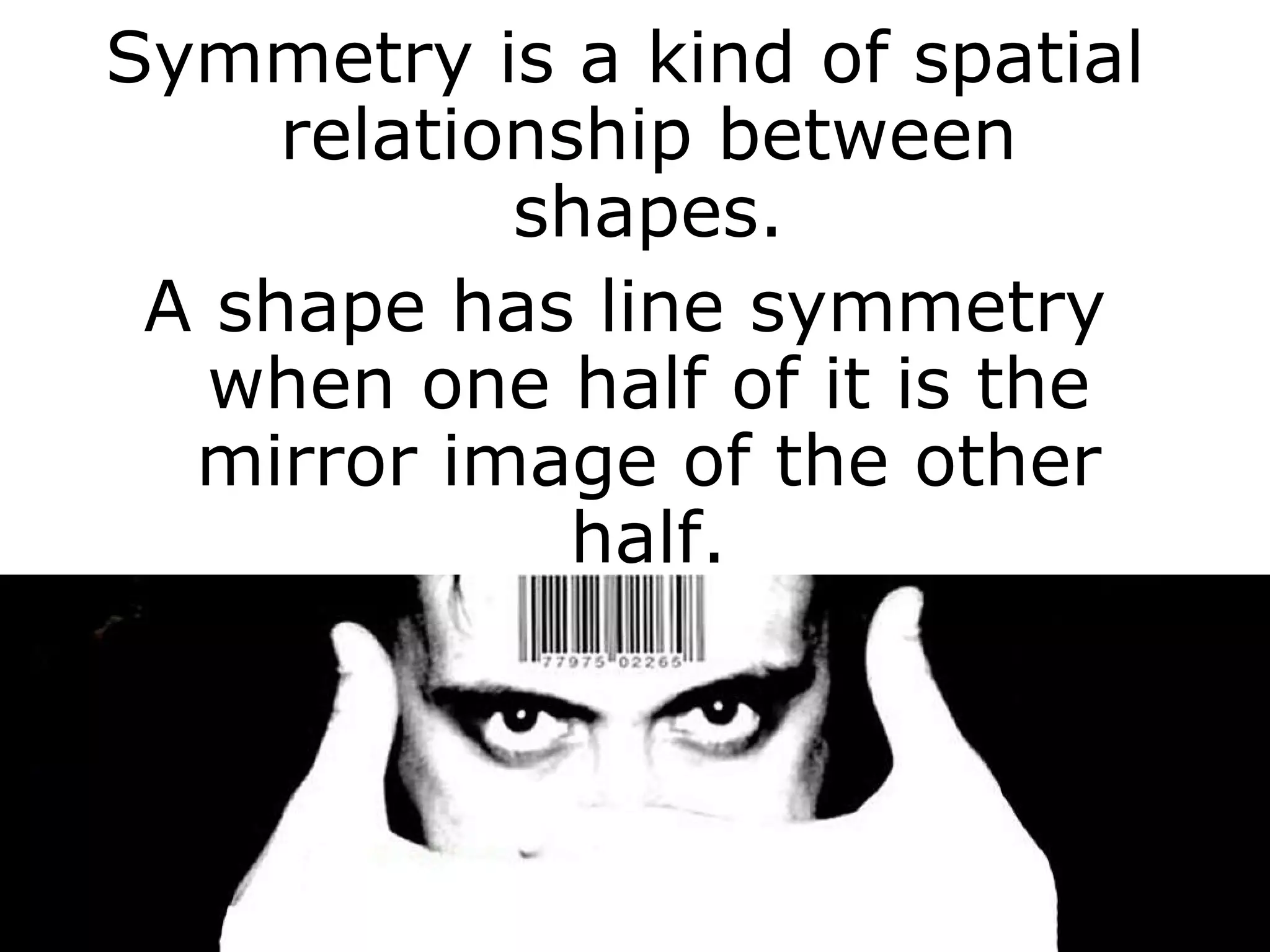
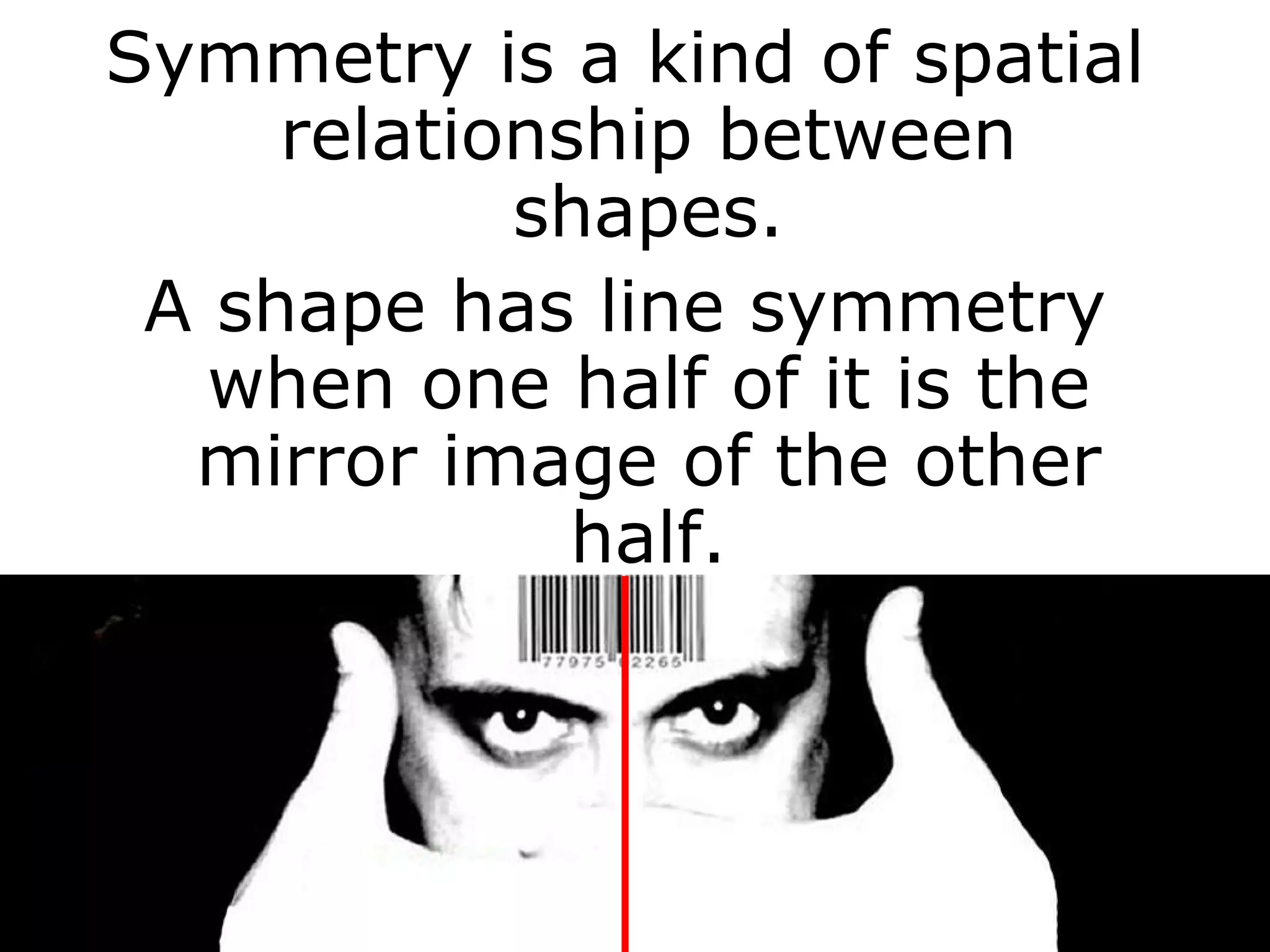
