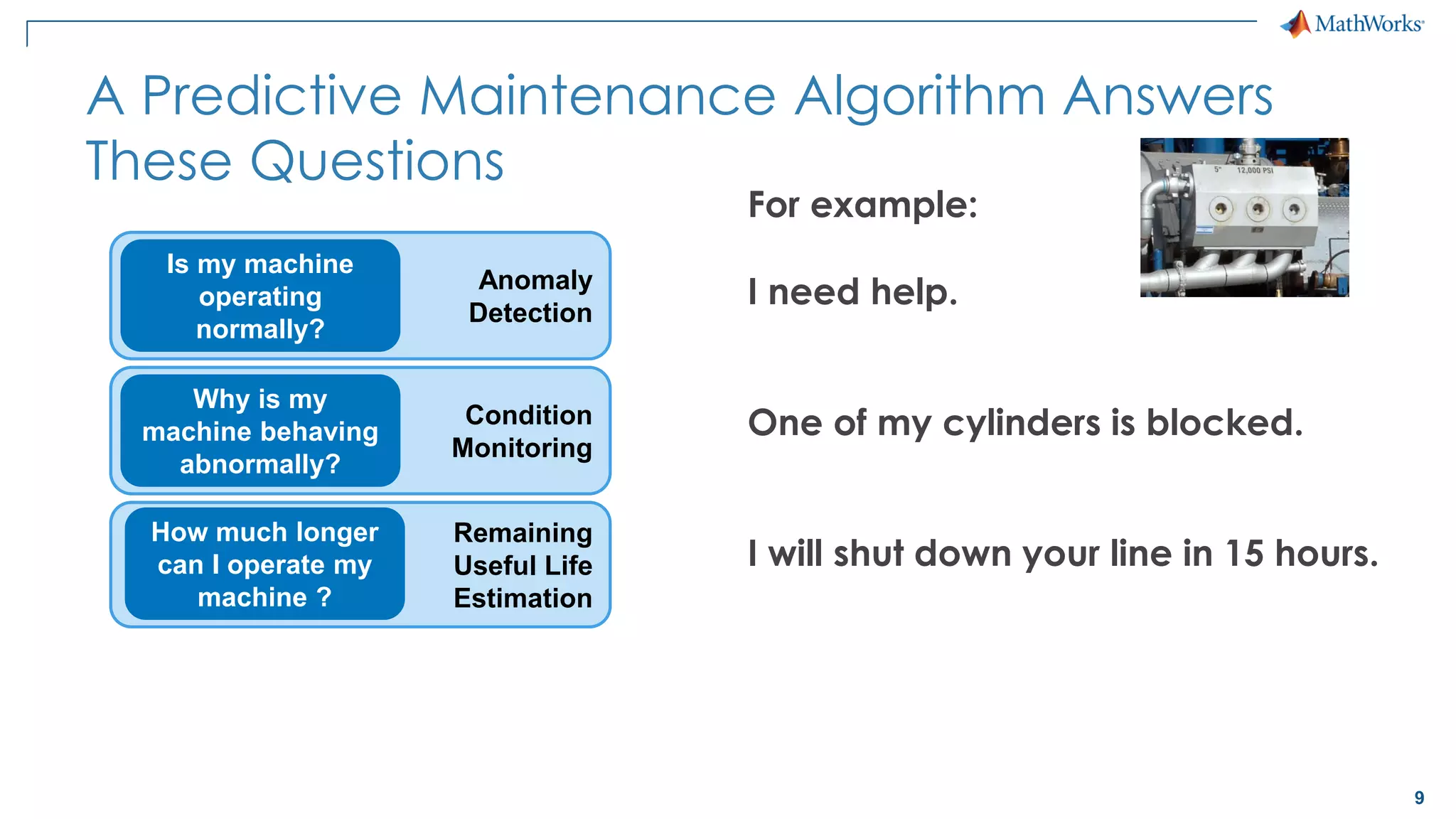
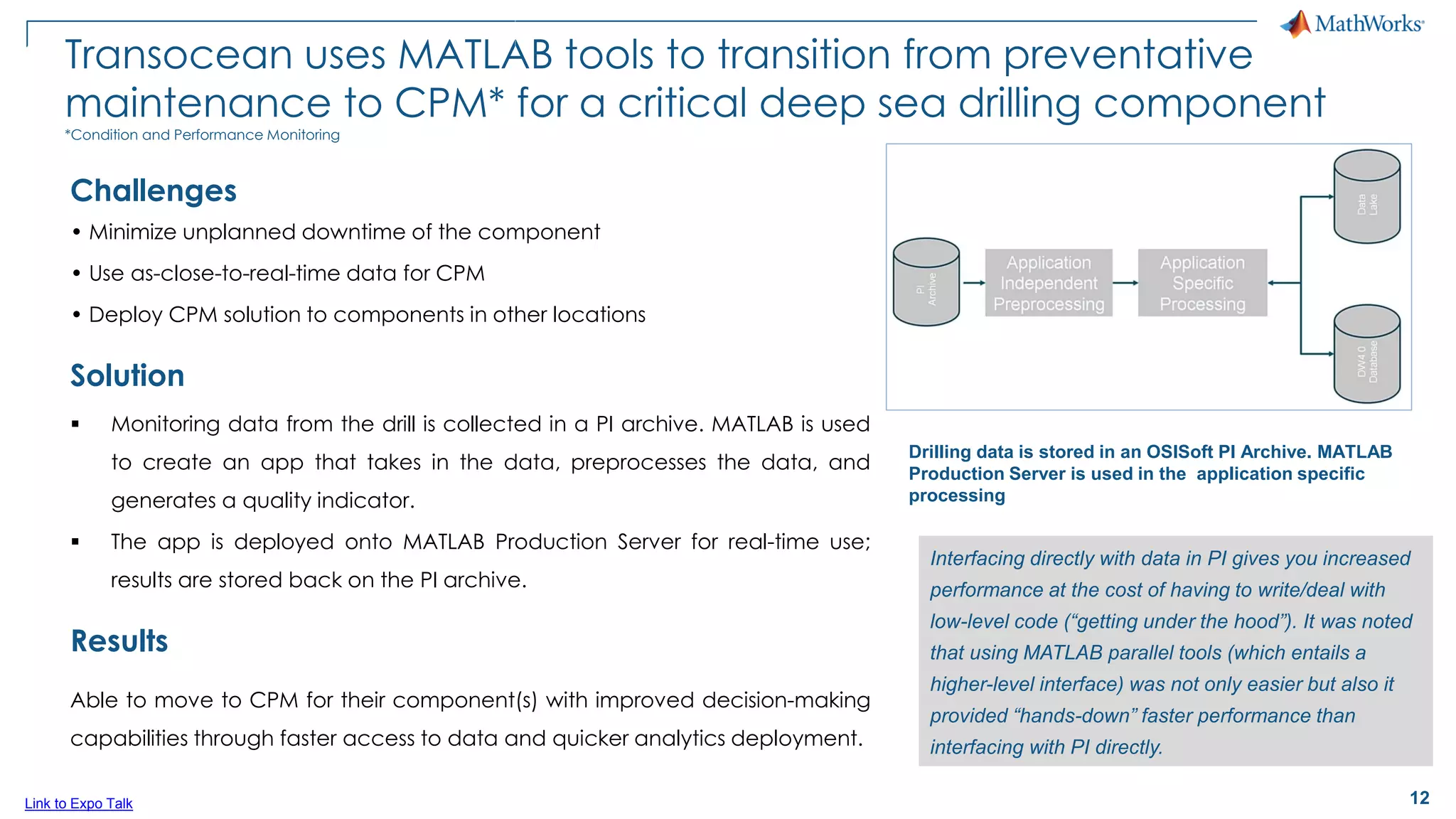
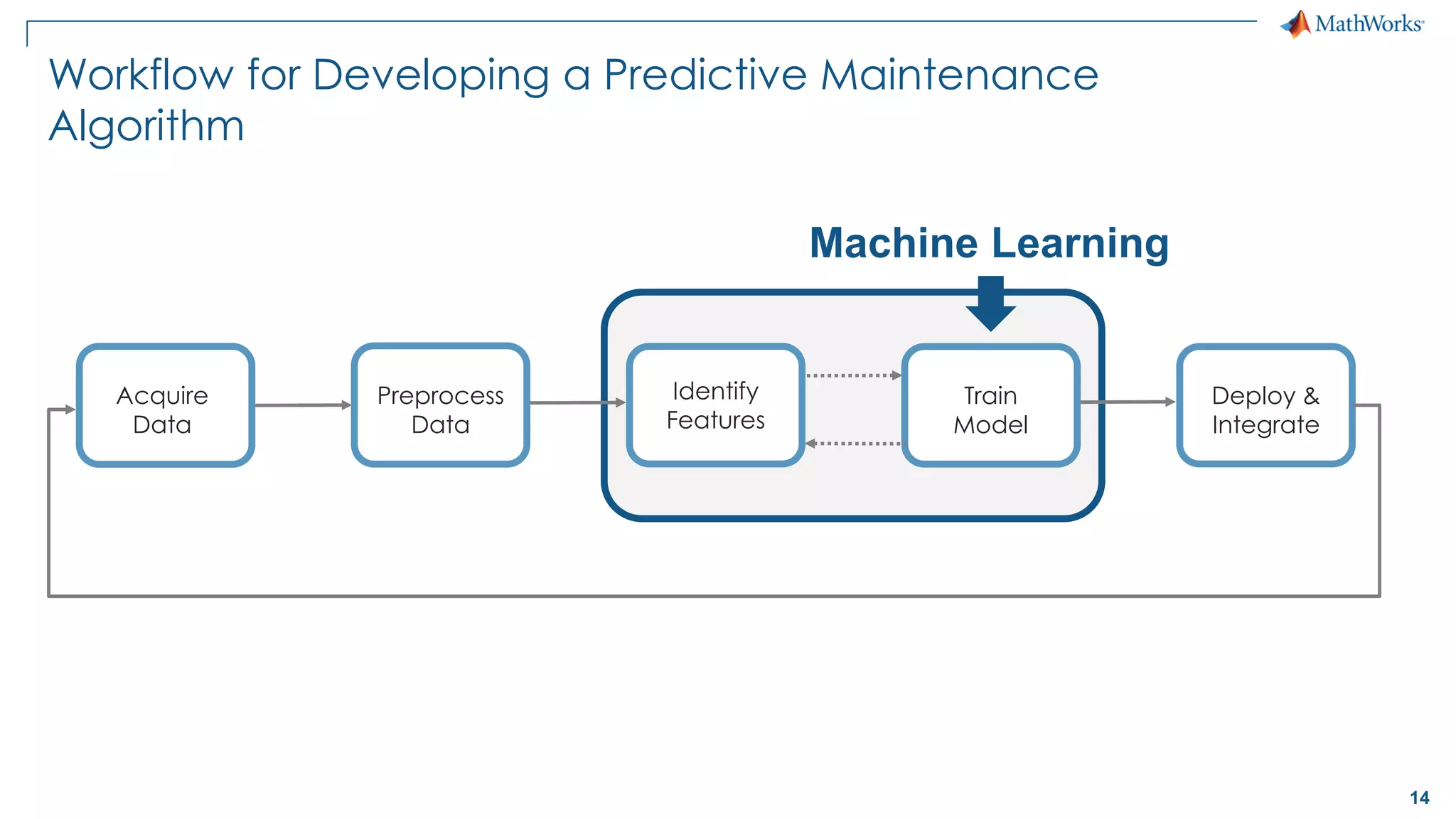
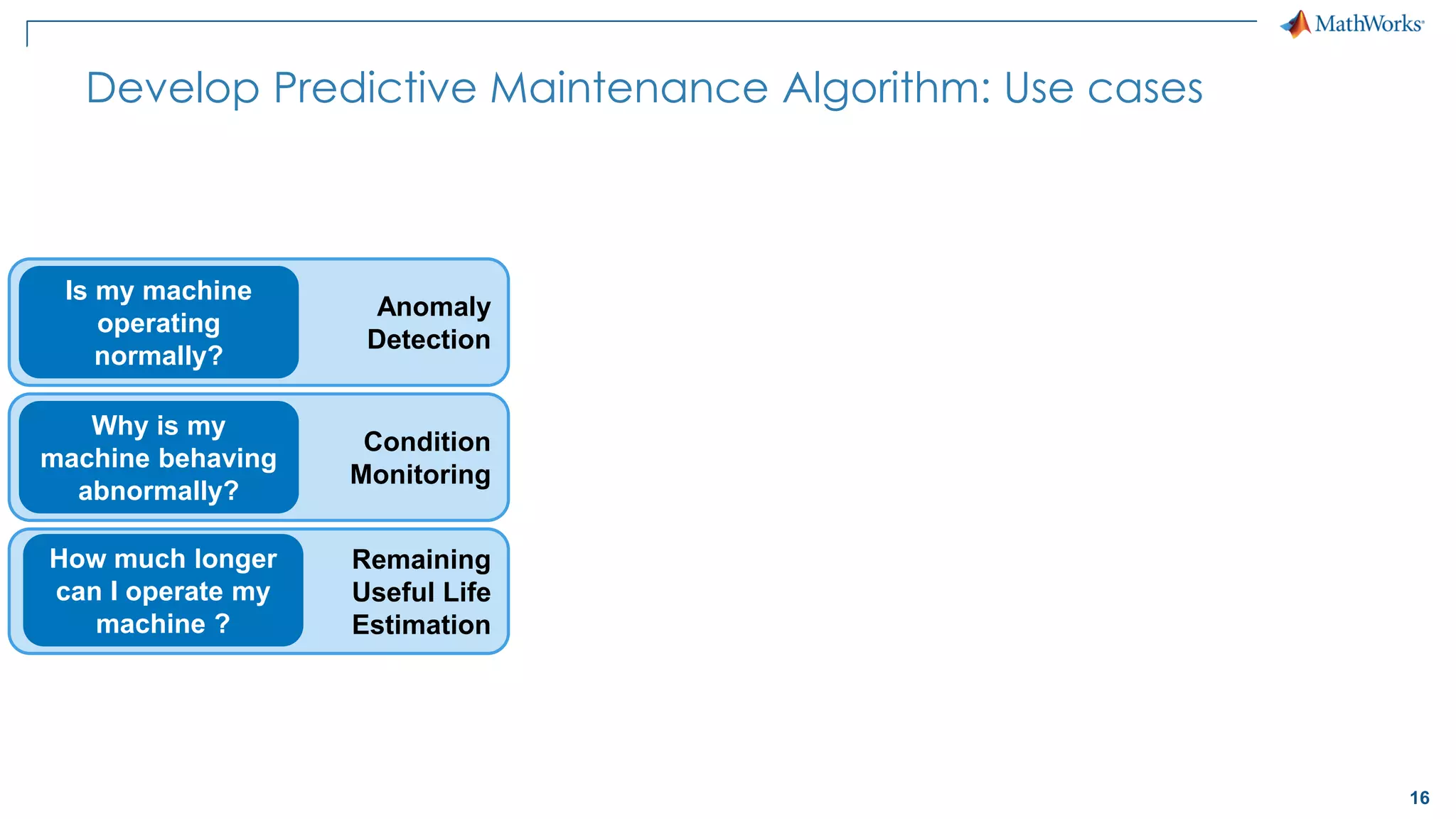
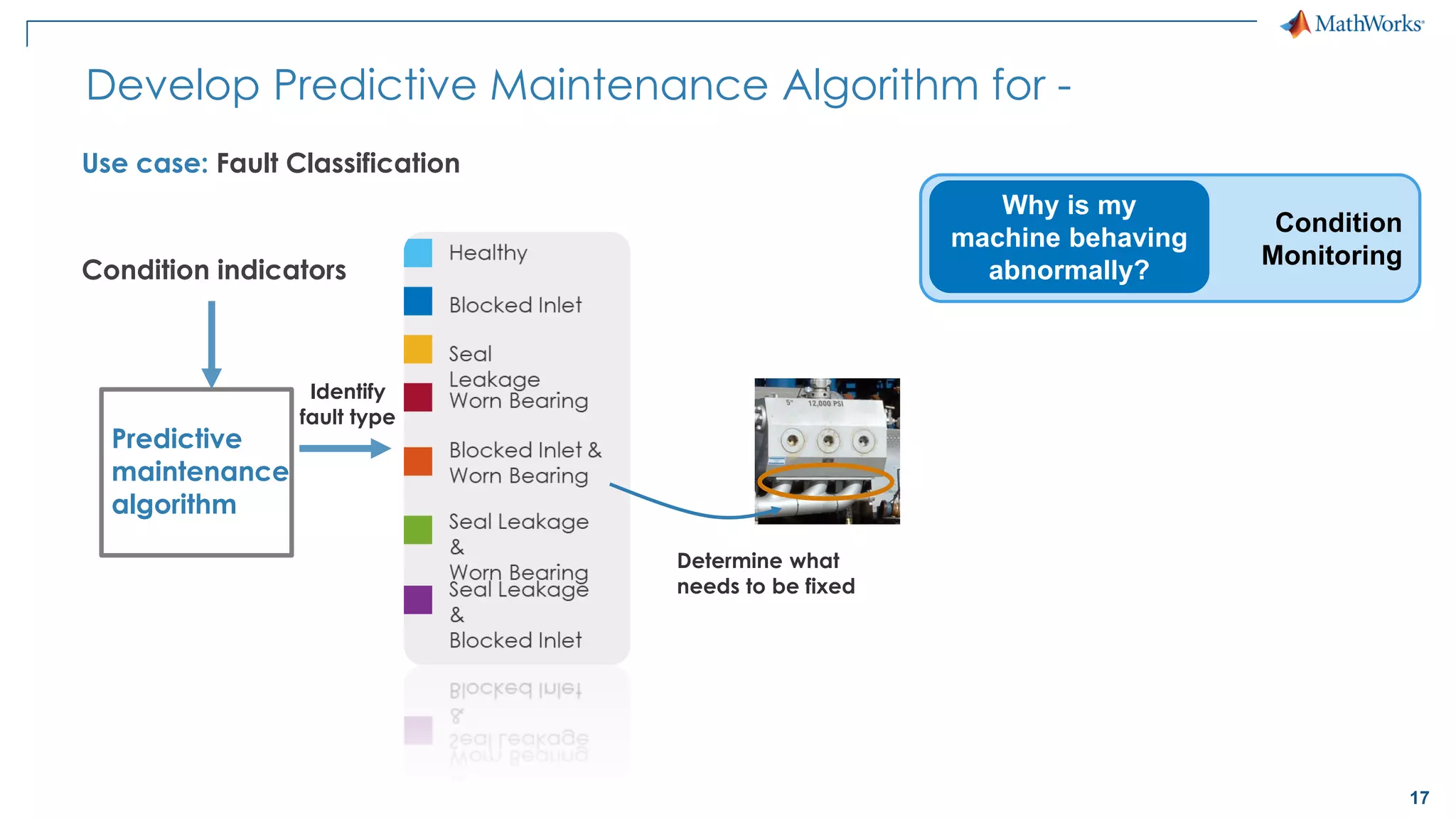
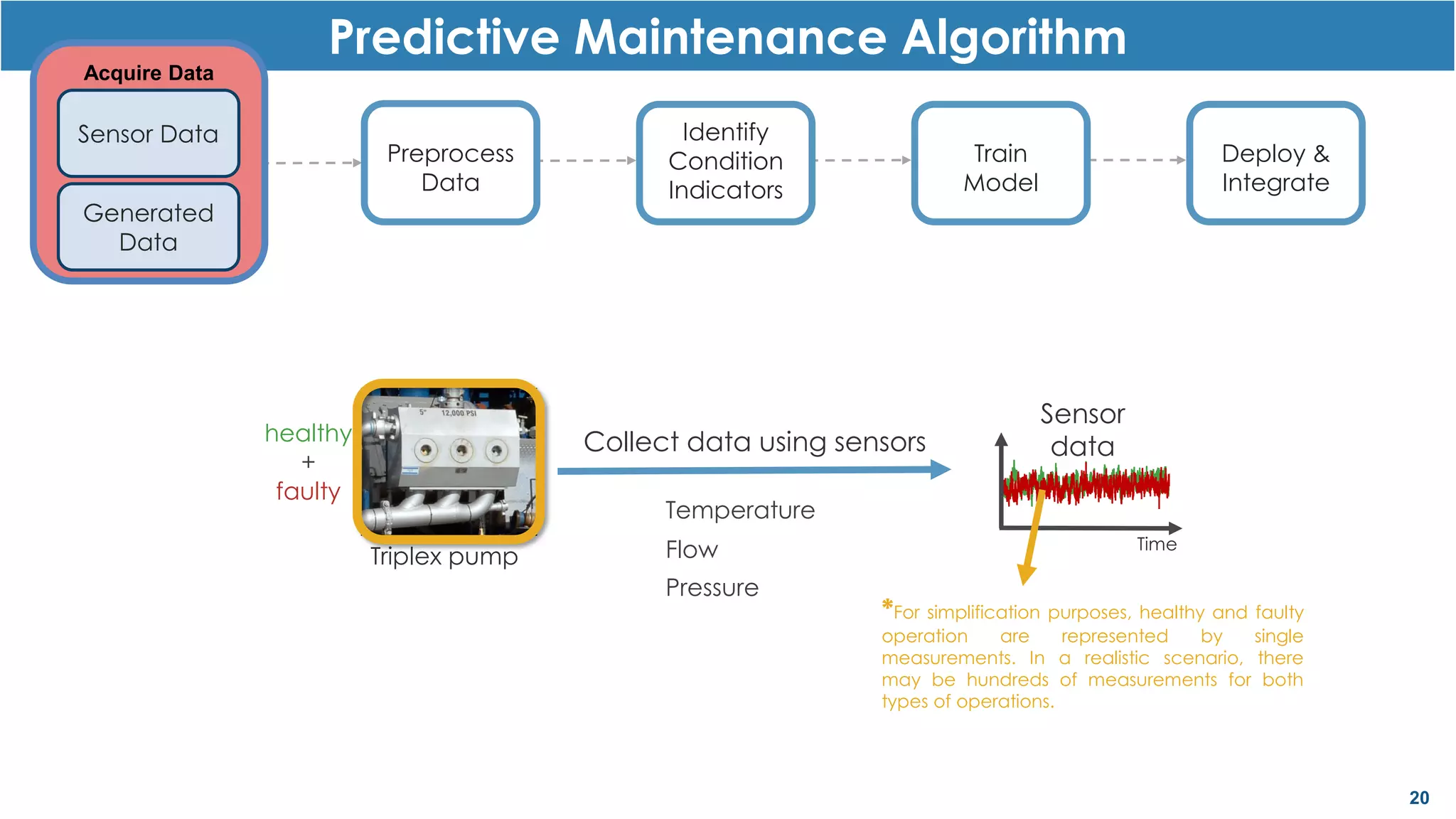
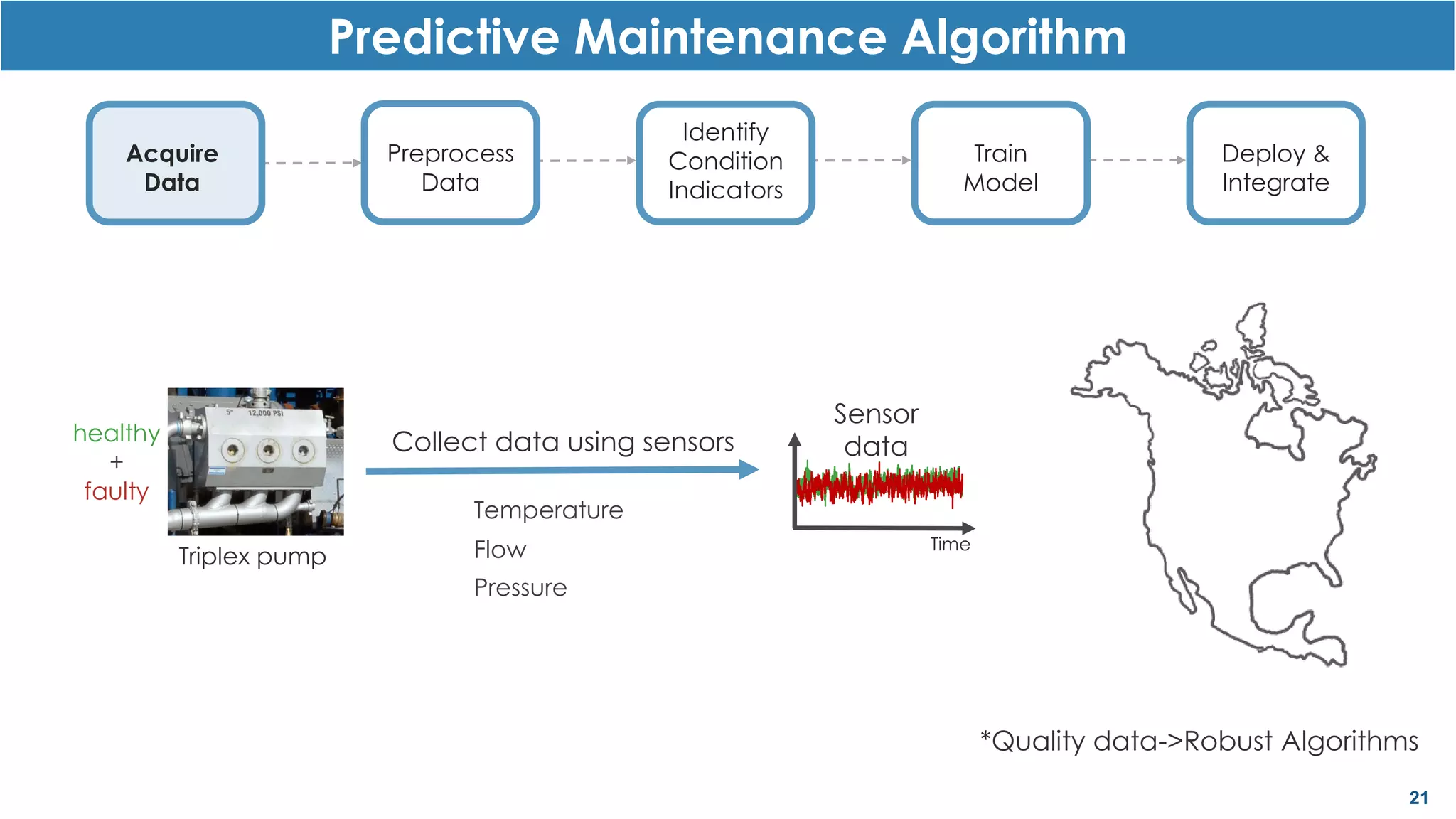
