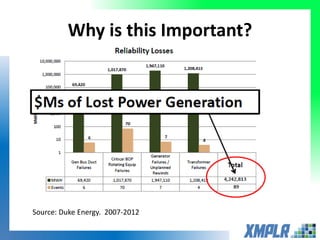
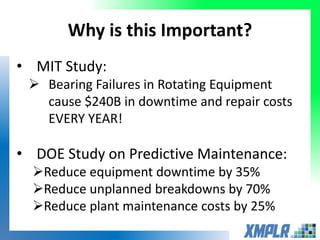
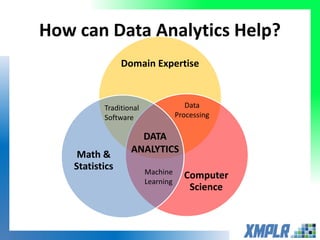
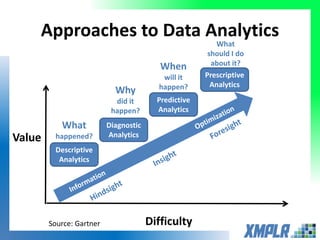
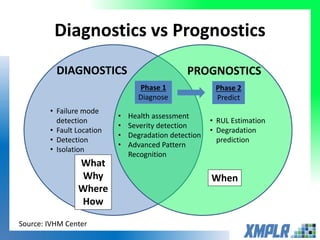
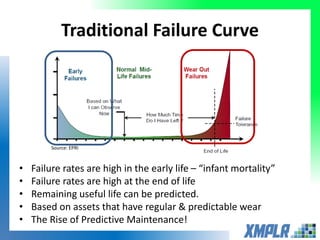
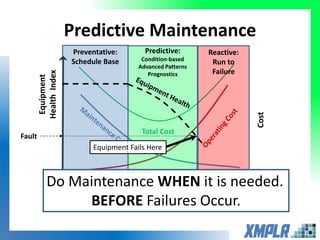
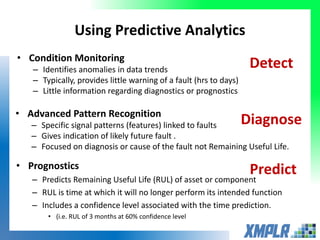
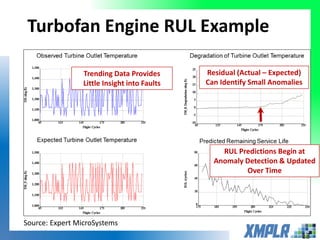
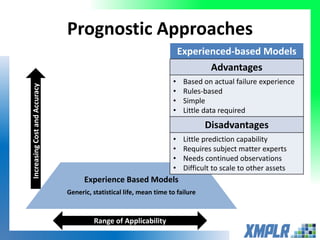
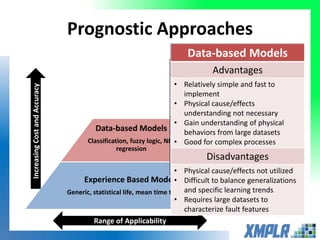
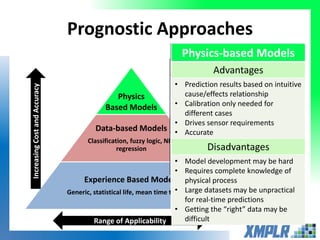
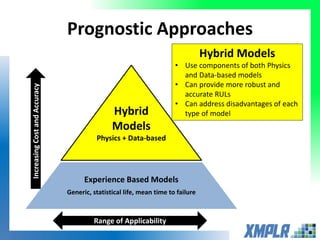
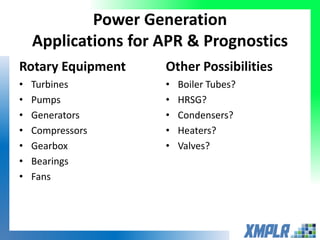
This document discusses opportunities for using data analytics in power generation. It outlines key areas where data analytics can provide benefits, such as improving efficiency, reliability, emissions compliance, and flexibility. The focus is on using data analytics and prognostics to predict equipment failures. Several approaches to prognostics are described, including experience-based, data-based, and physics-based models. Power generation equipment that could benefit from advanced pattern recognition and prognostics includes turbines, pumps, generators, compressors, gearboxes, and bearings. Challenges to implementing these techniques include ensuring access to relevant data, validating prediction accuracy, and addressing data security concerns.