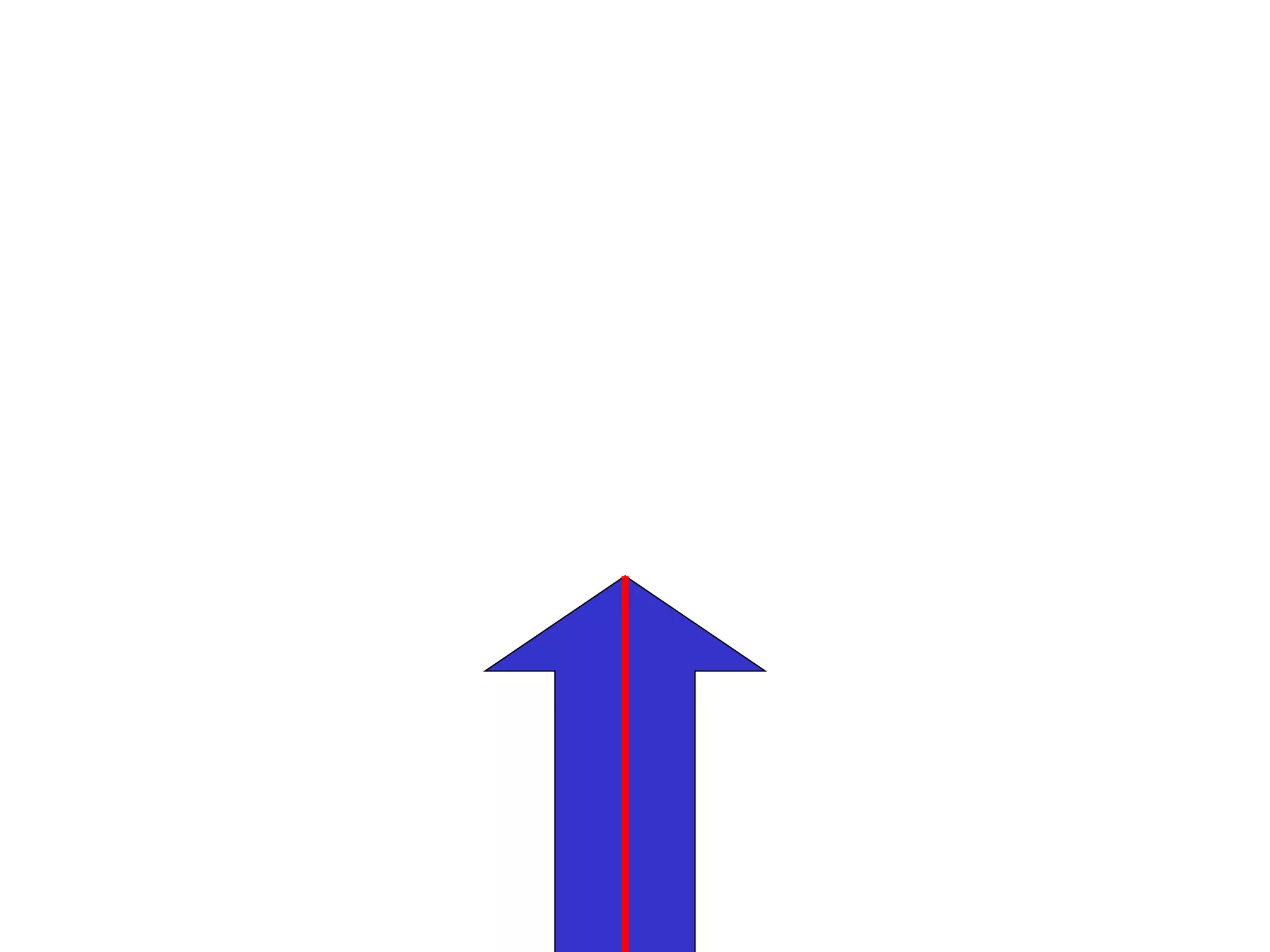
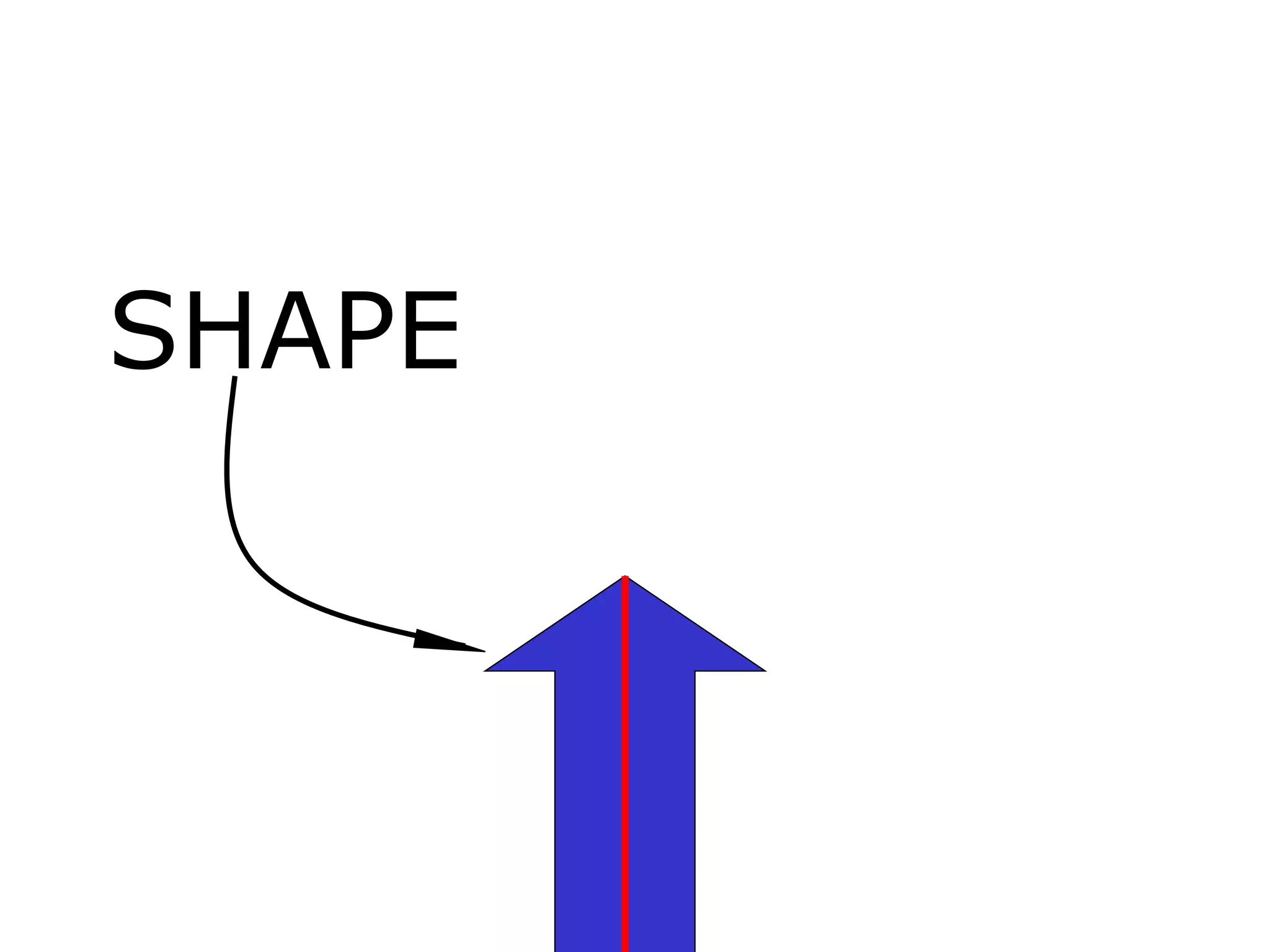