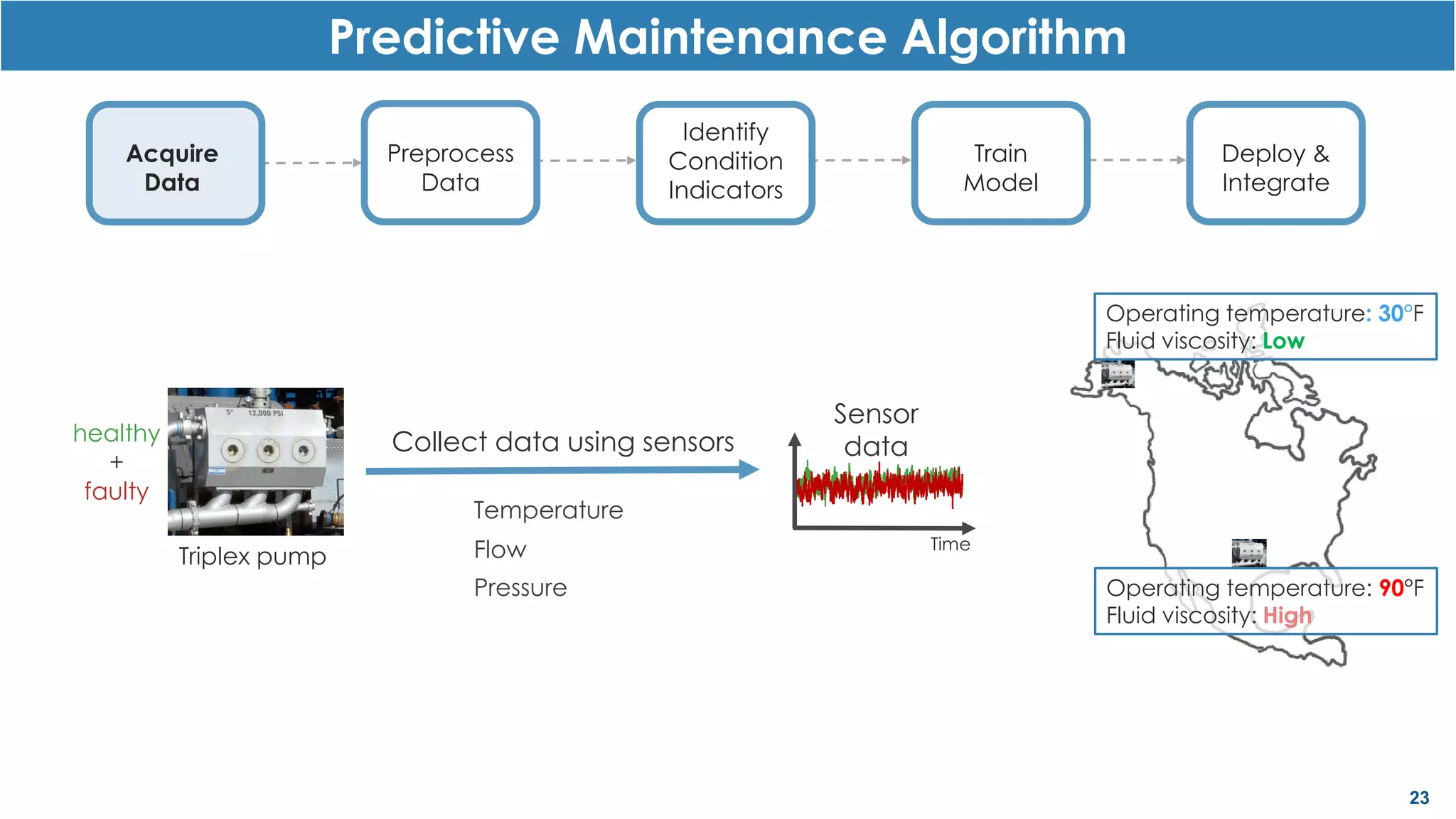
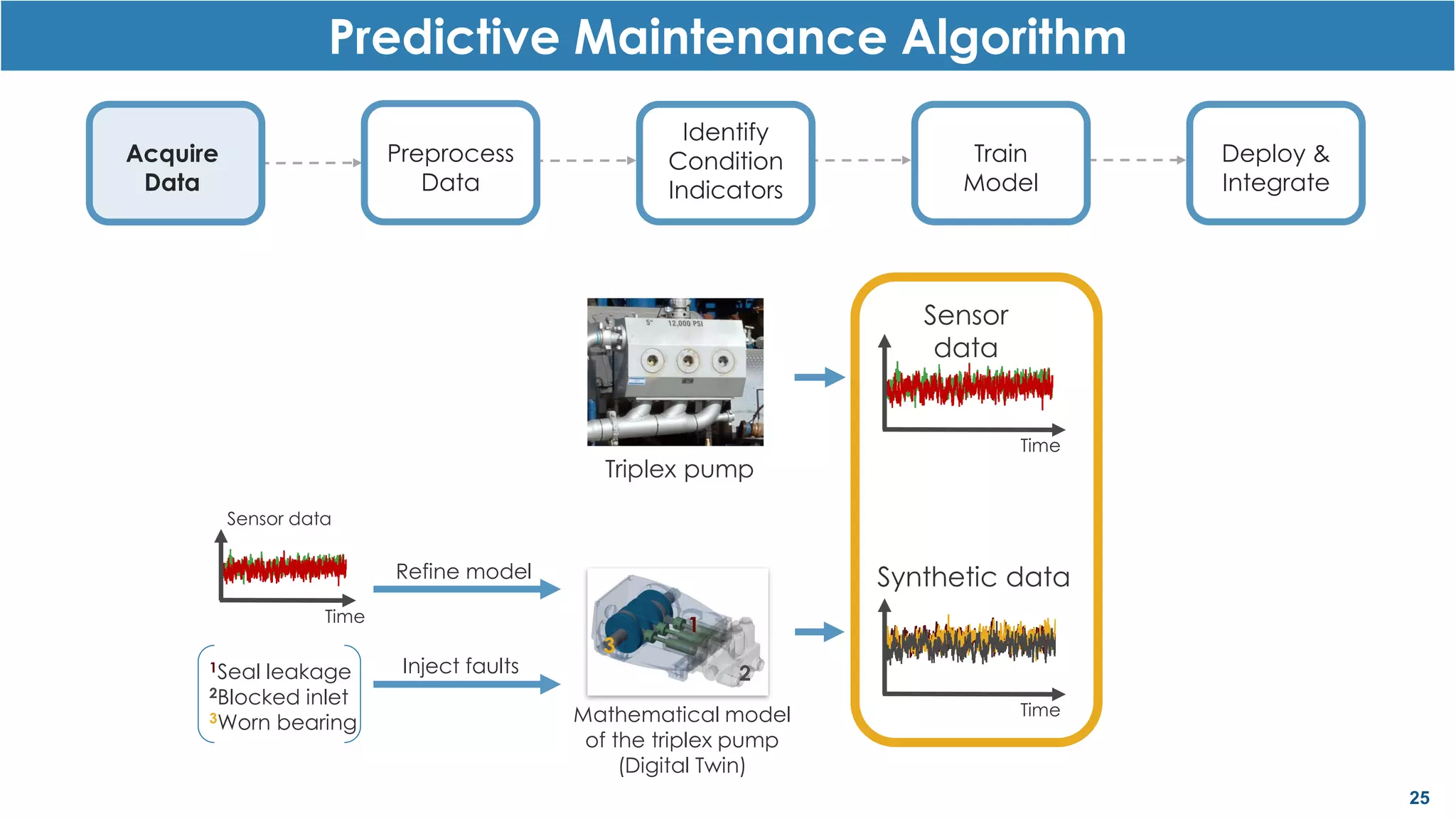
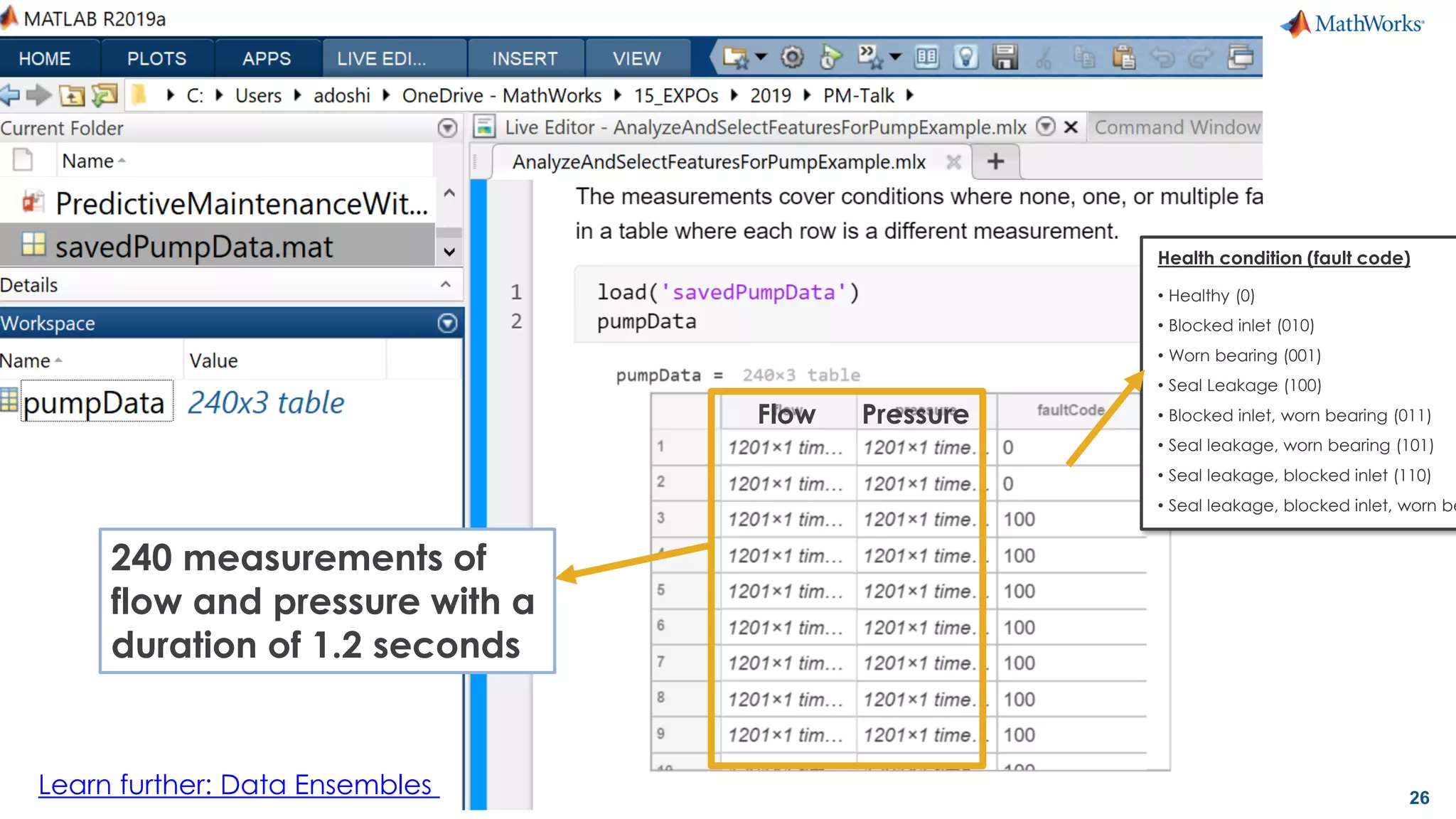
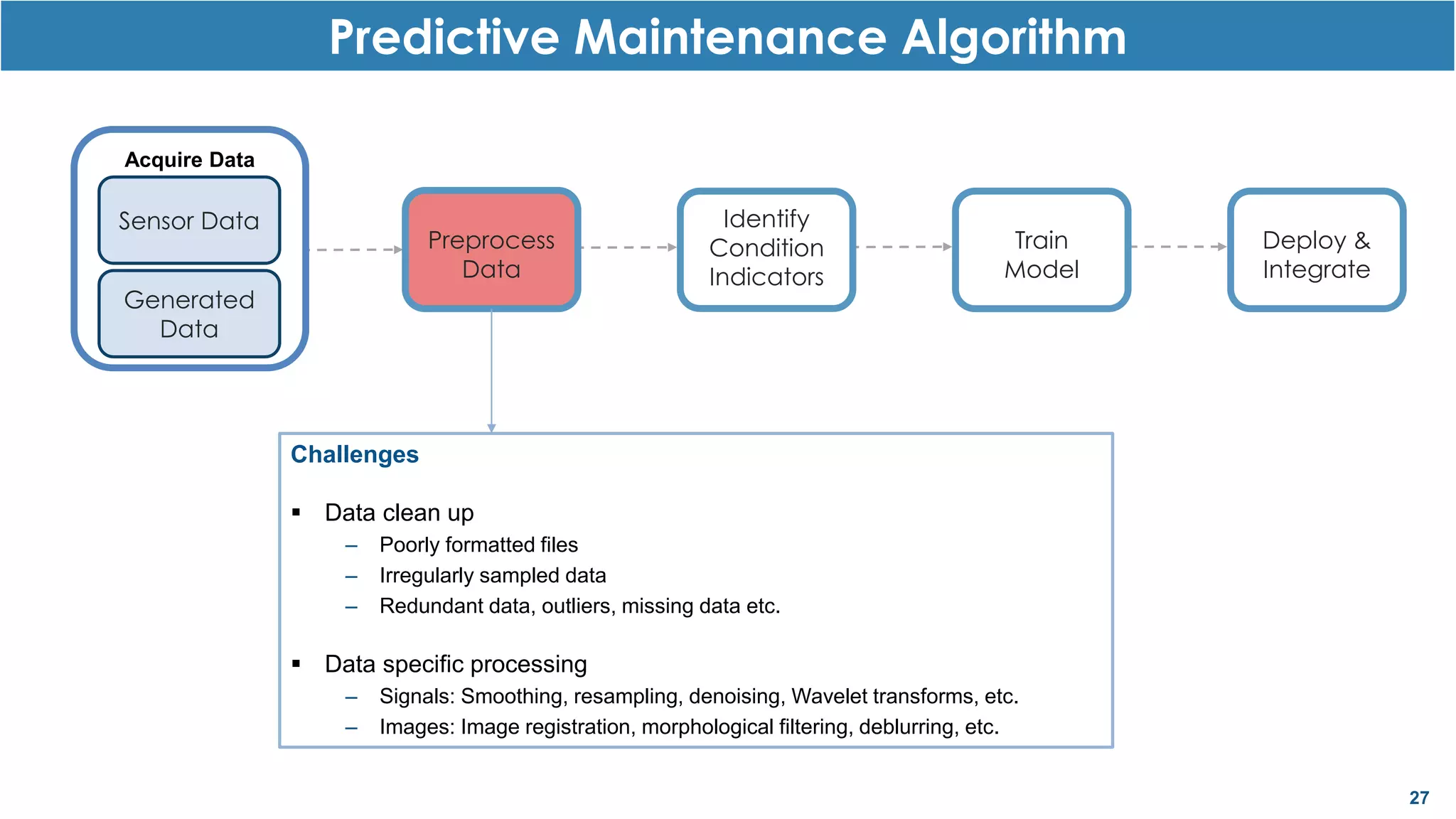
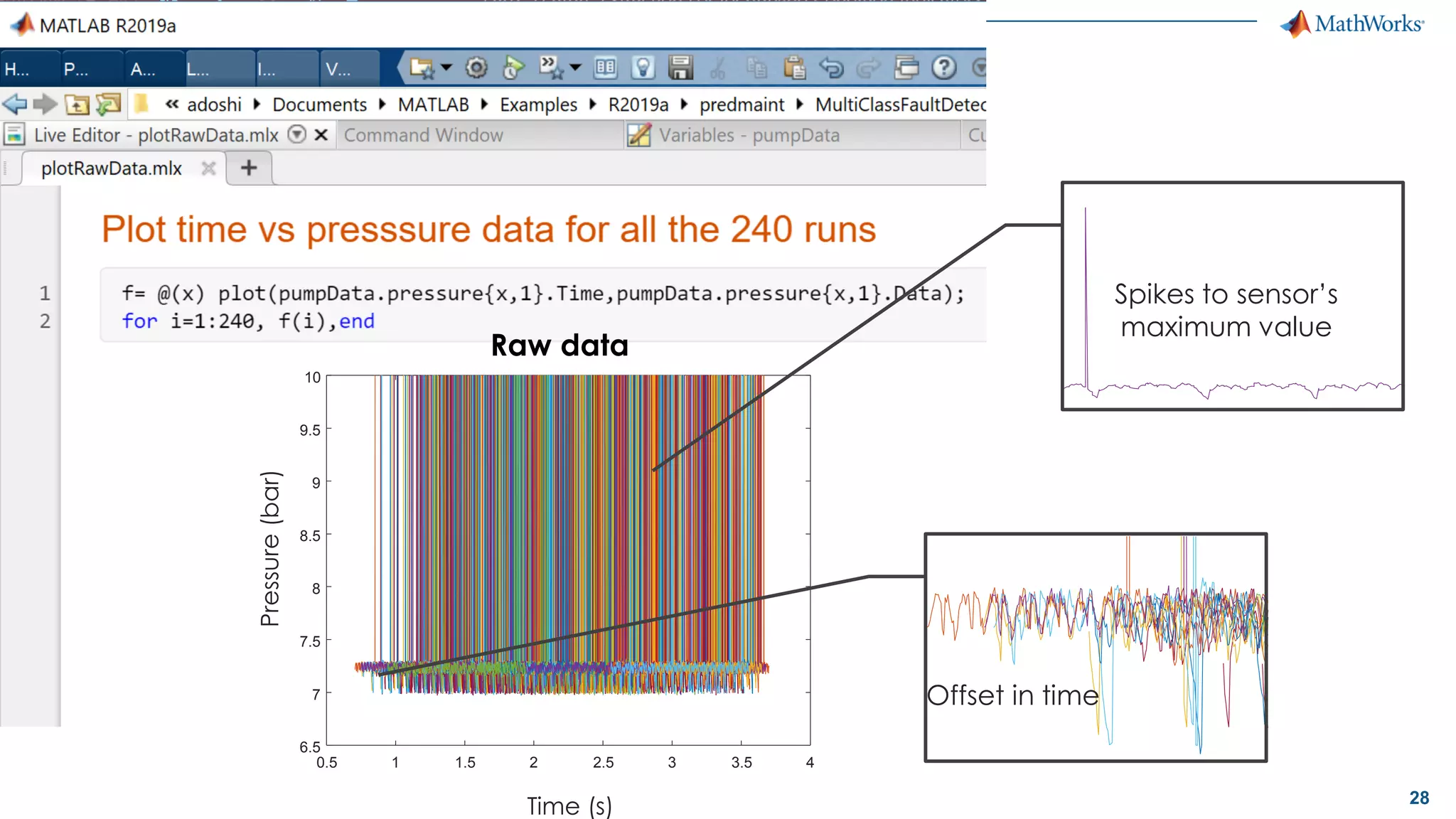
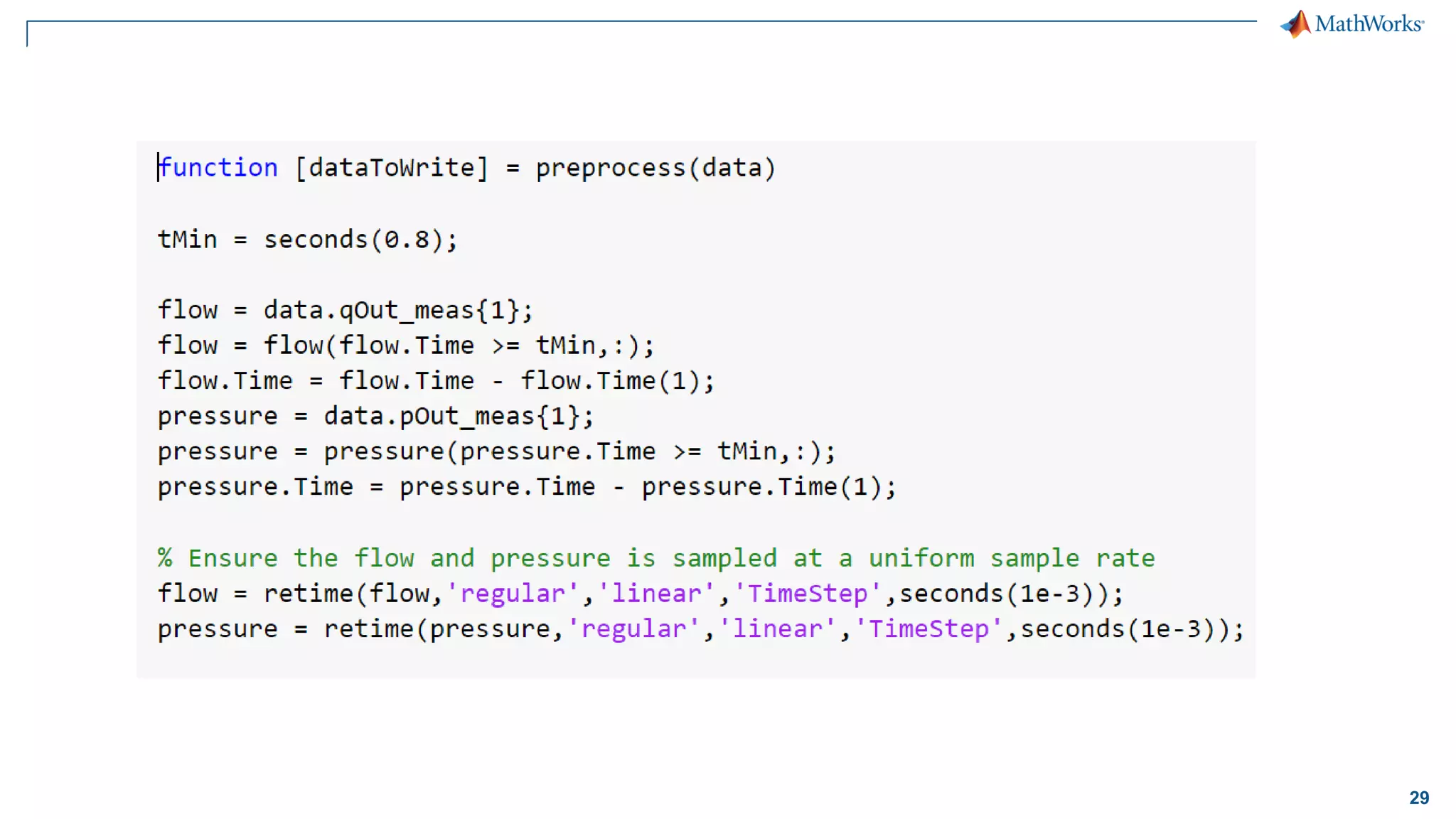