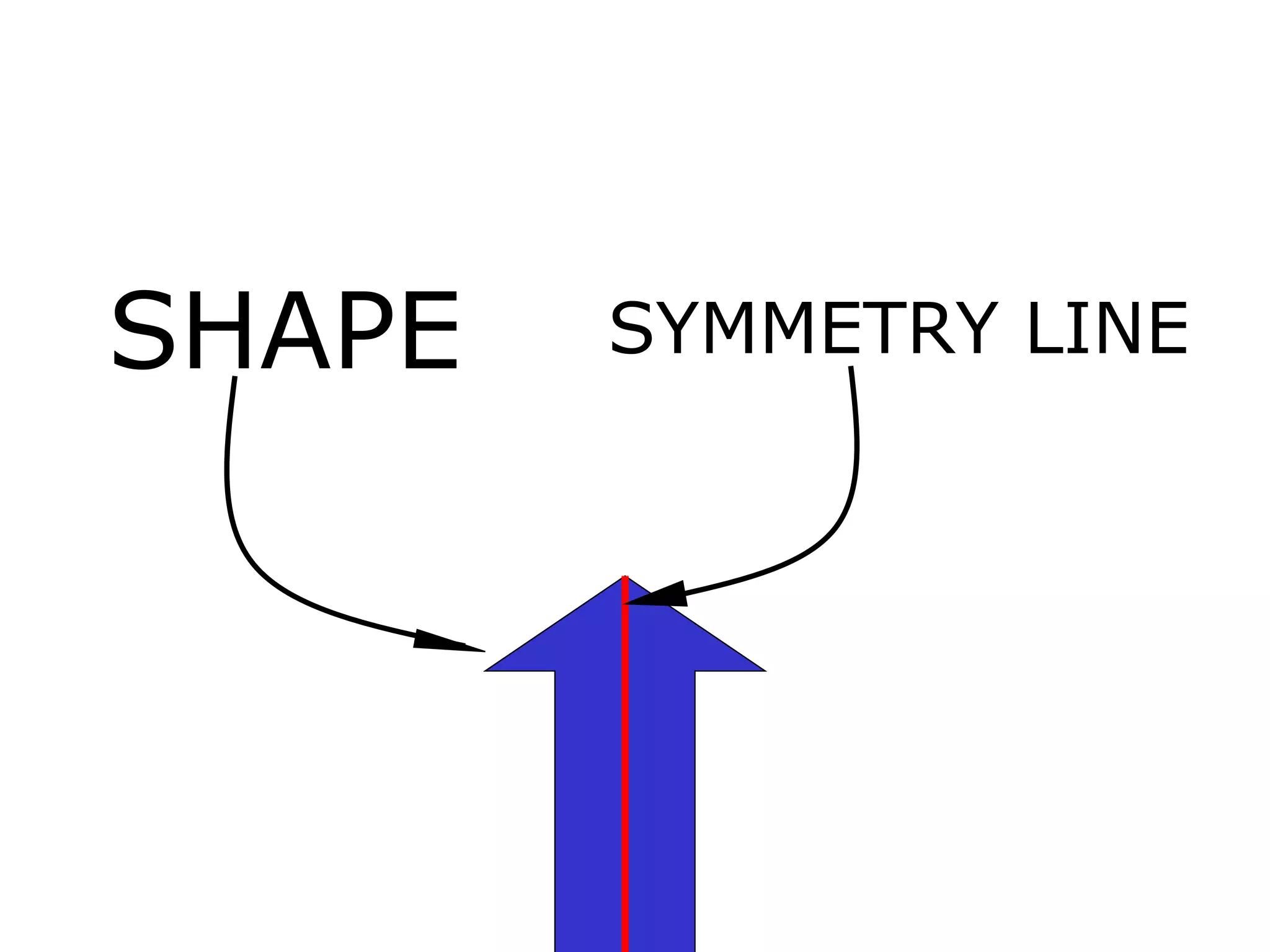
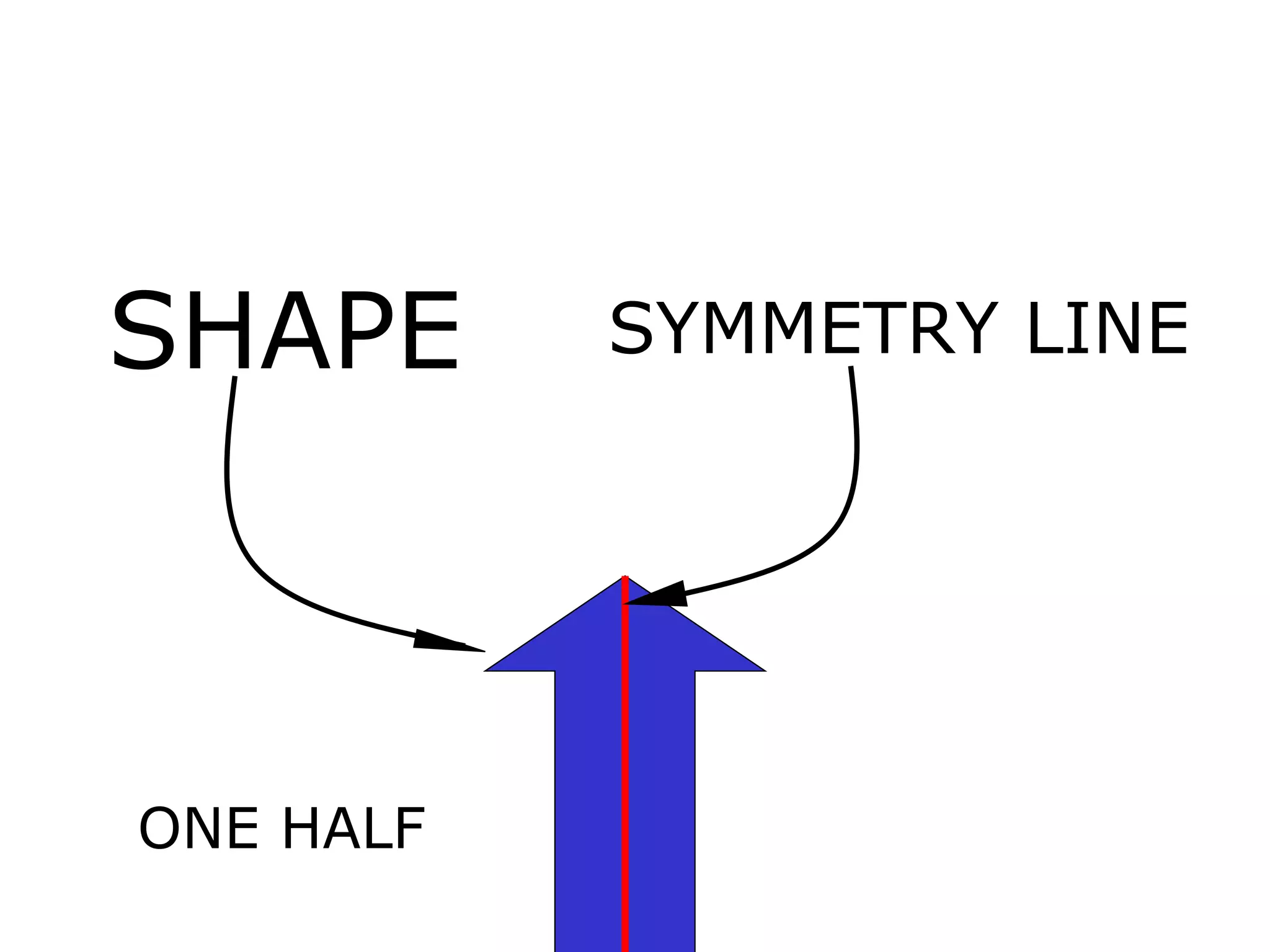
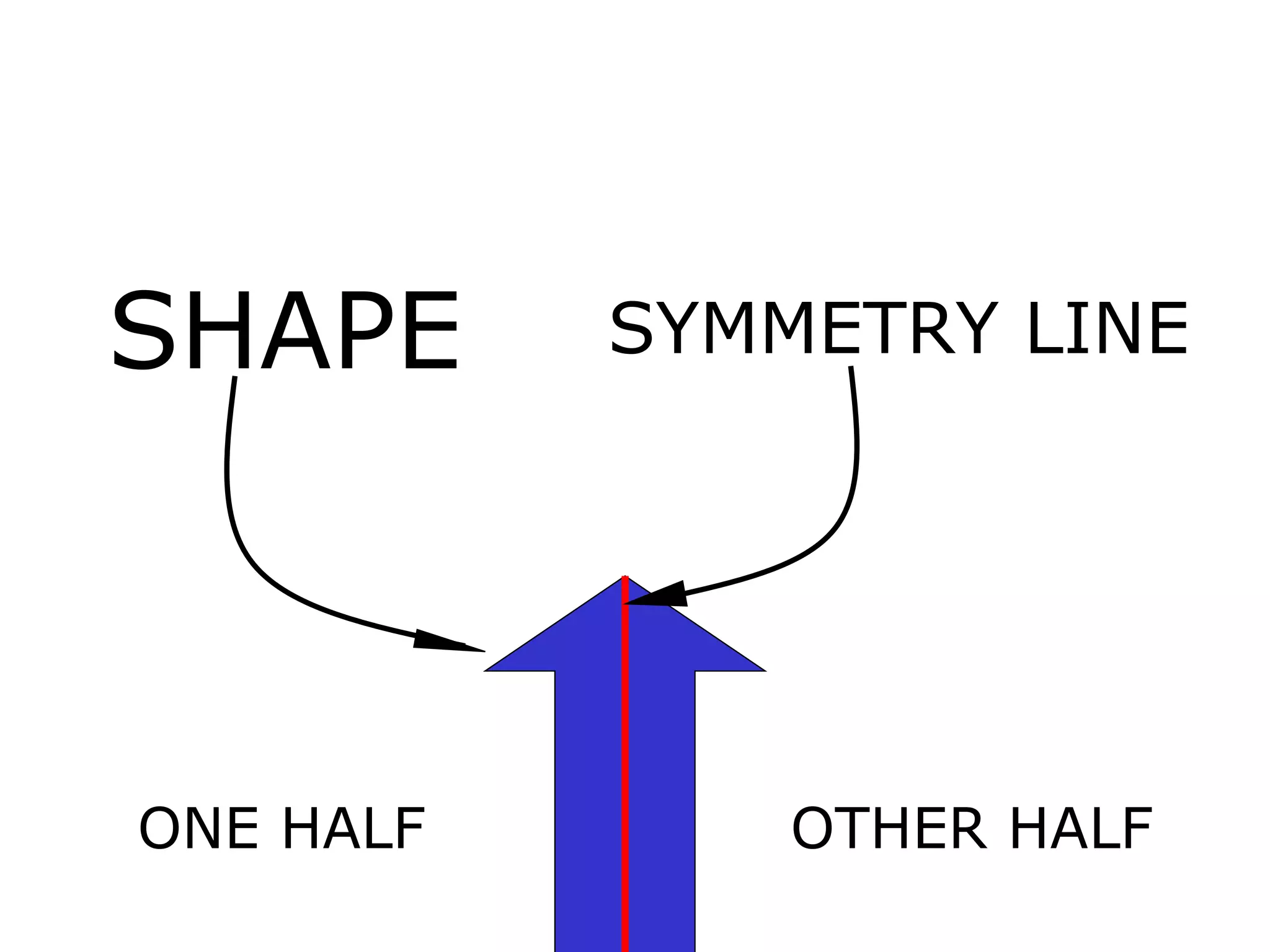
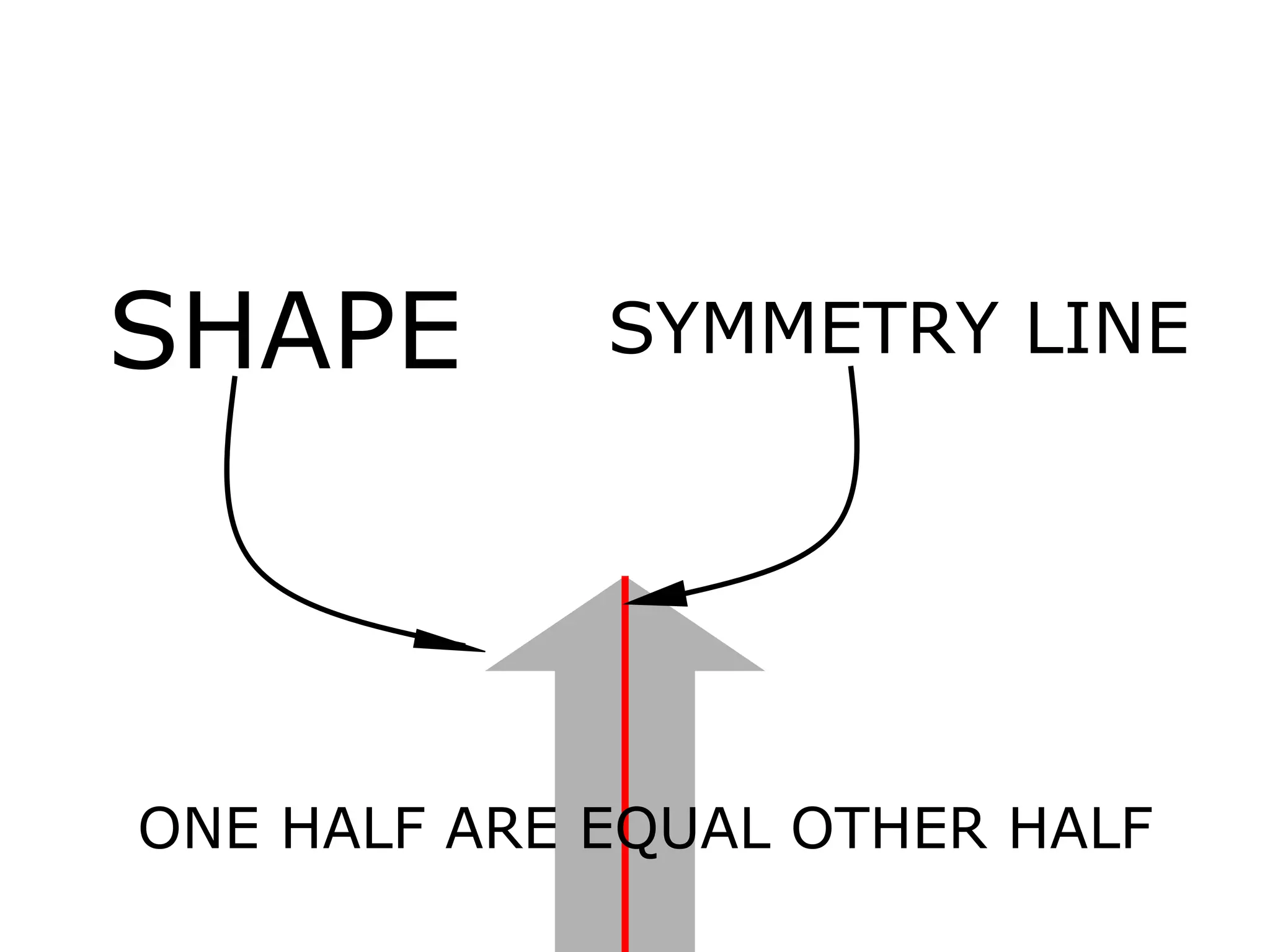
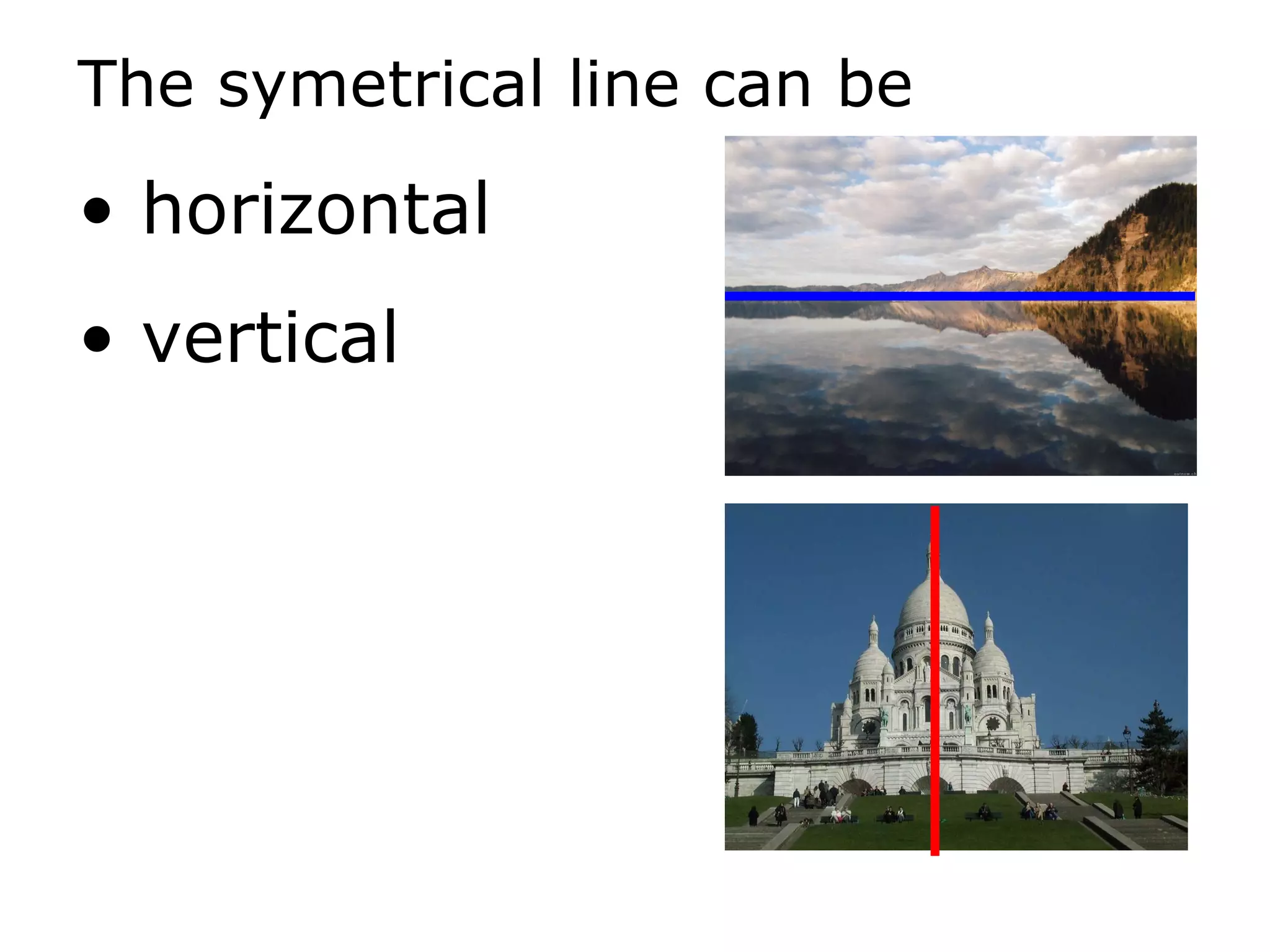