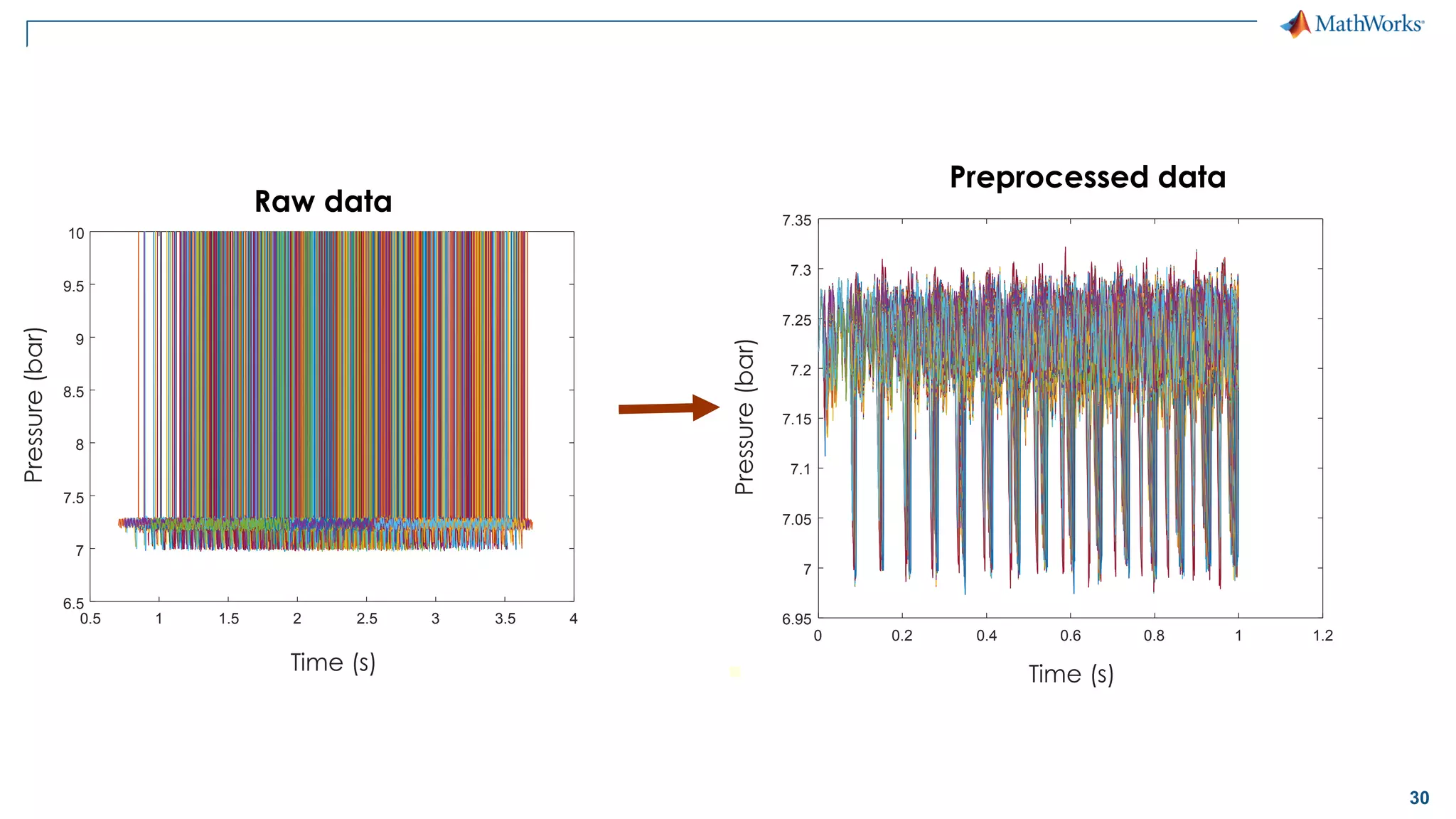
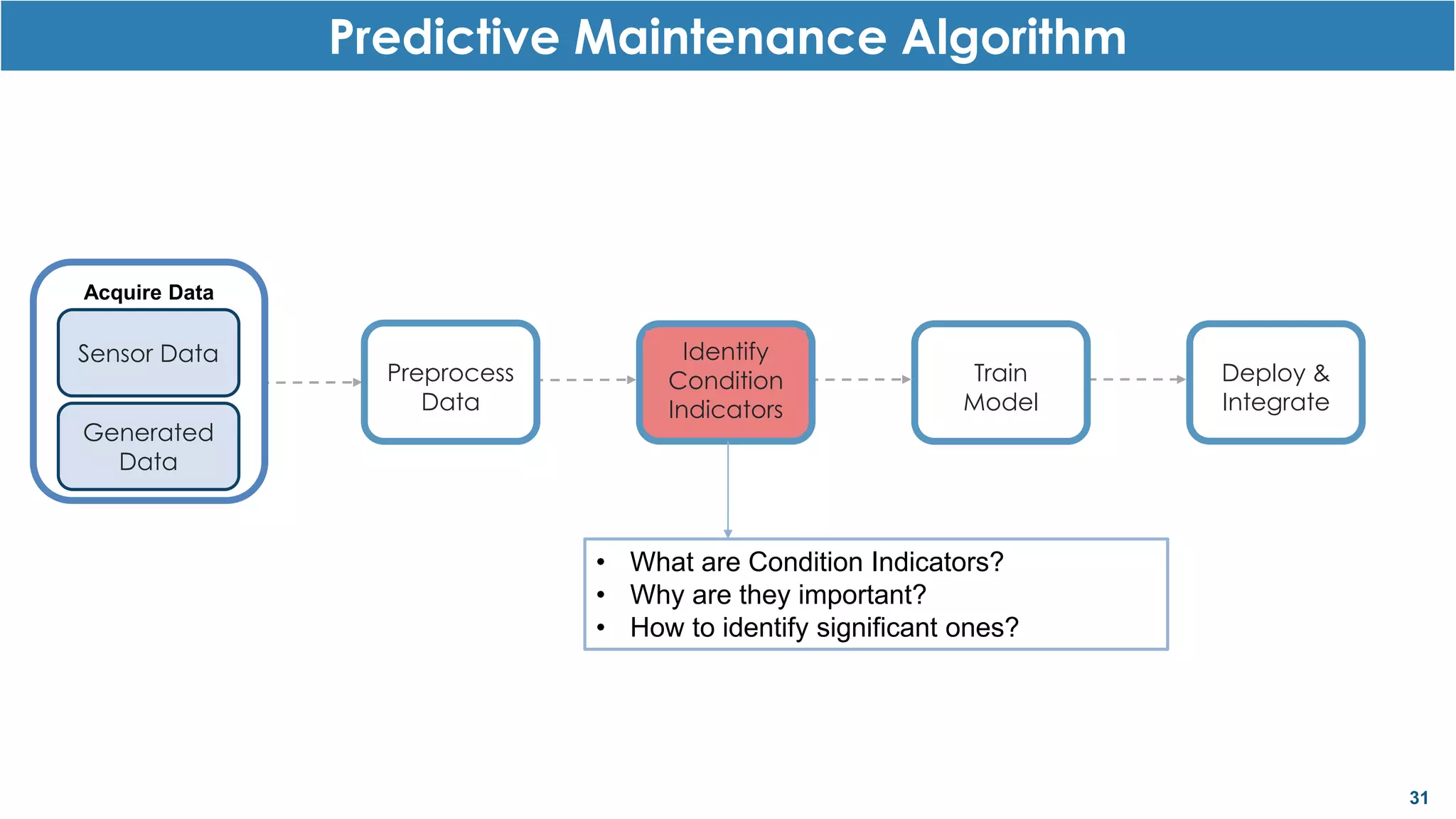
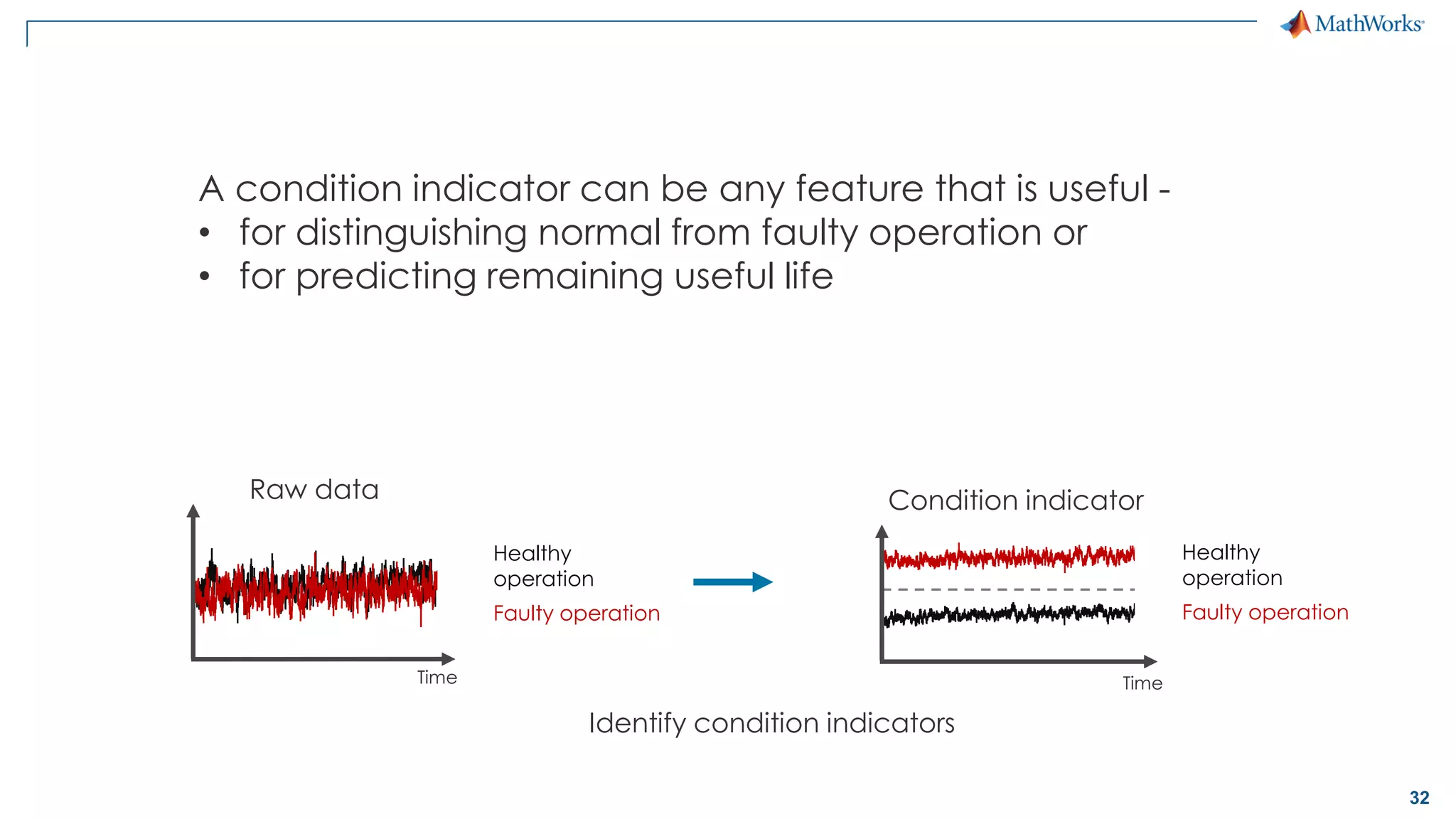
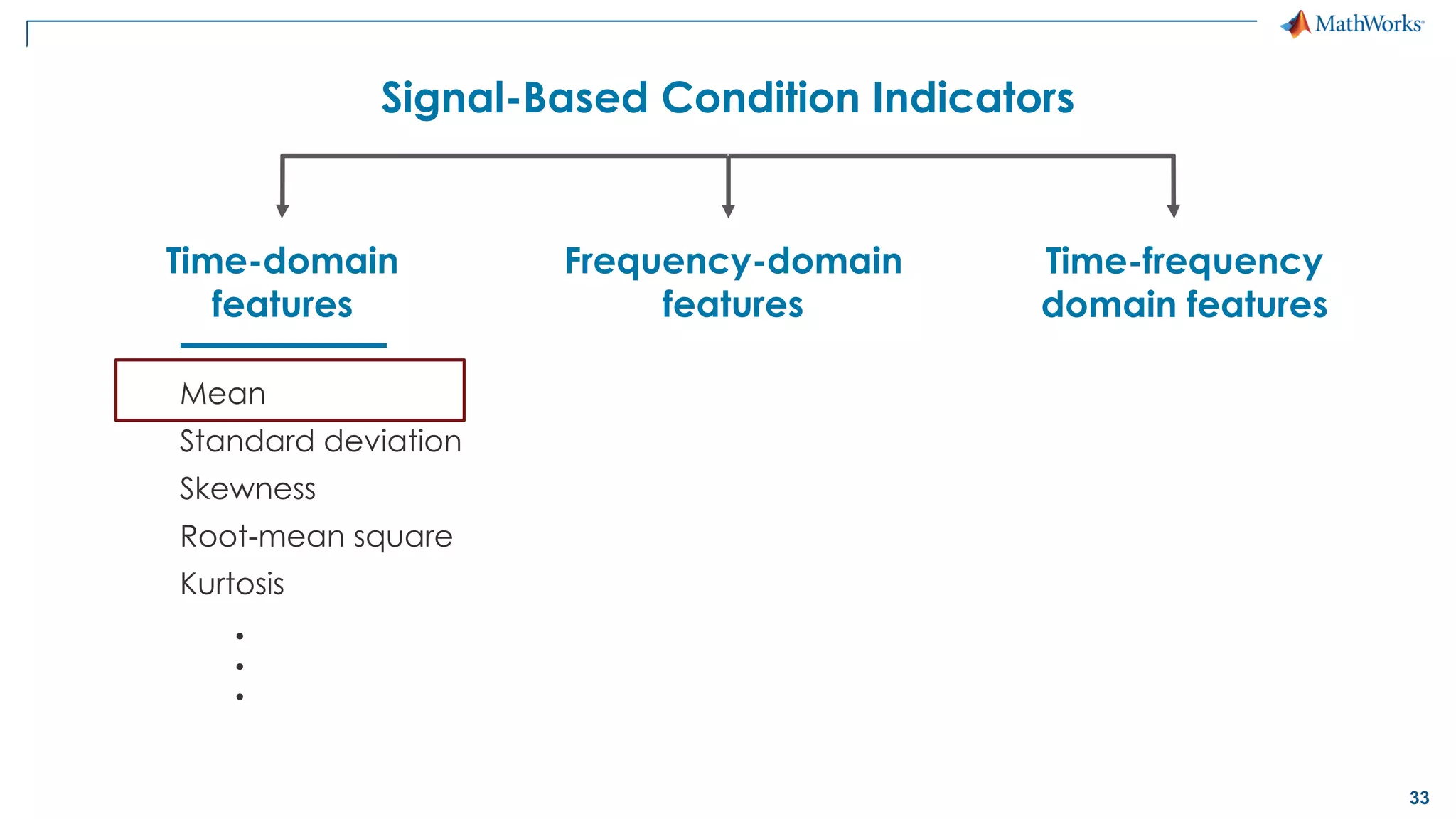
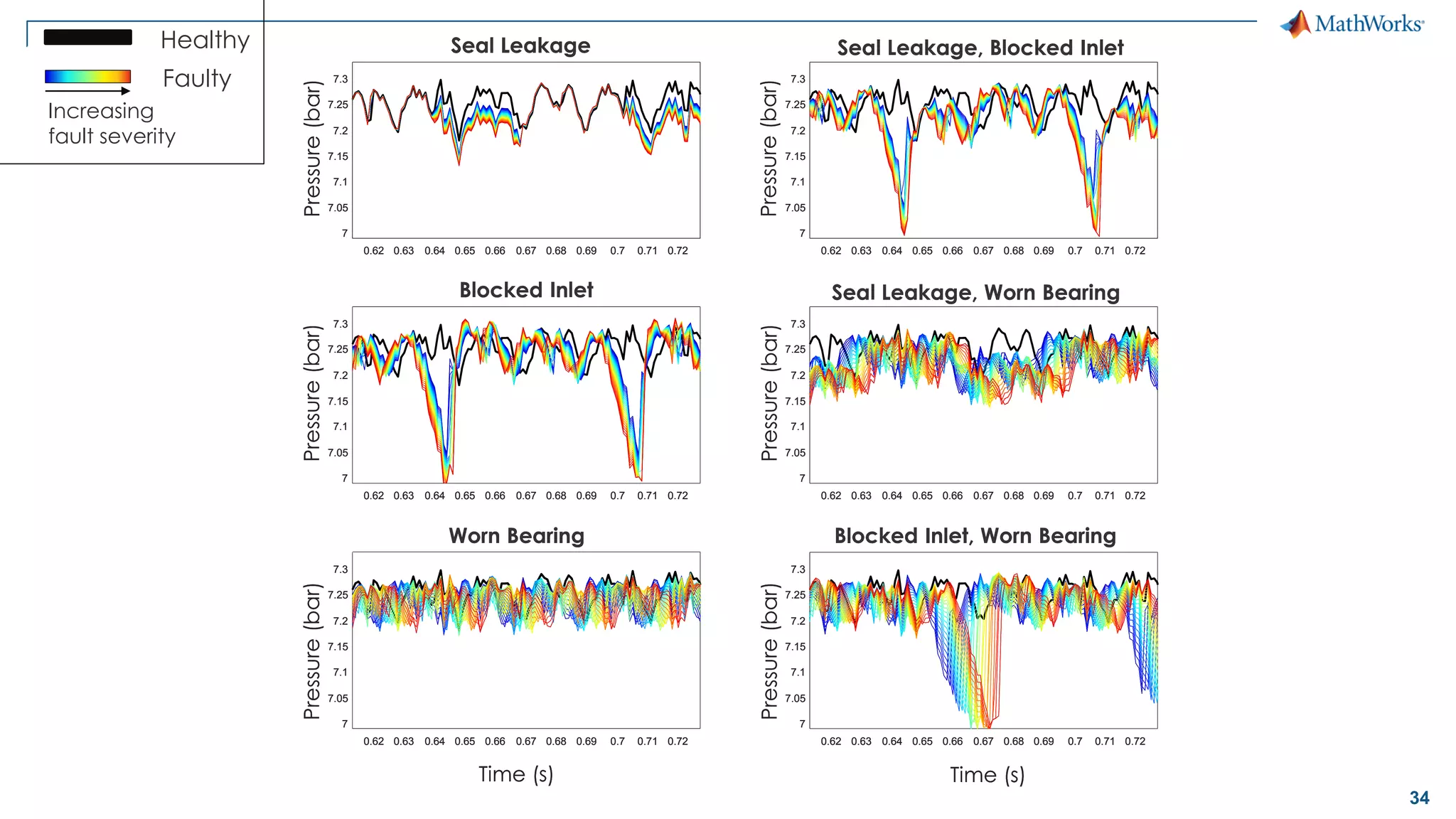
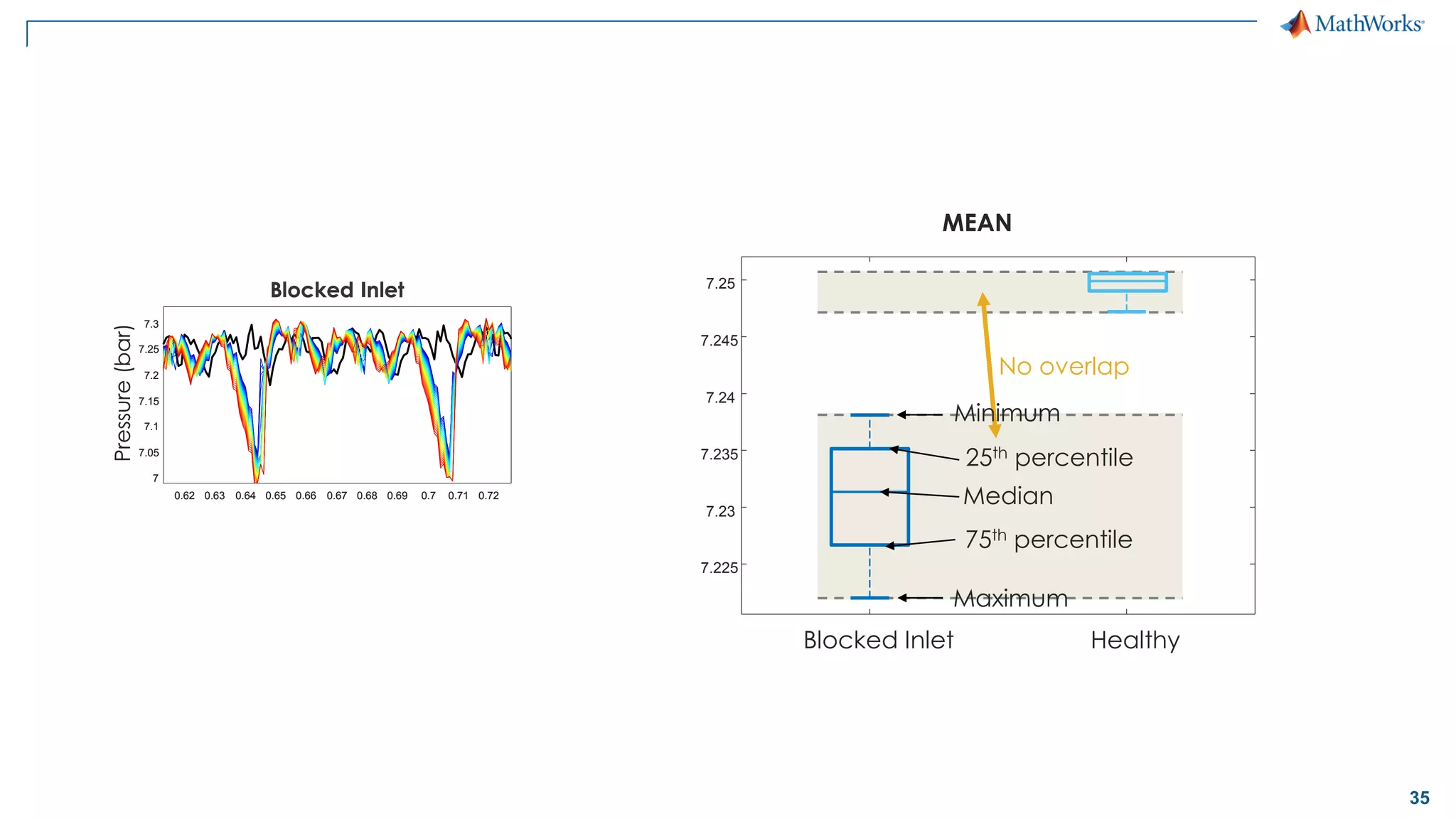
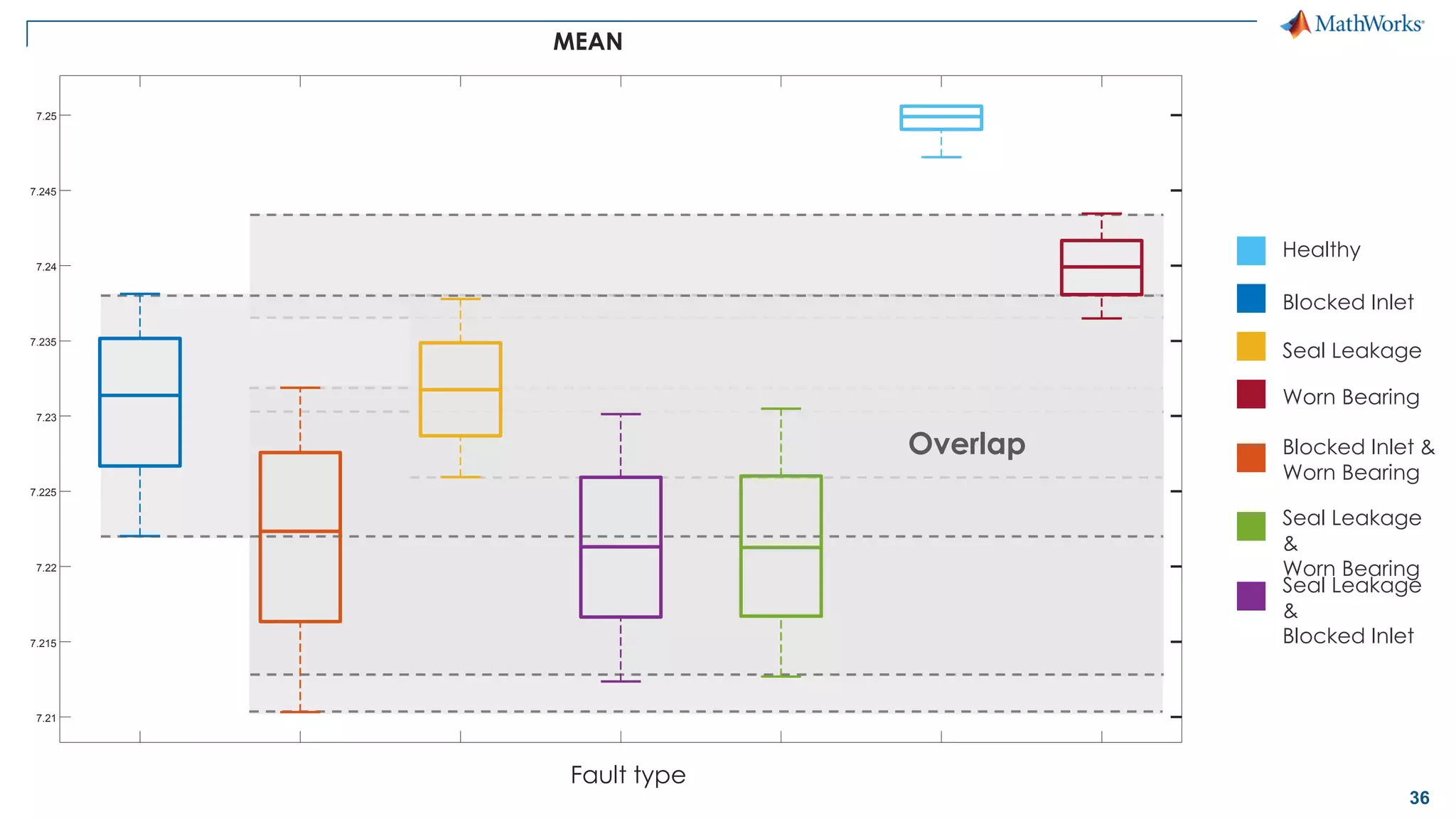
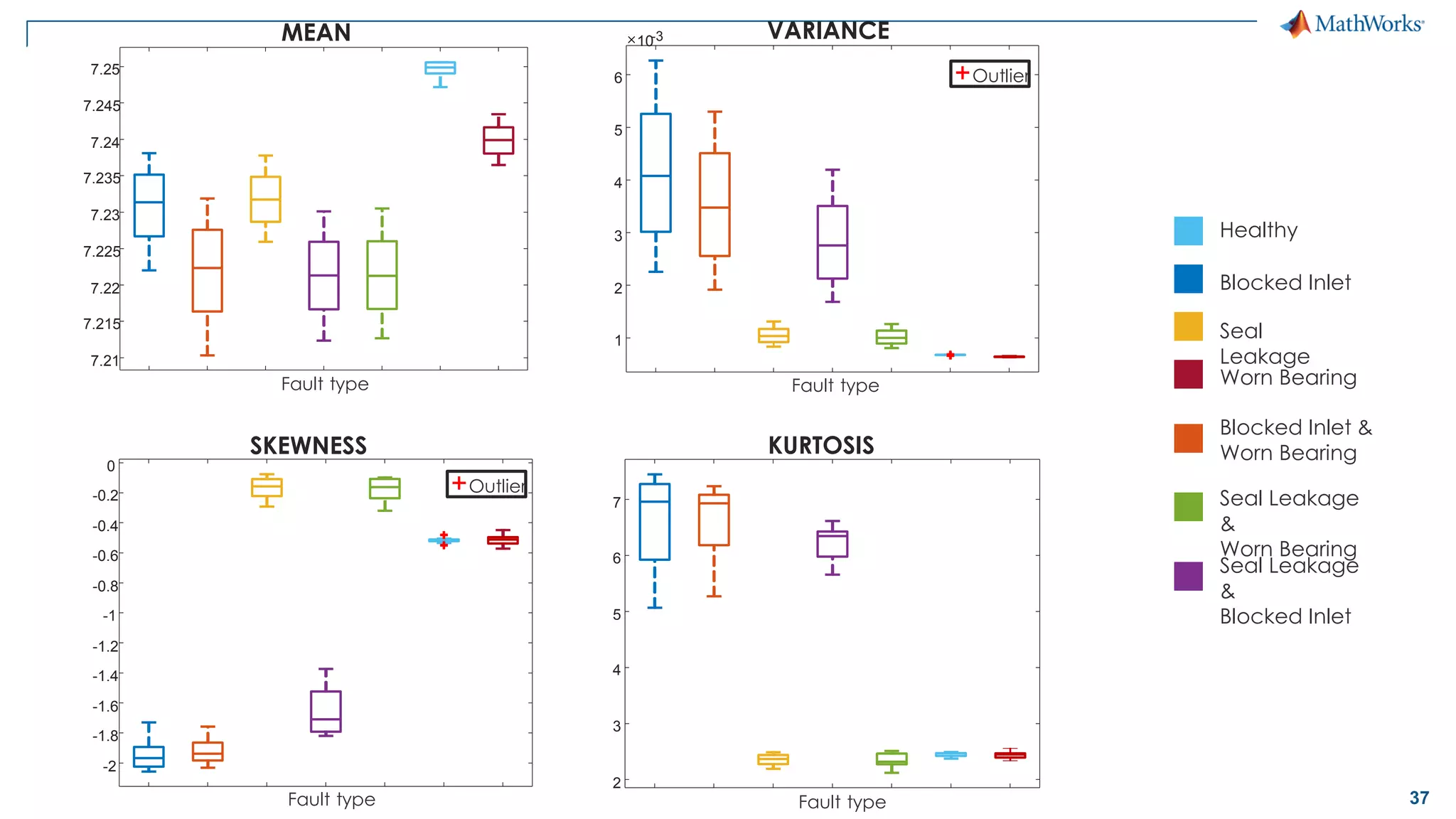
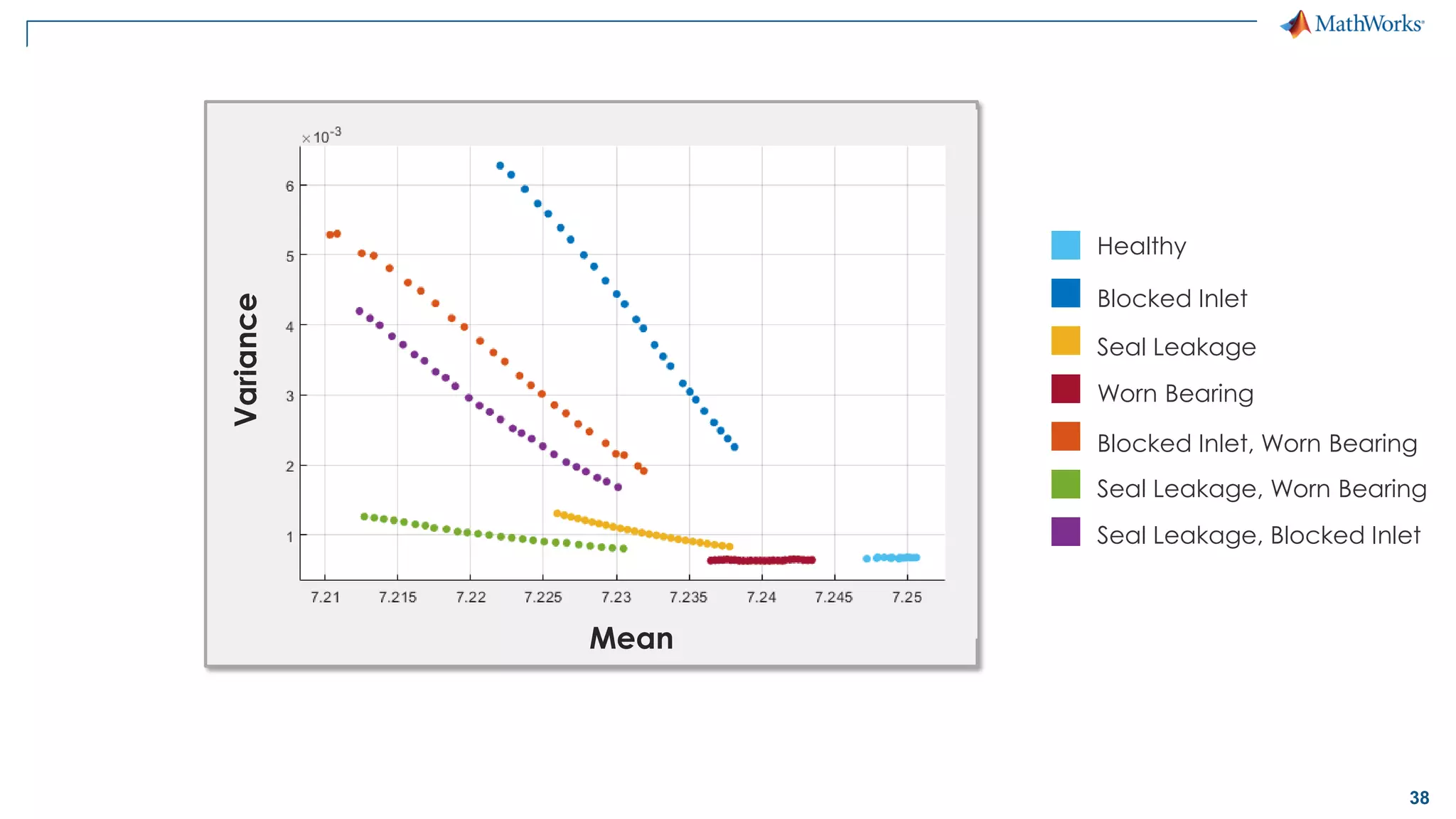
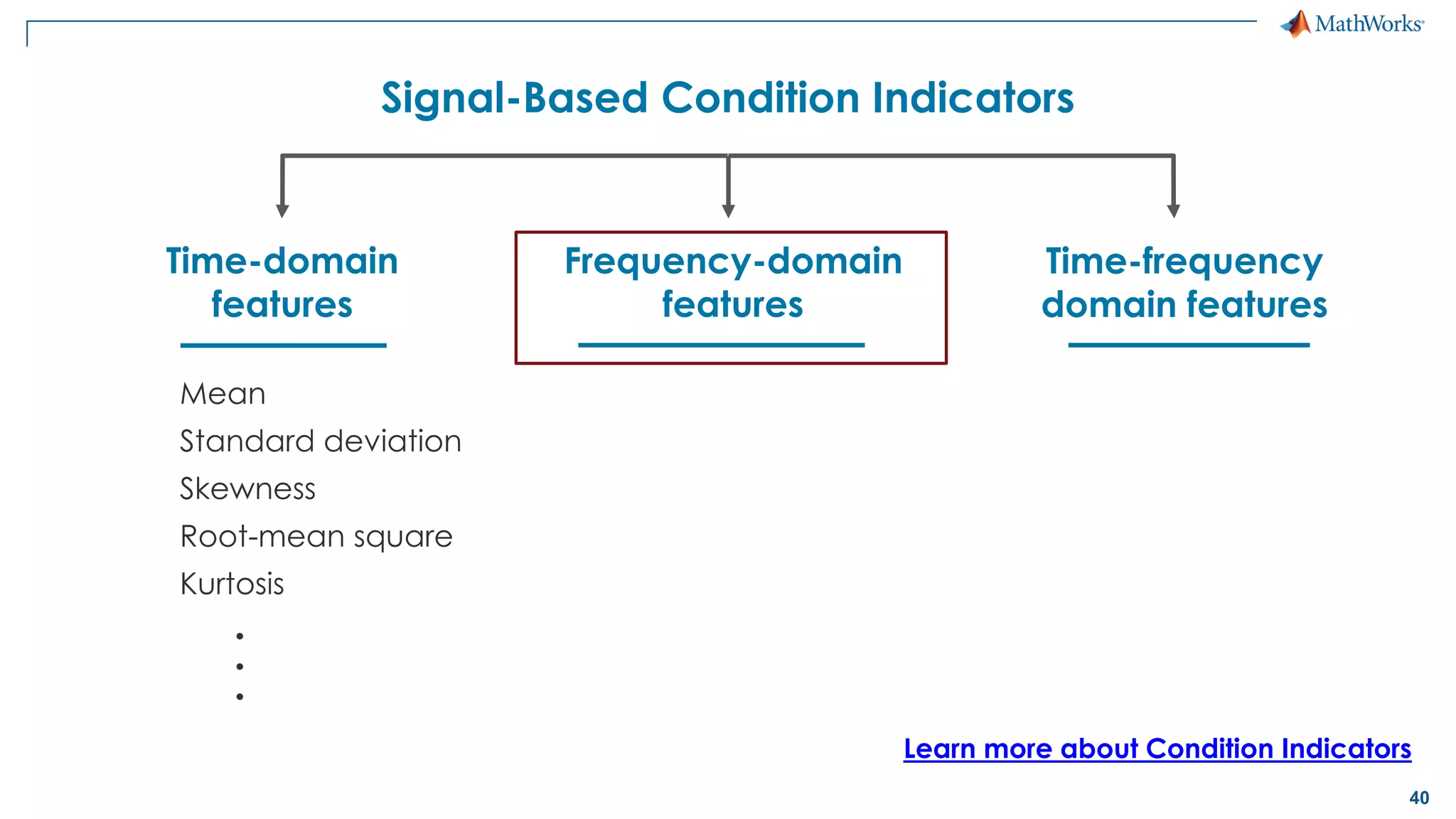
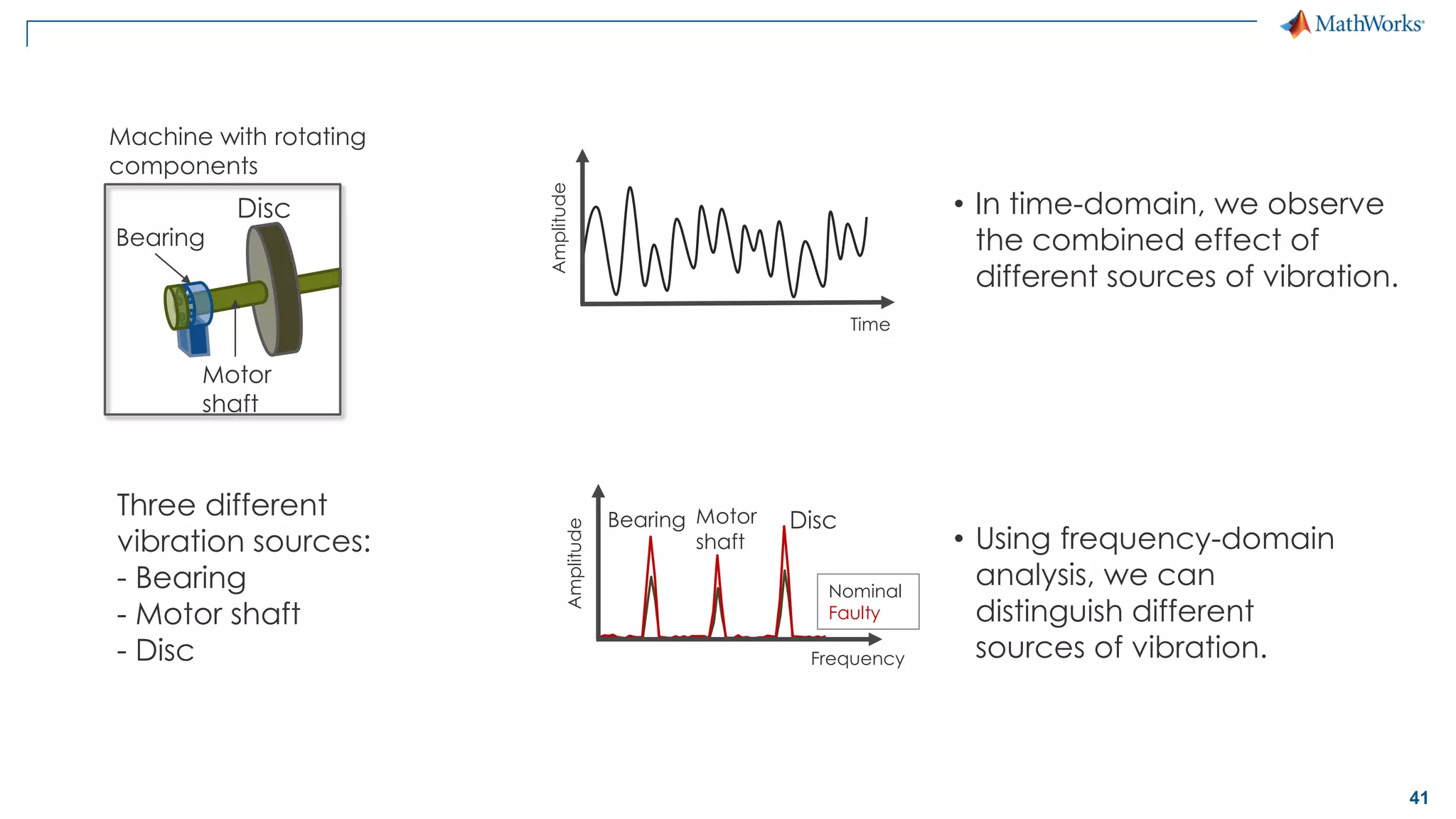
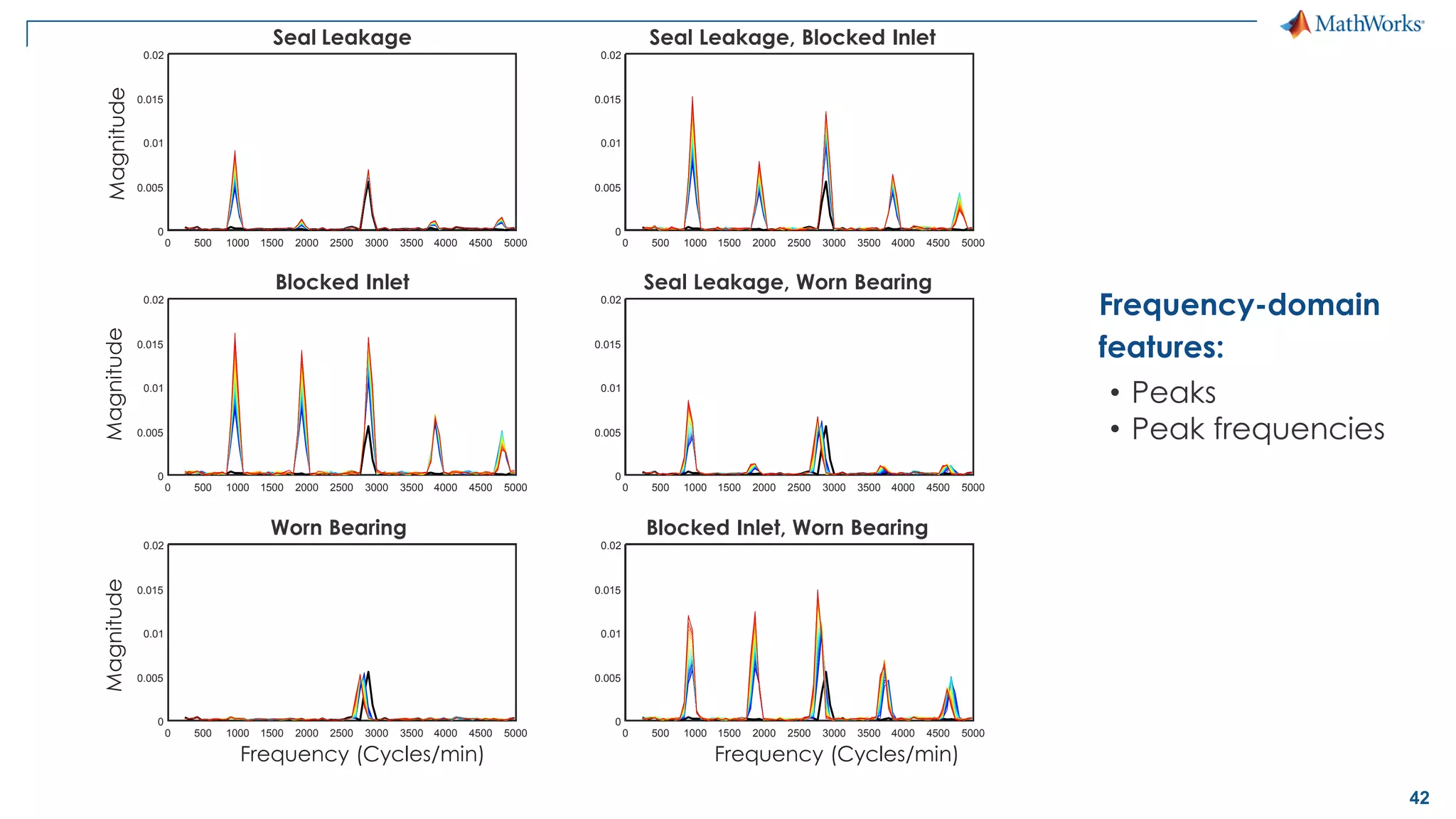
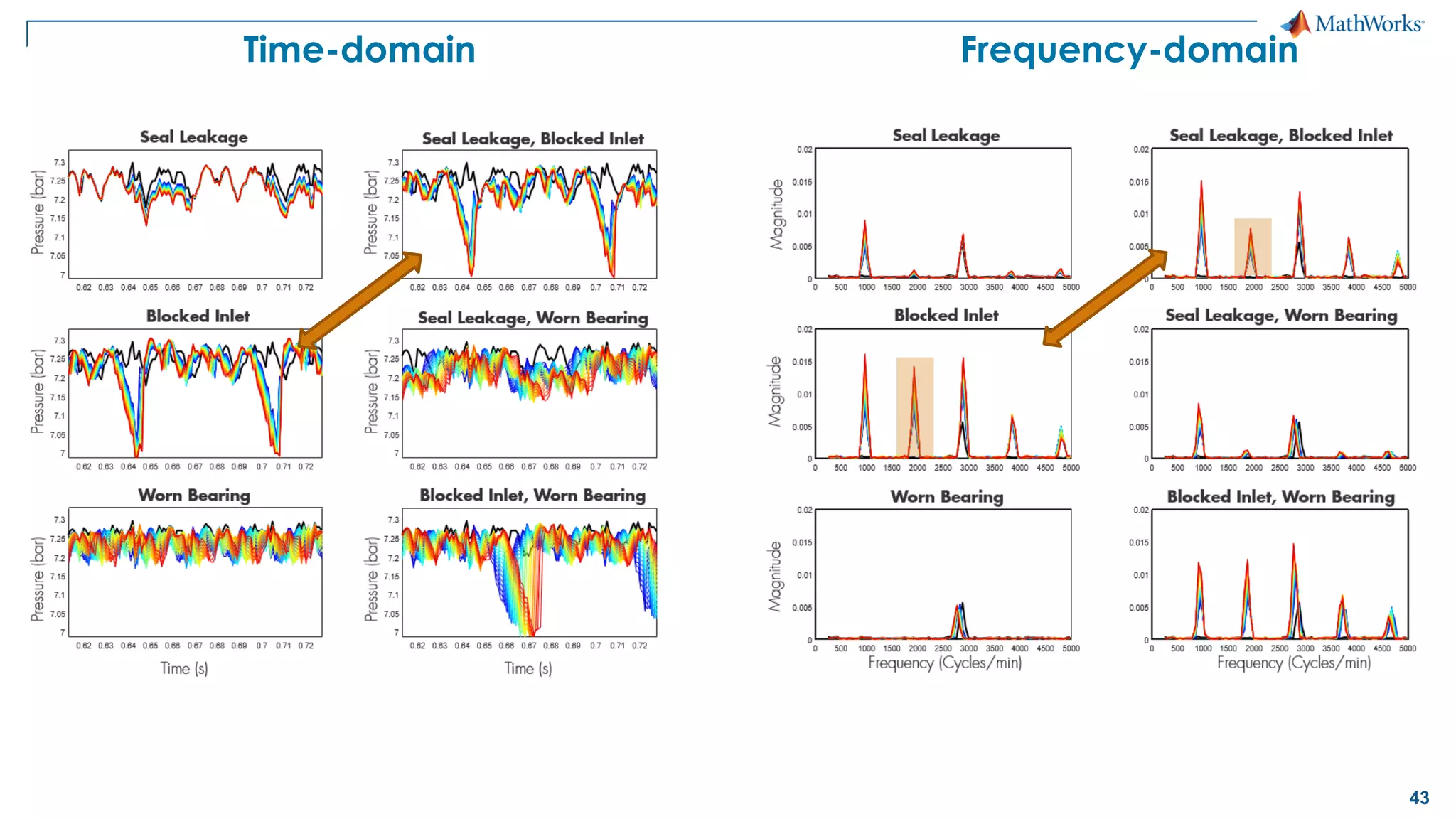