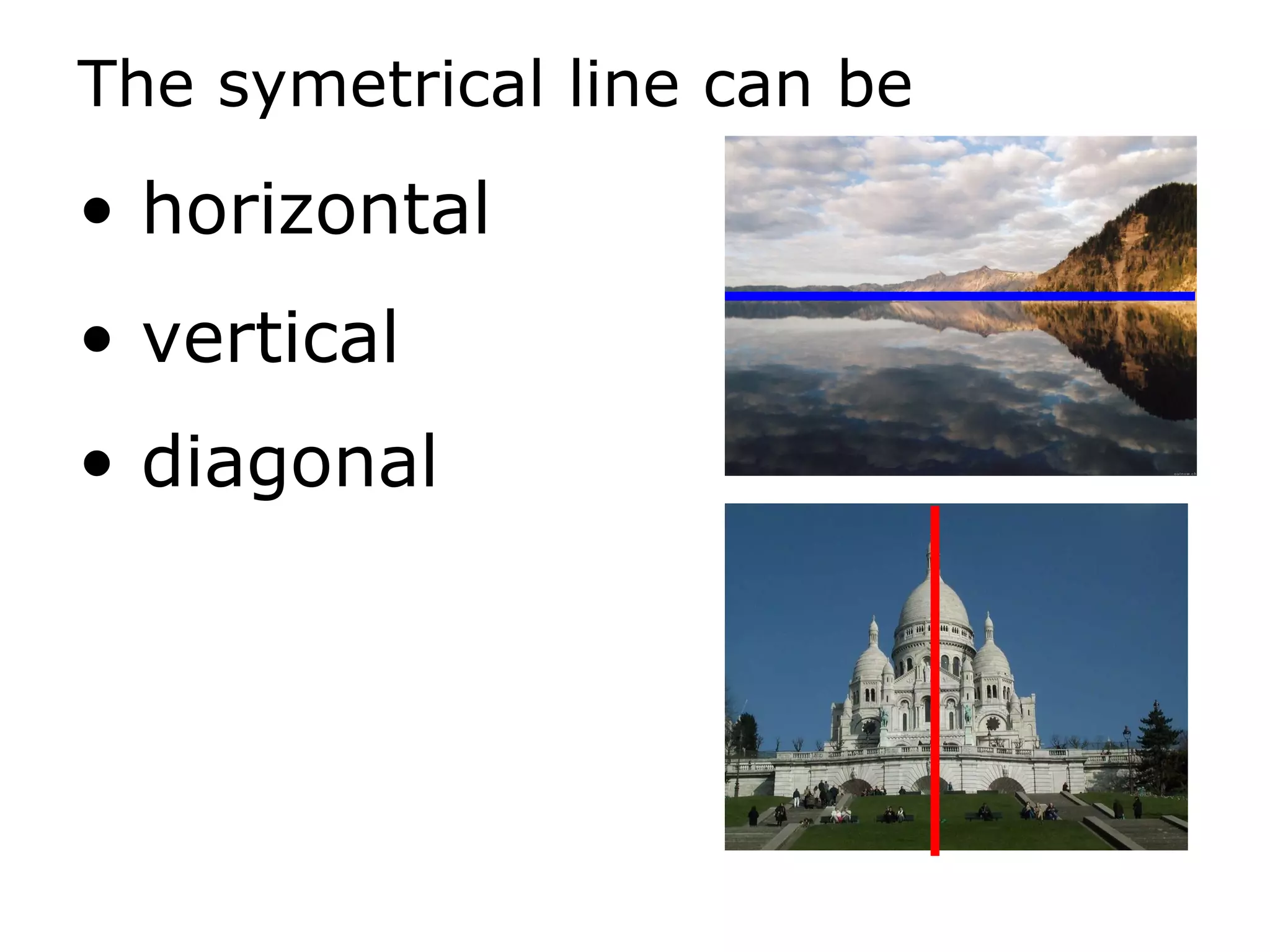
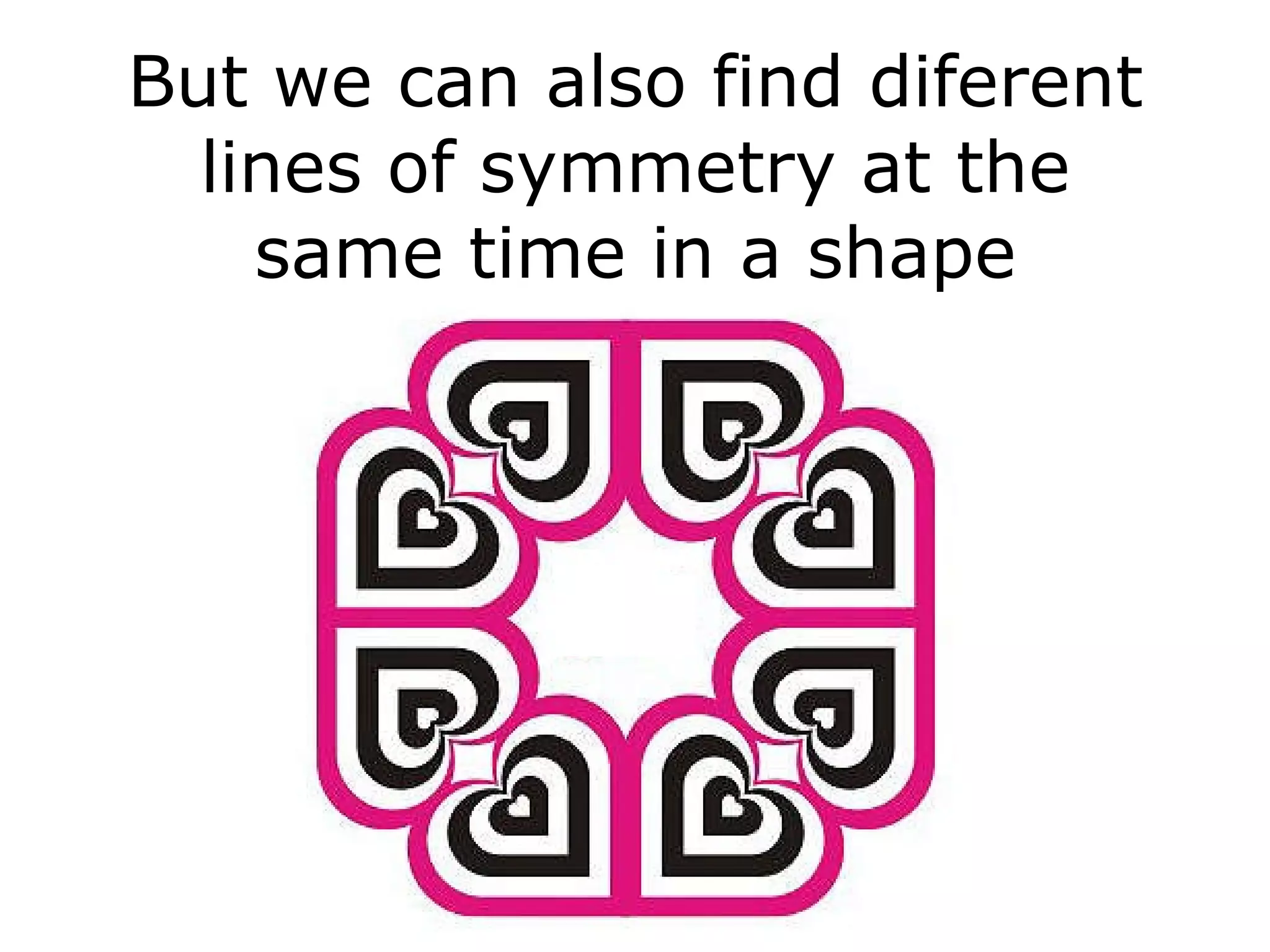