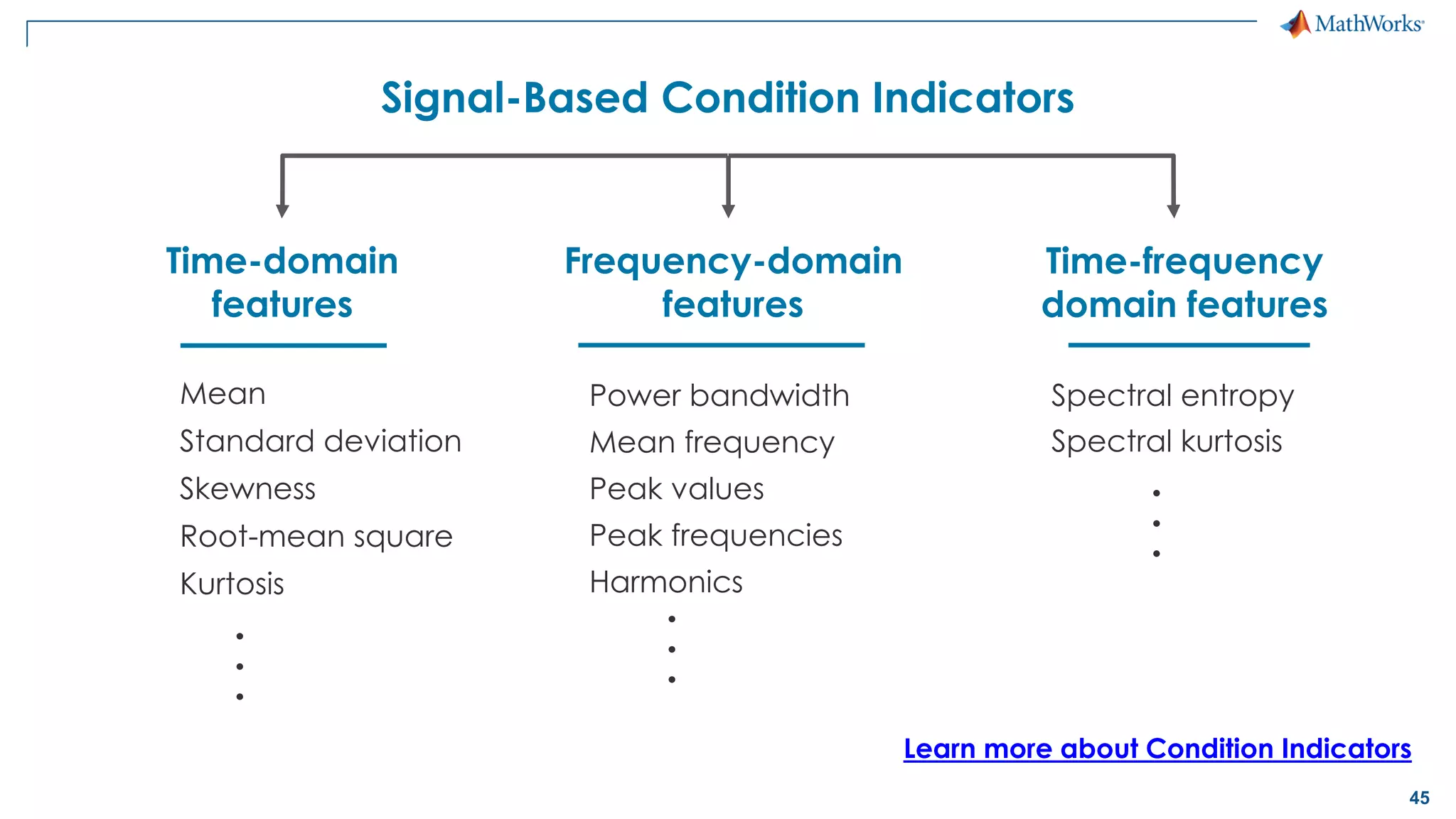
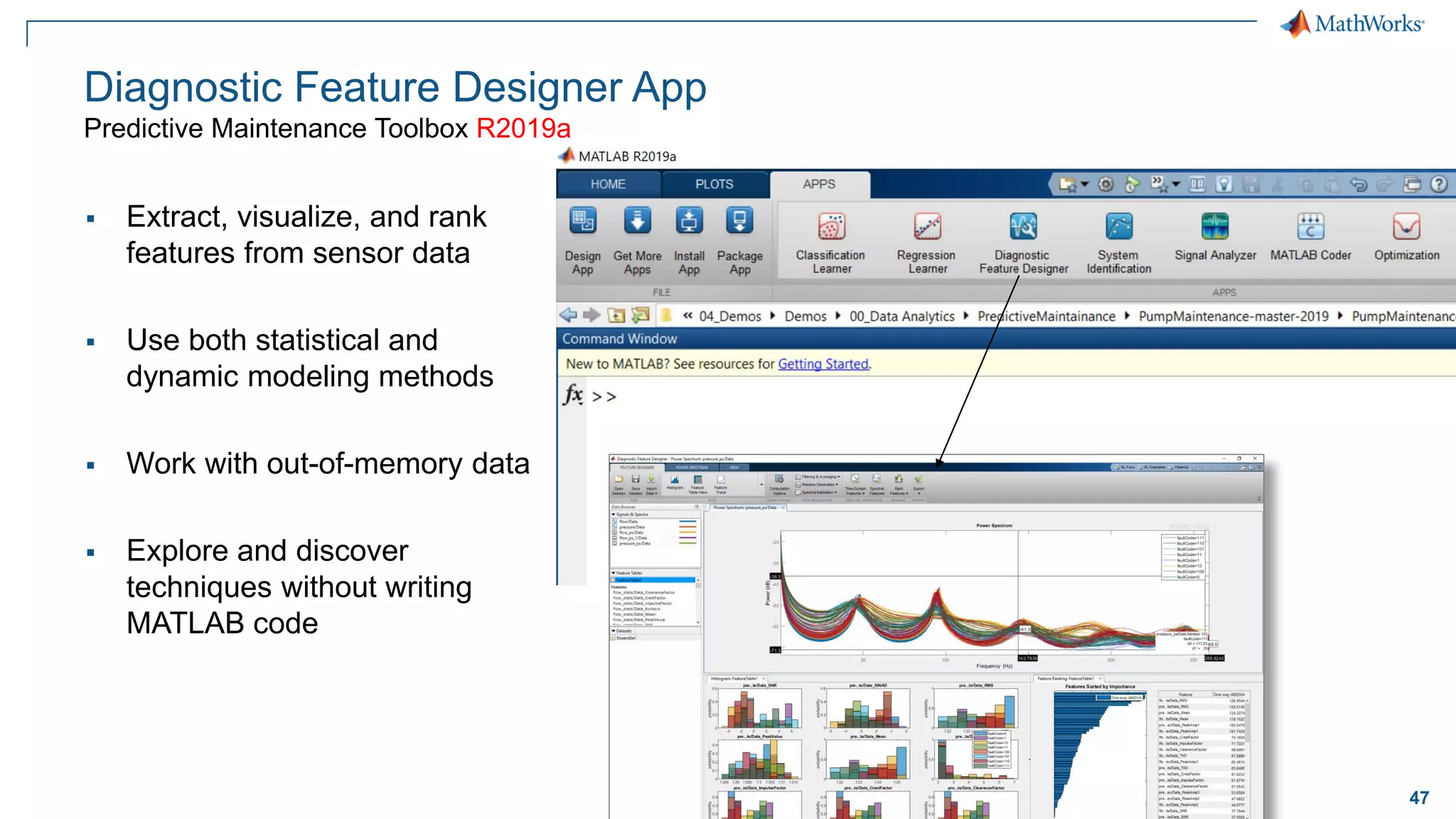
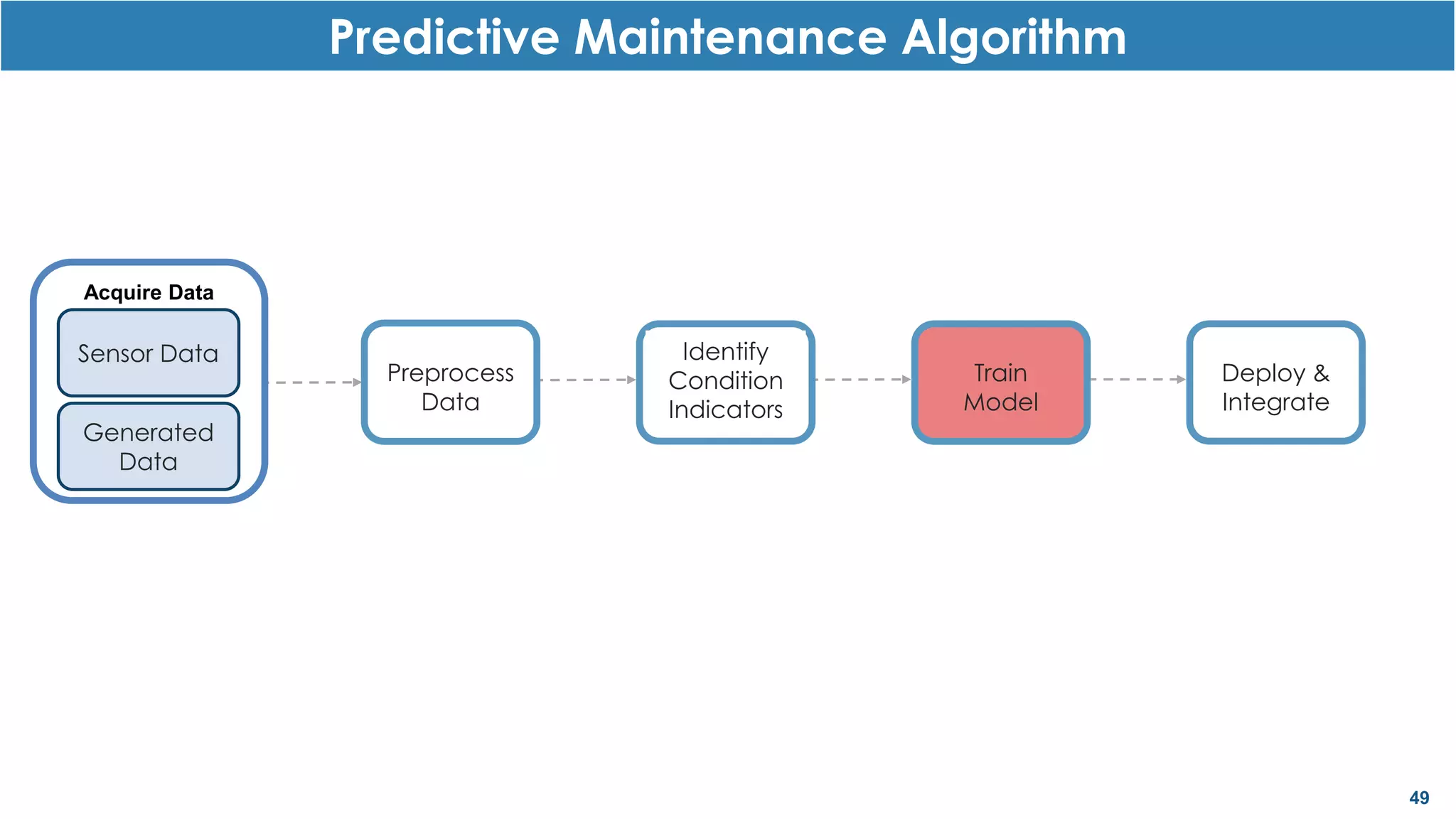
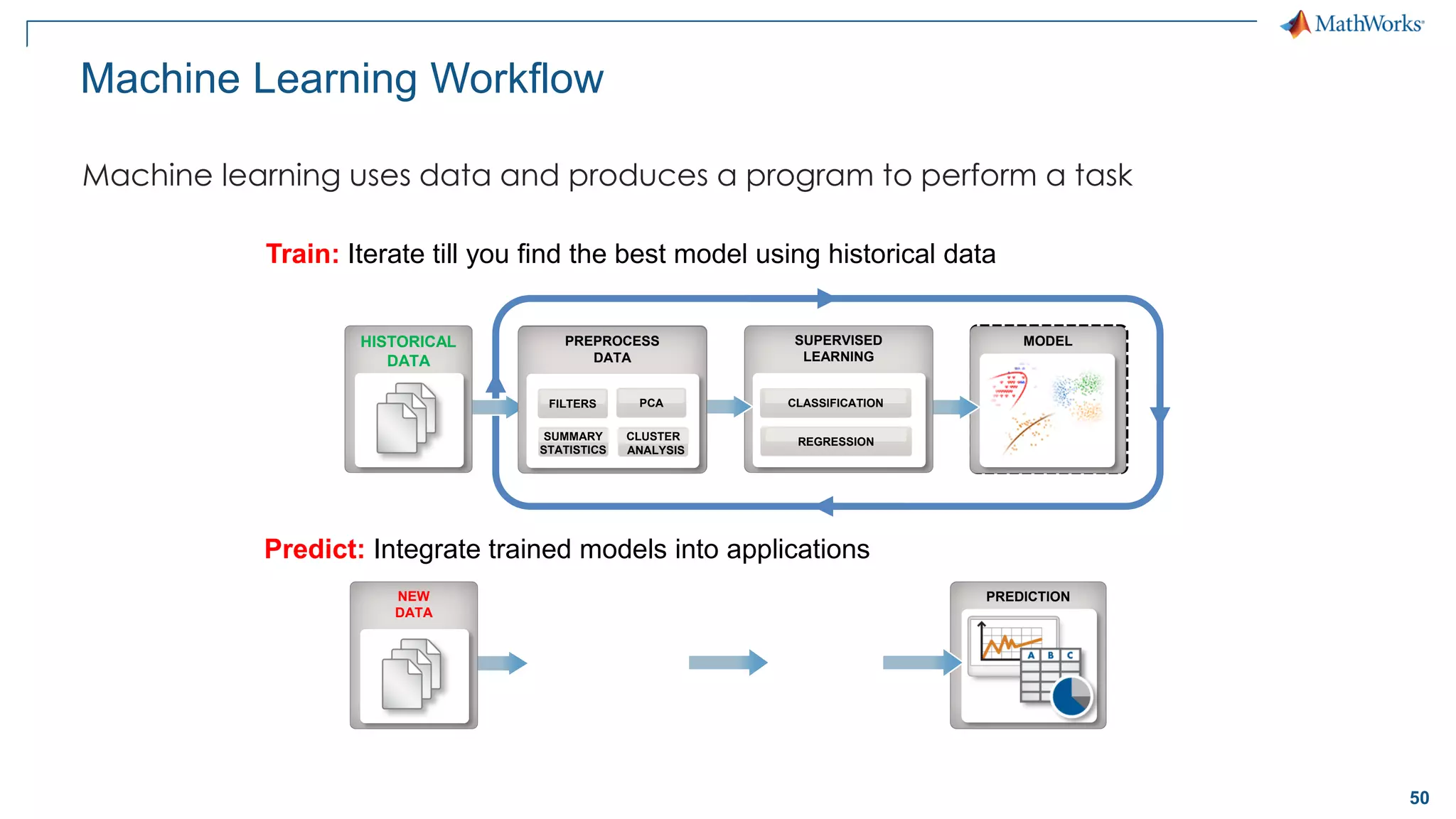
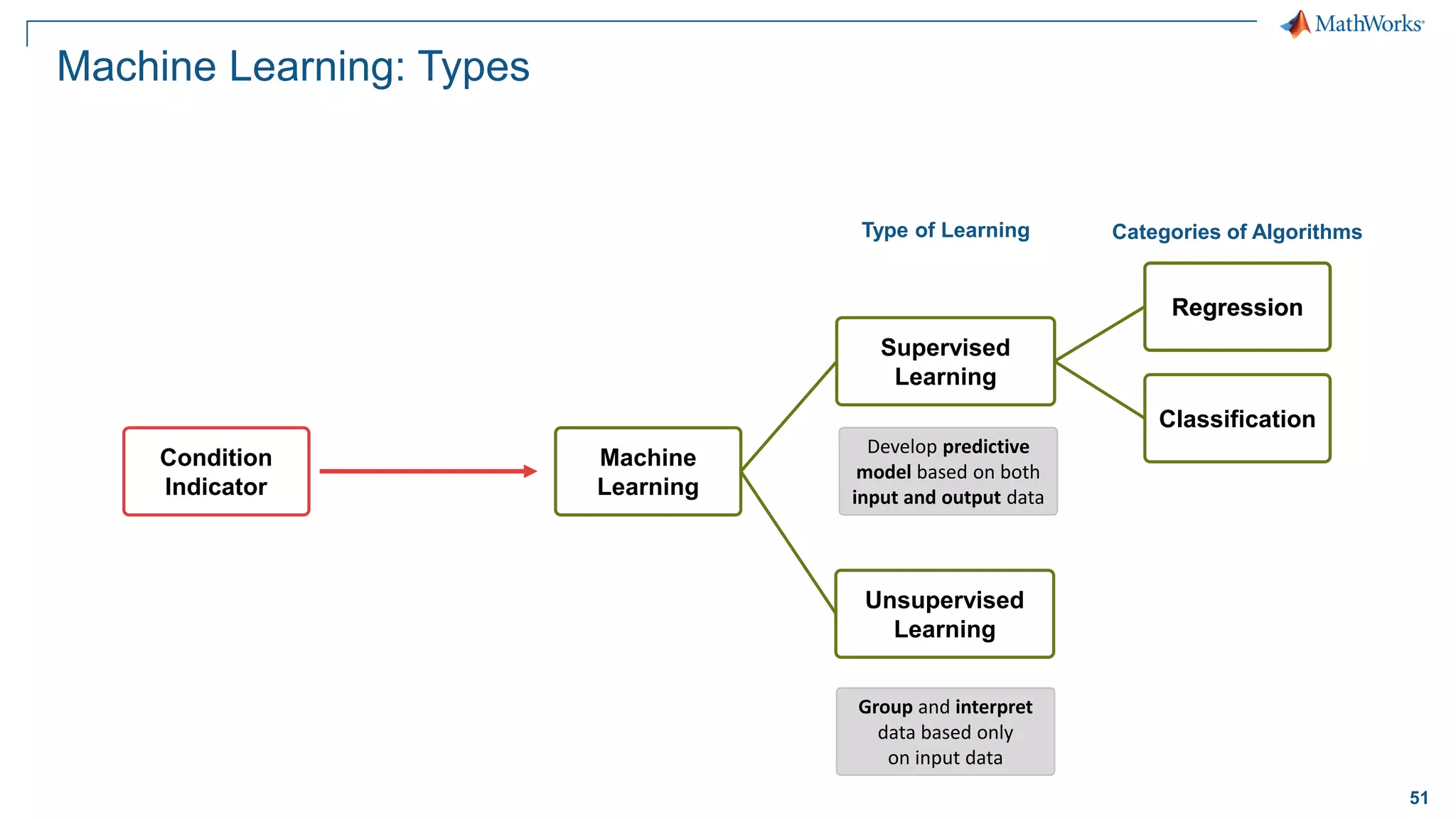
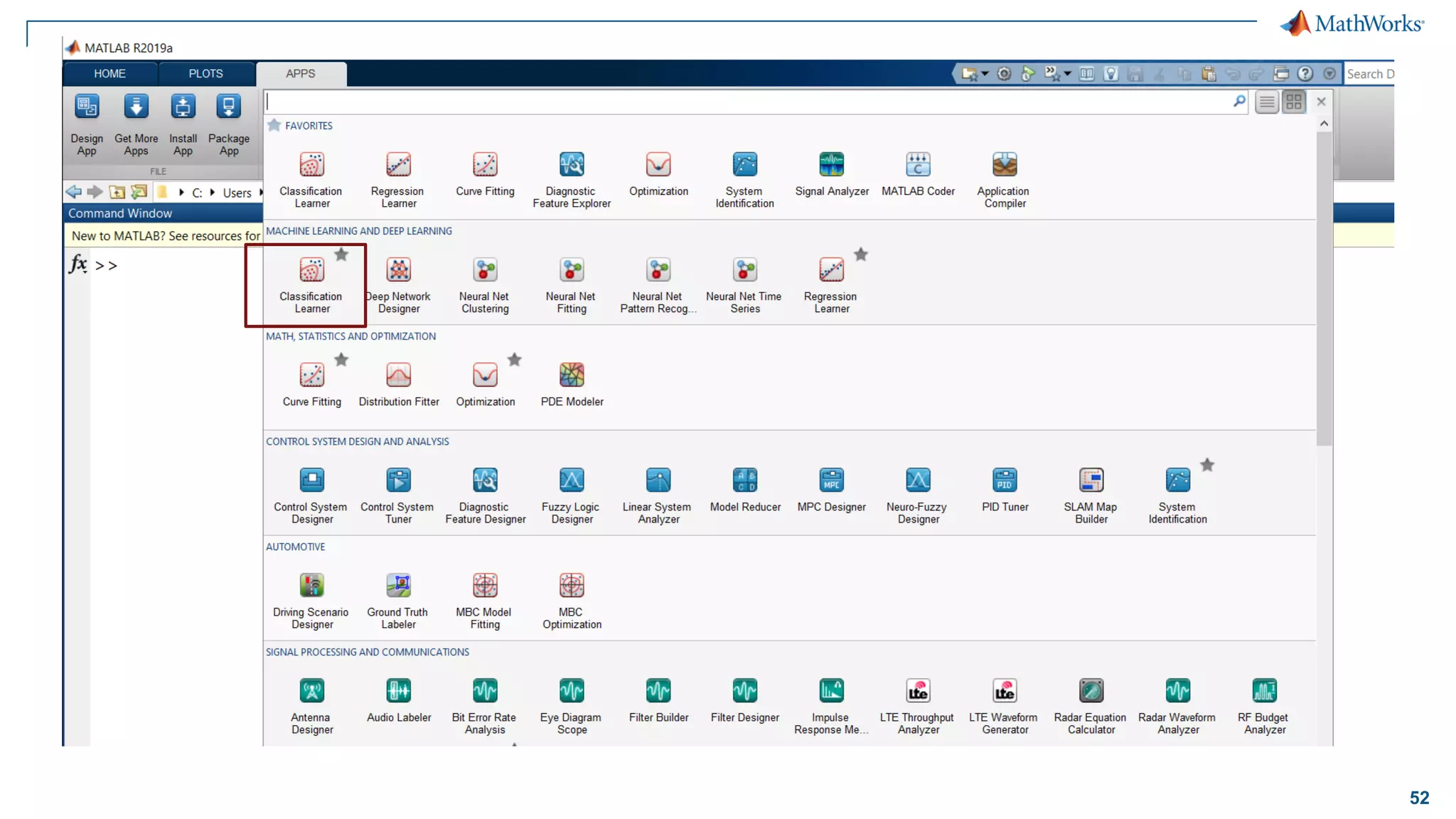
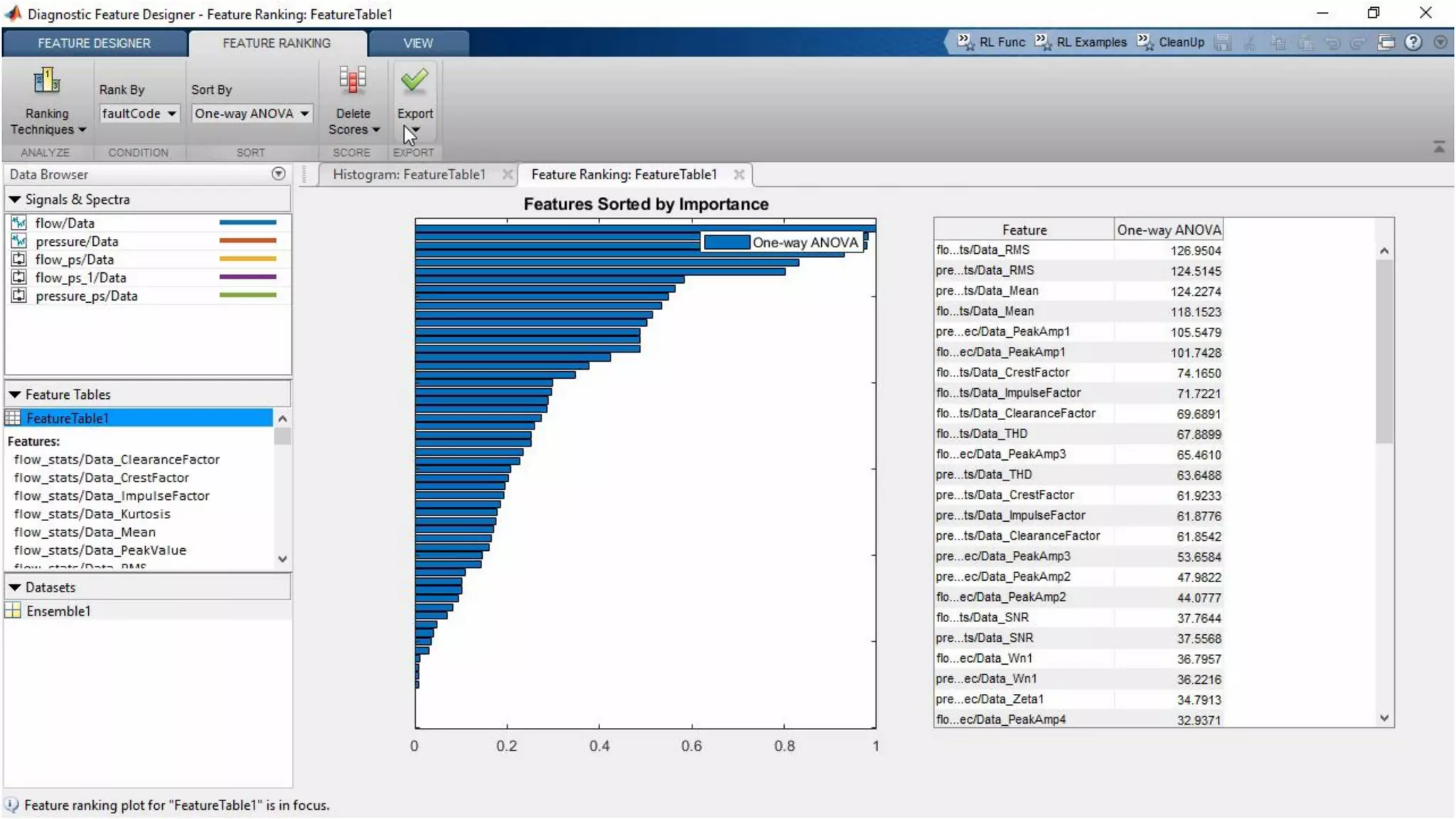