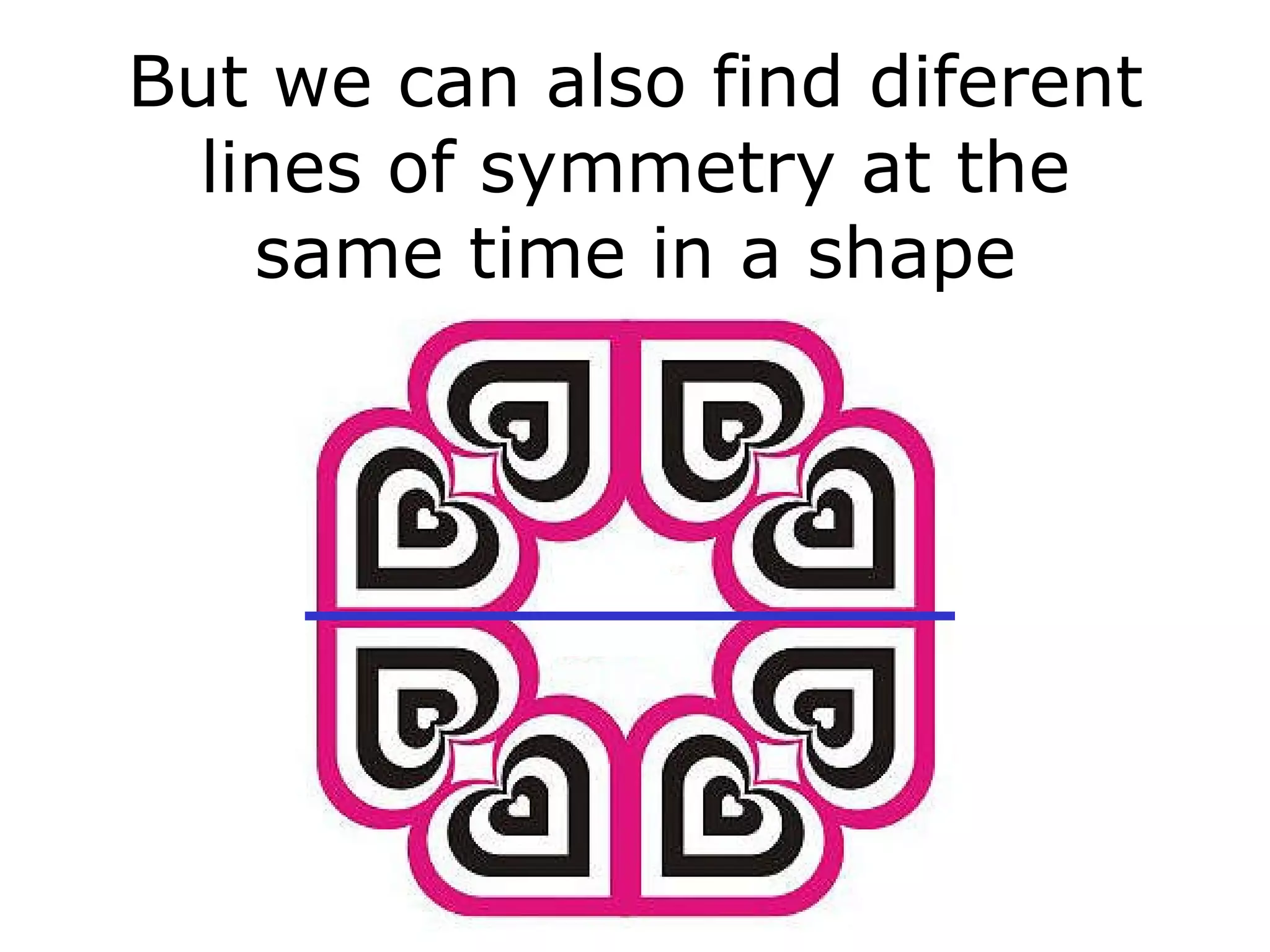
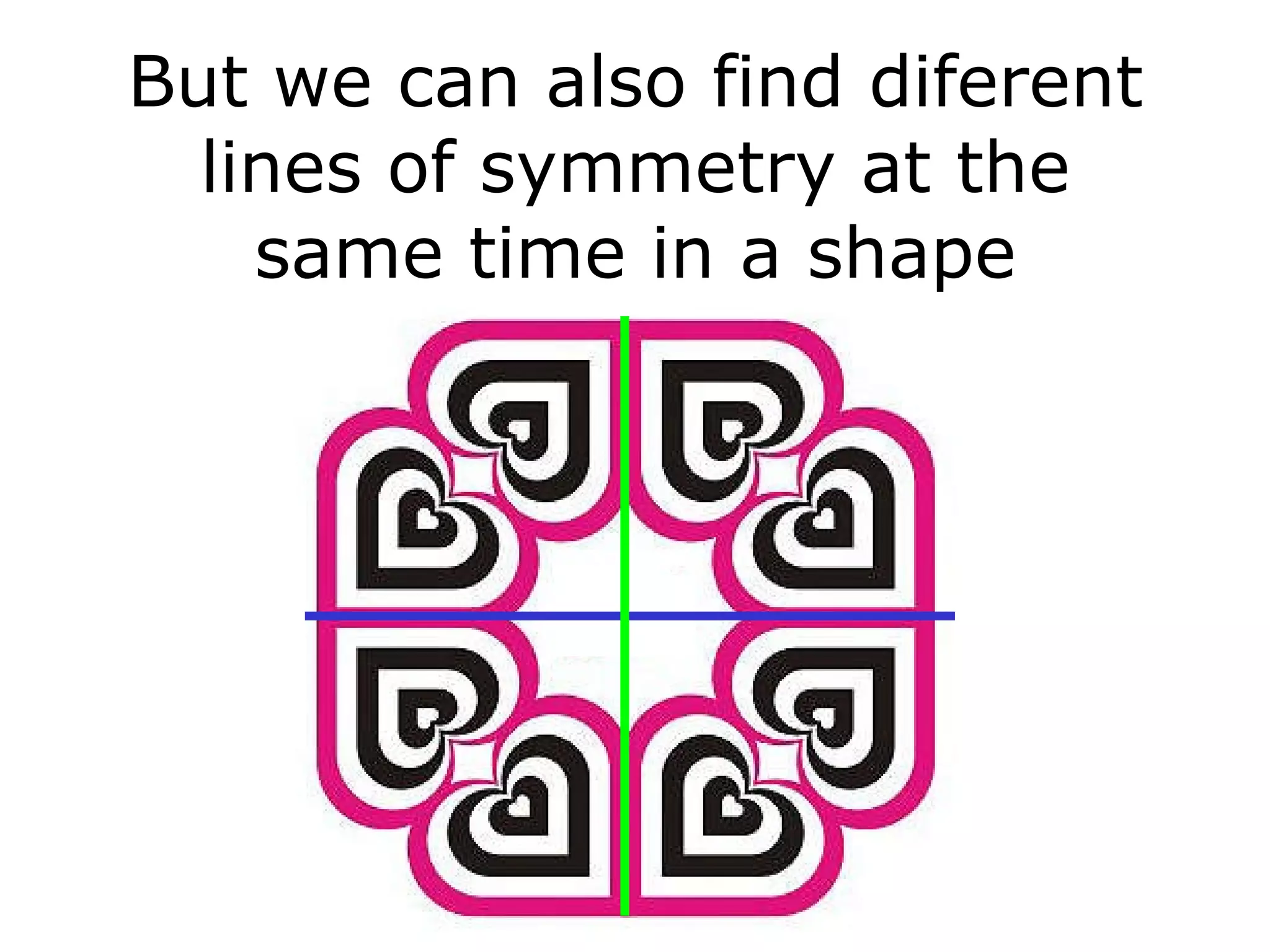
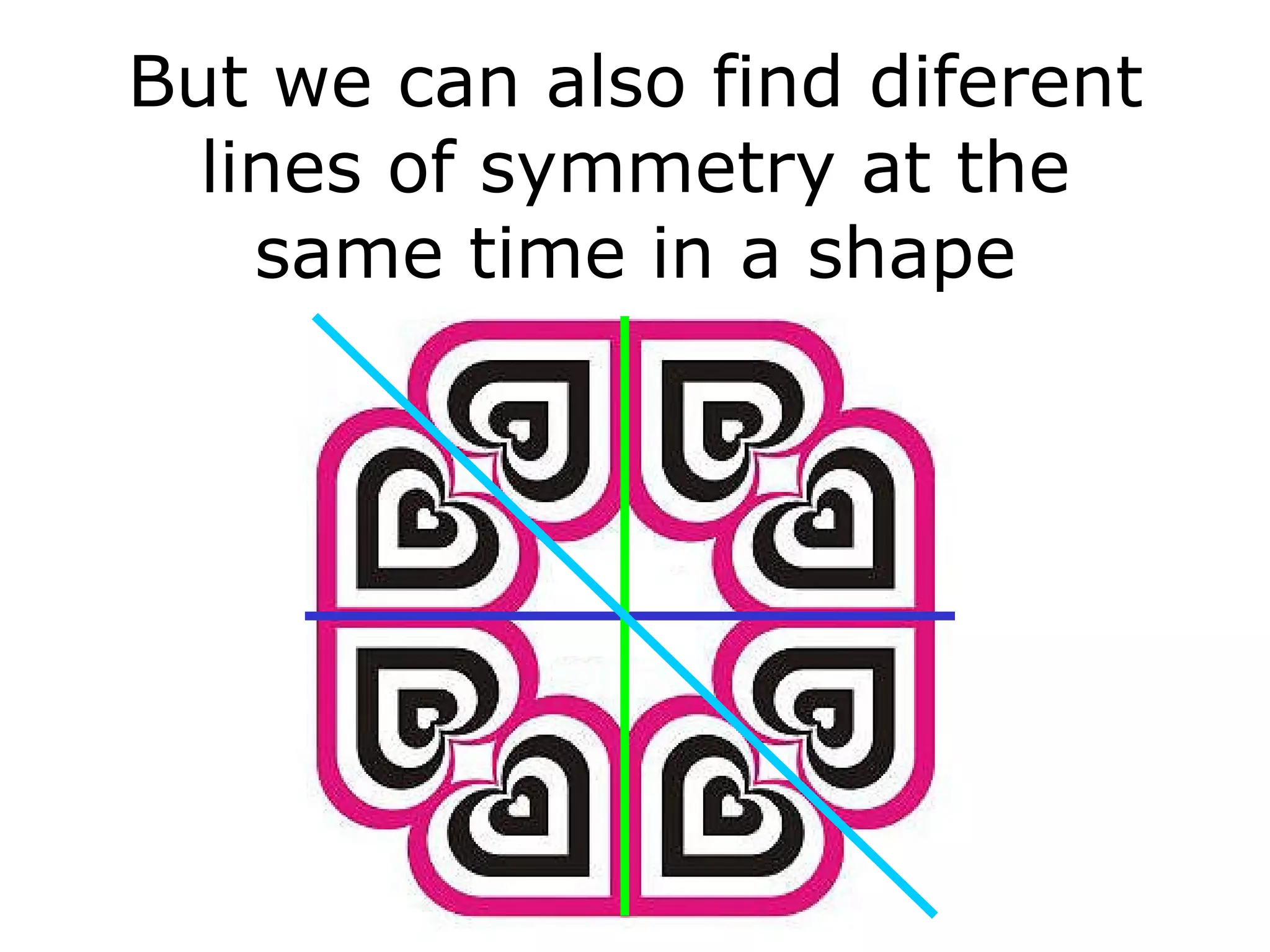
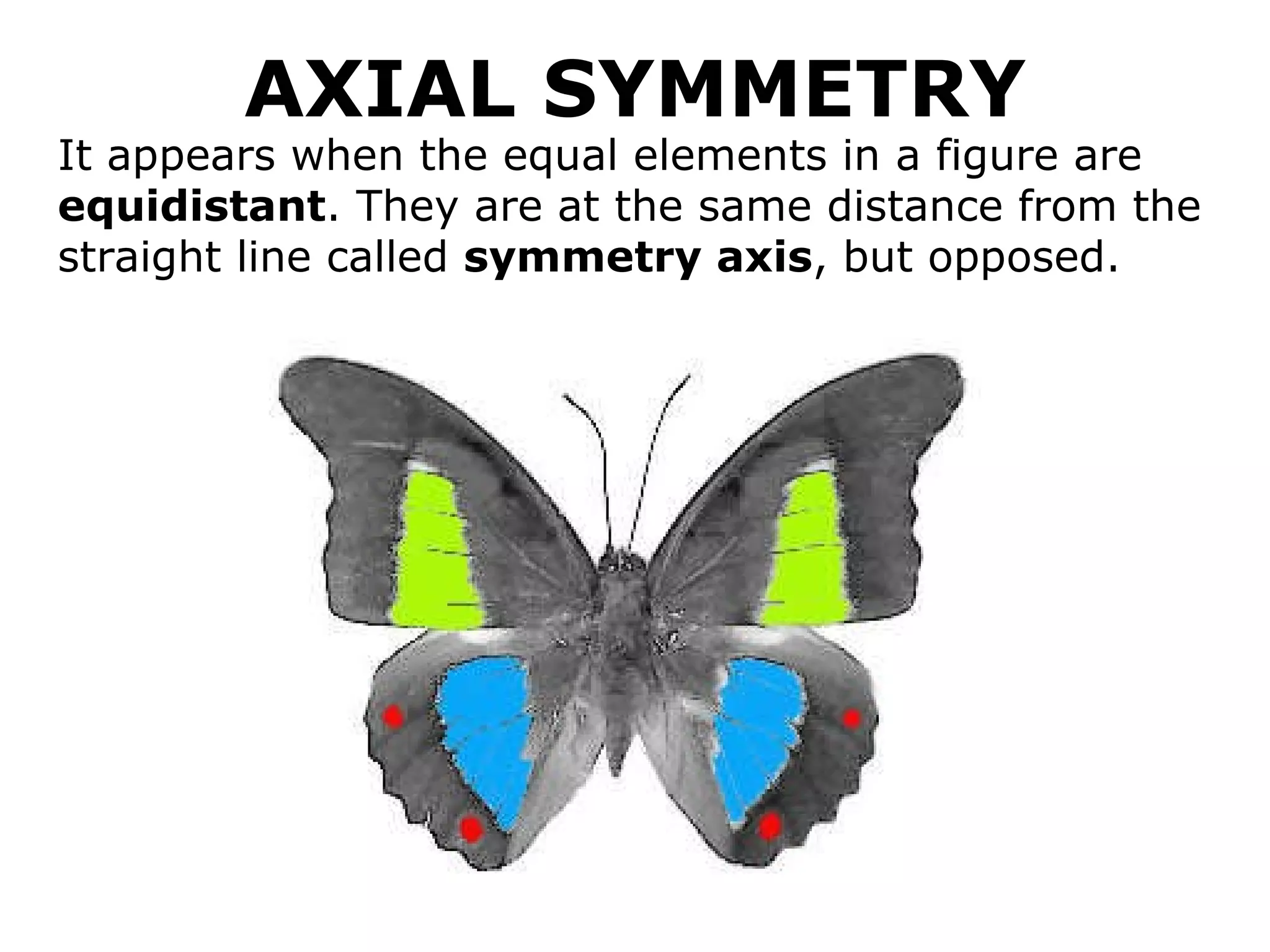
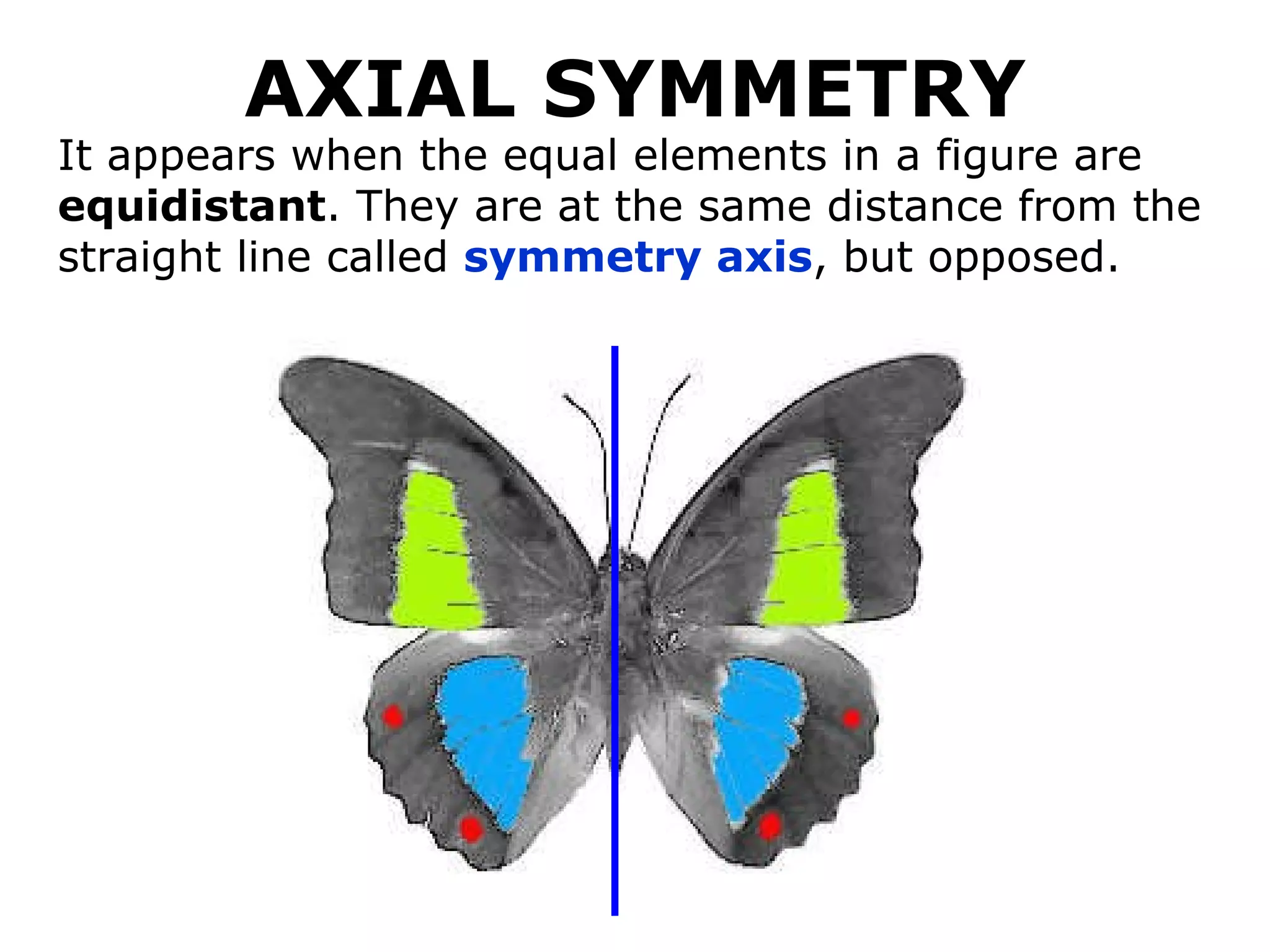