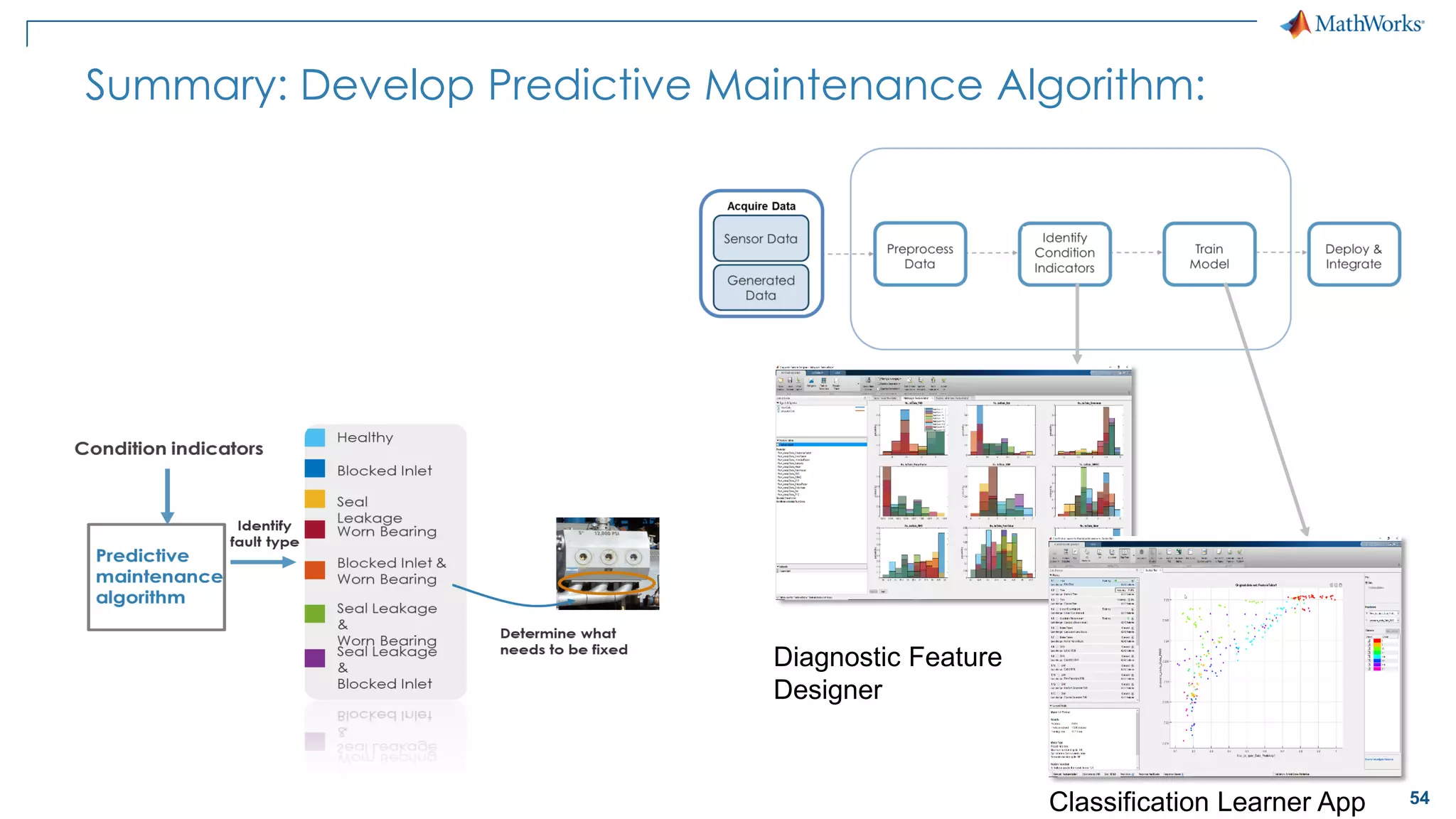
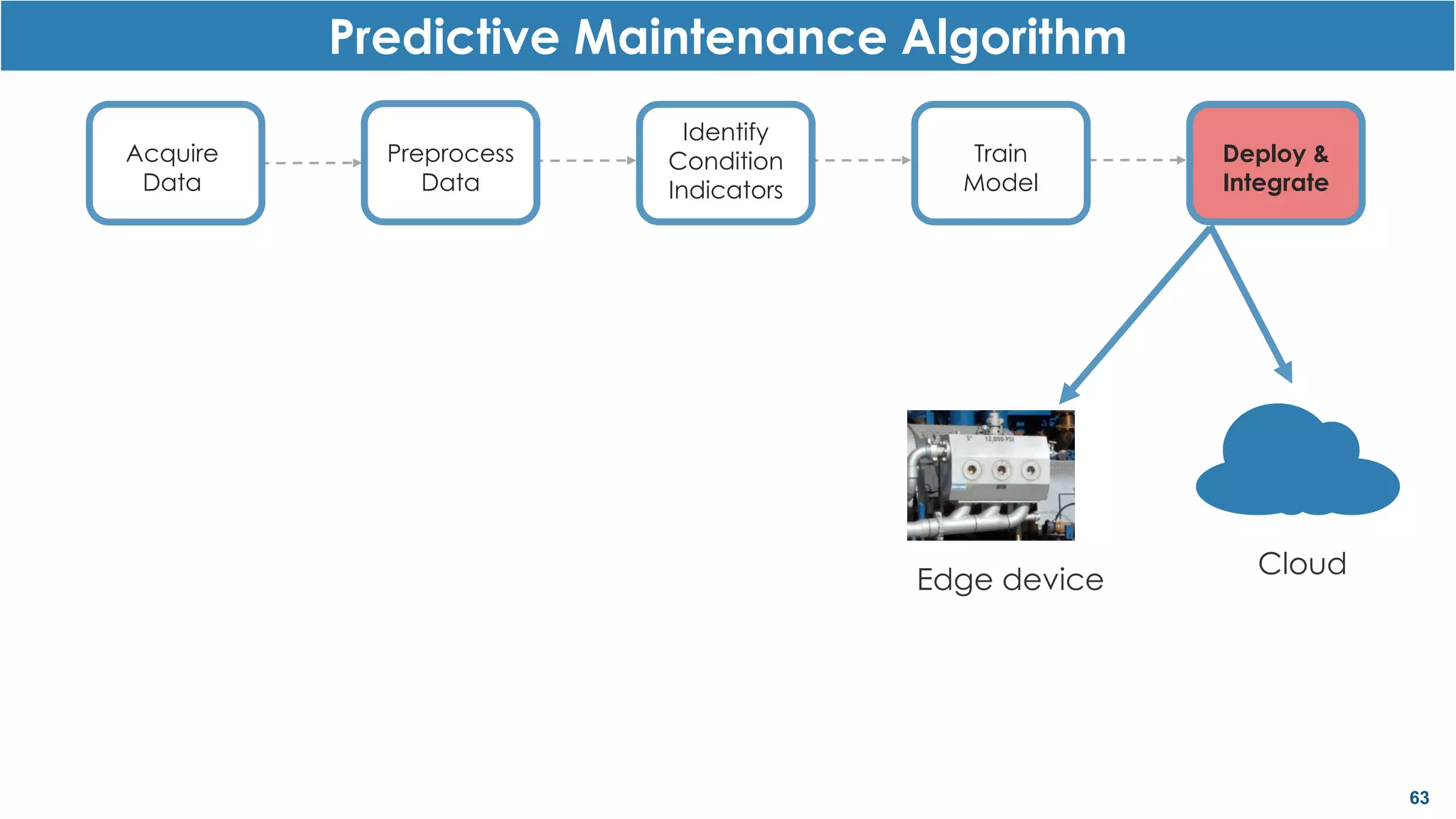
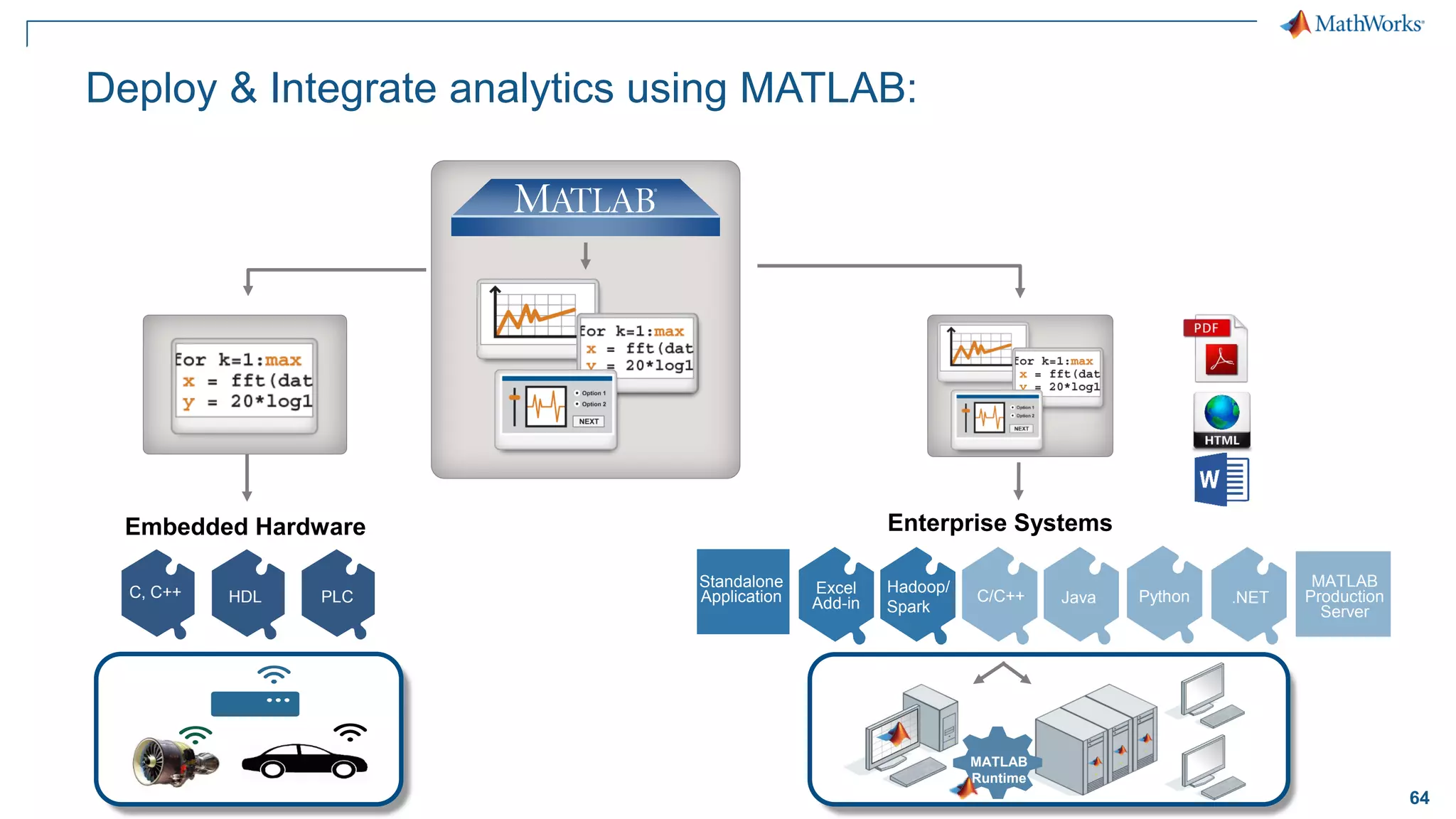
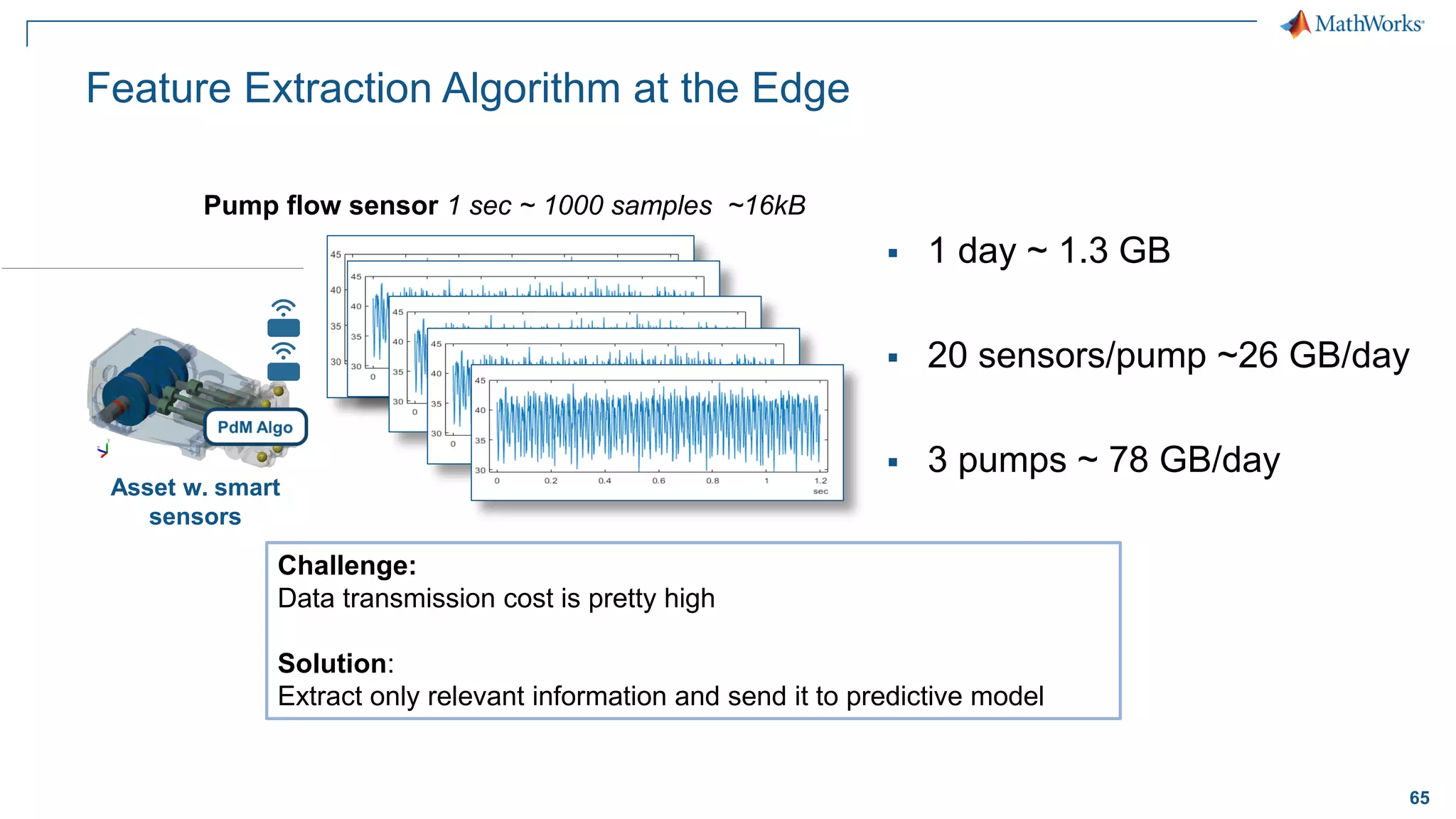
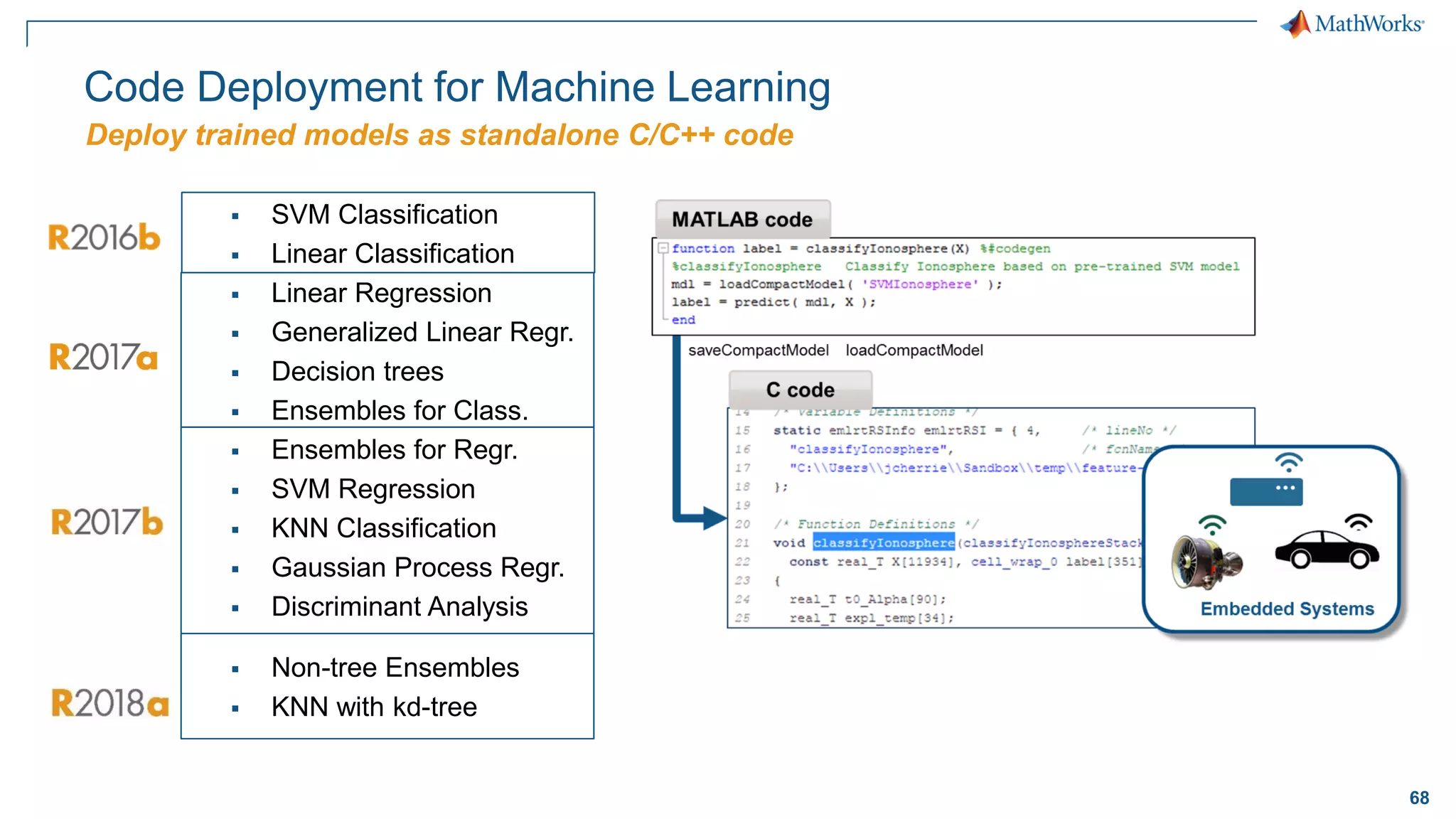
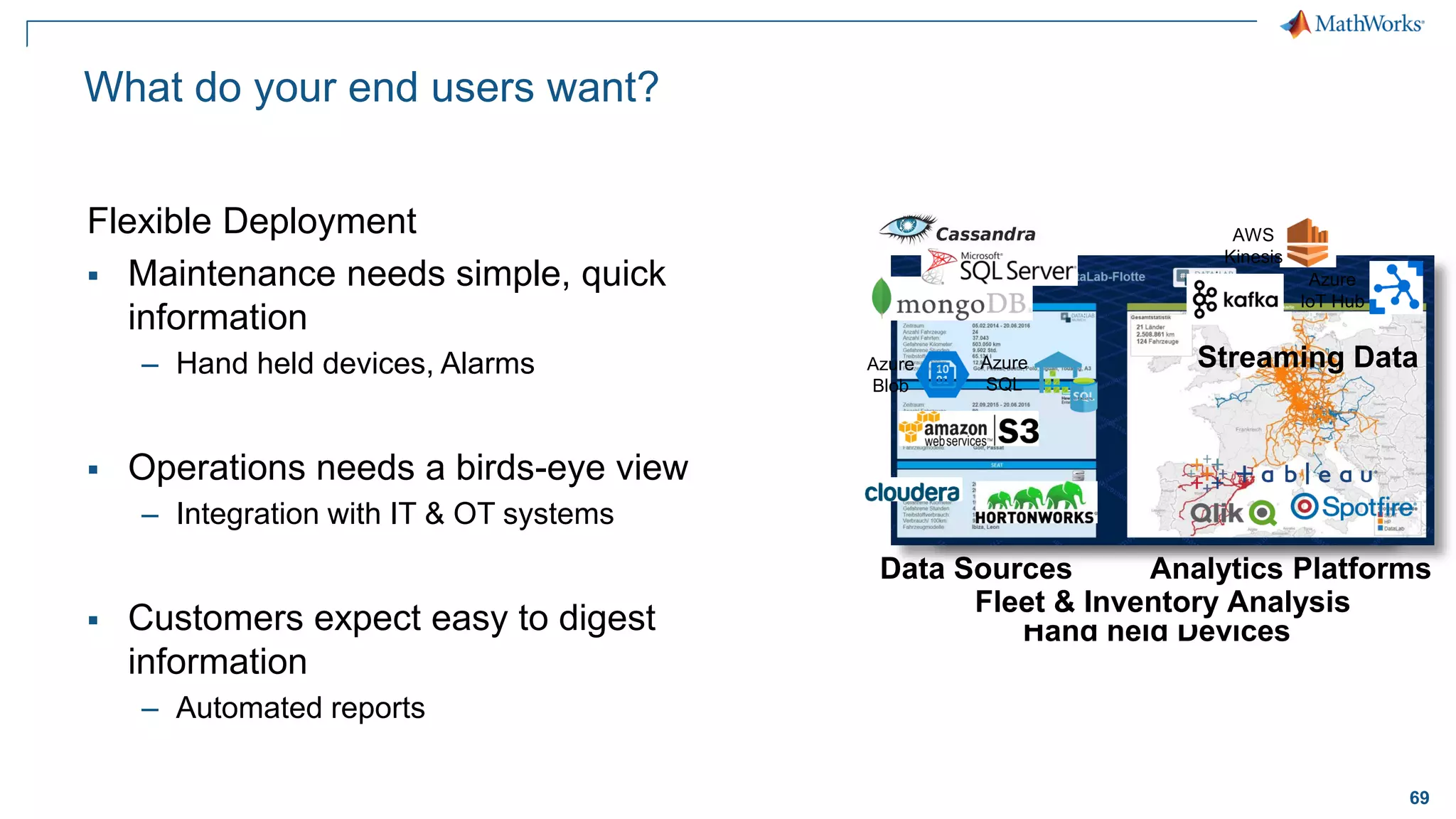
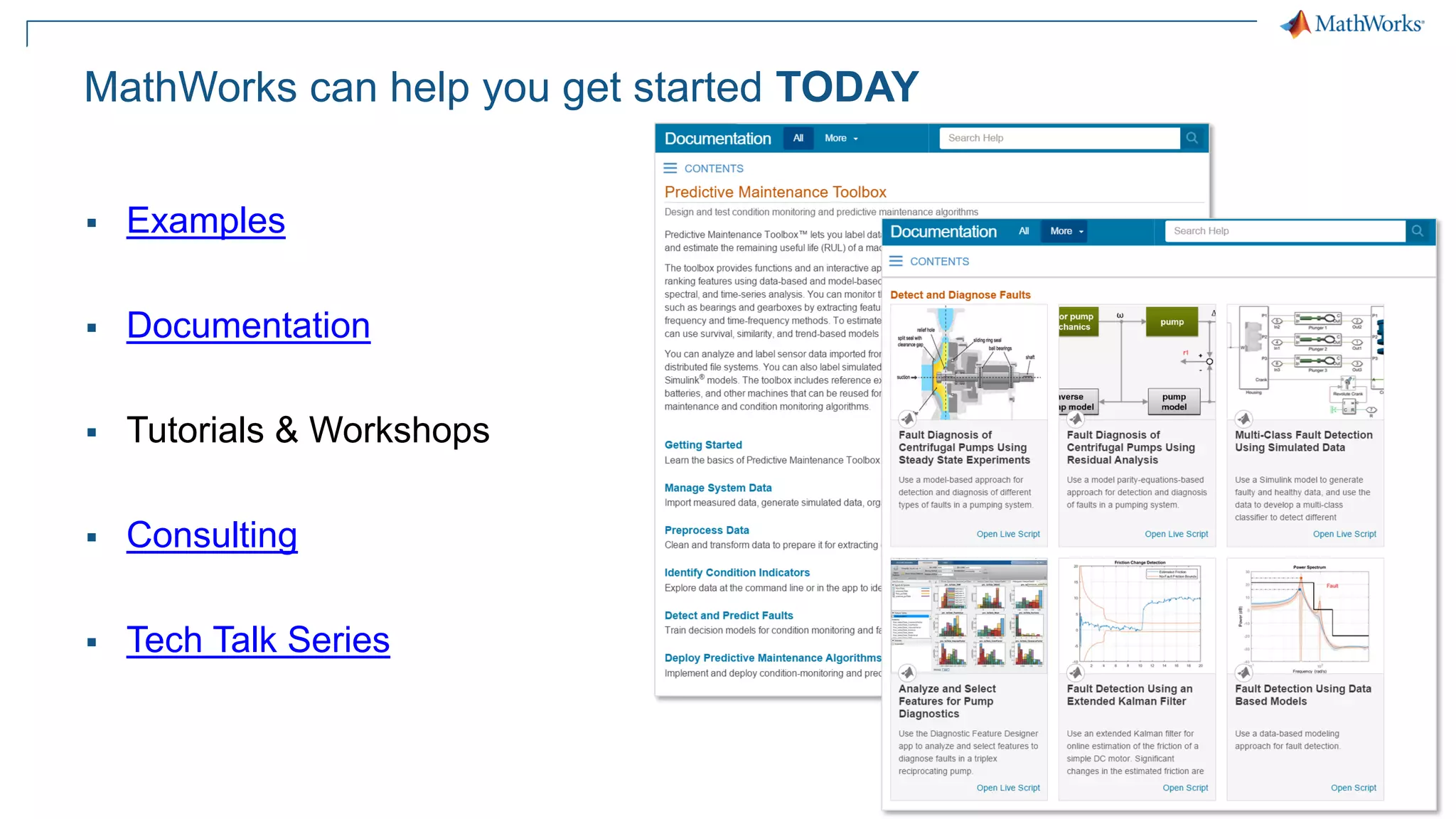
This document discusses predictive maintenance and how to develop predictive maintenance algorithms using MATLAB. It defines predictive, preventative, and reactive maintenance. It then outlines the steps to develop a predictive algorithm, including acquiring sensor data, preprocessing the data, identifying condition indicators, training a model, and deploying the model. It provides examples of developing algorithms for fault classification and remaining useful life estimation using sensor data from a triplex pump.