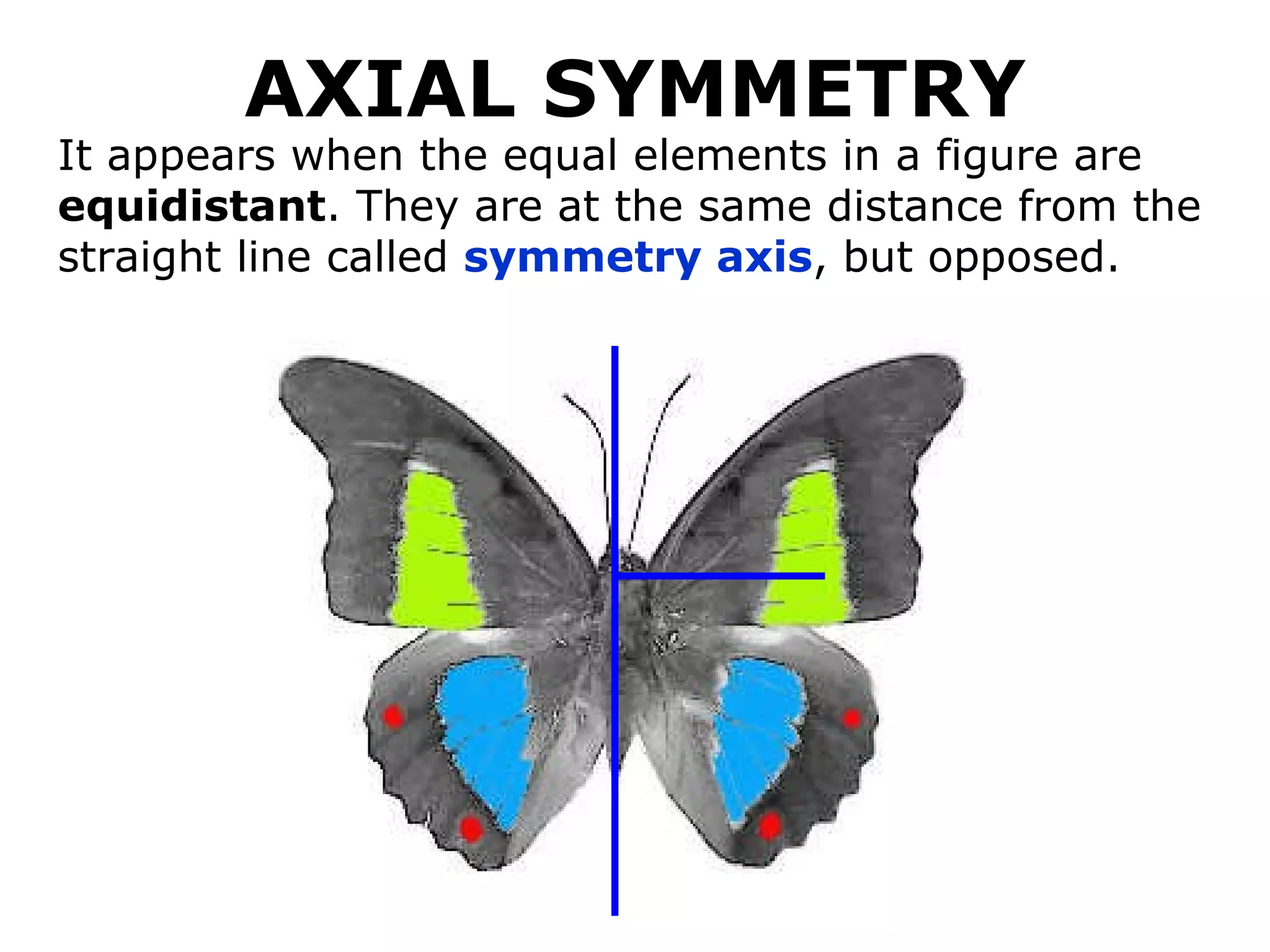
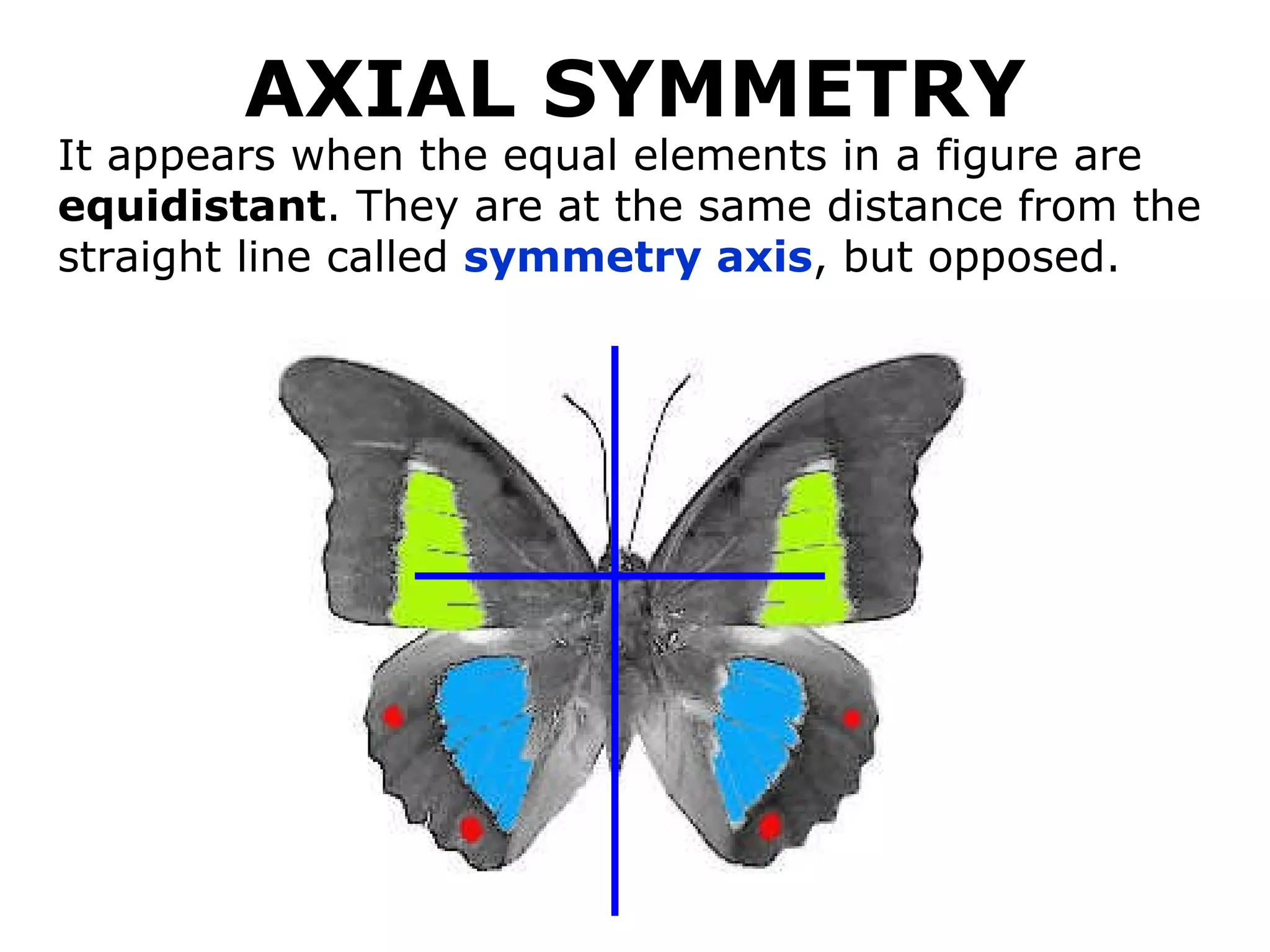
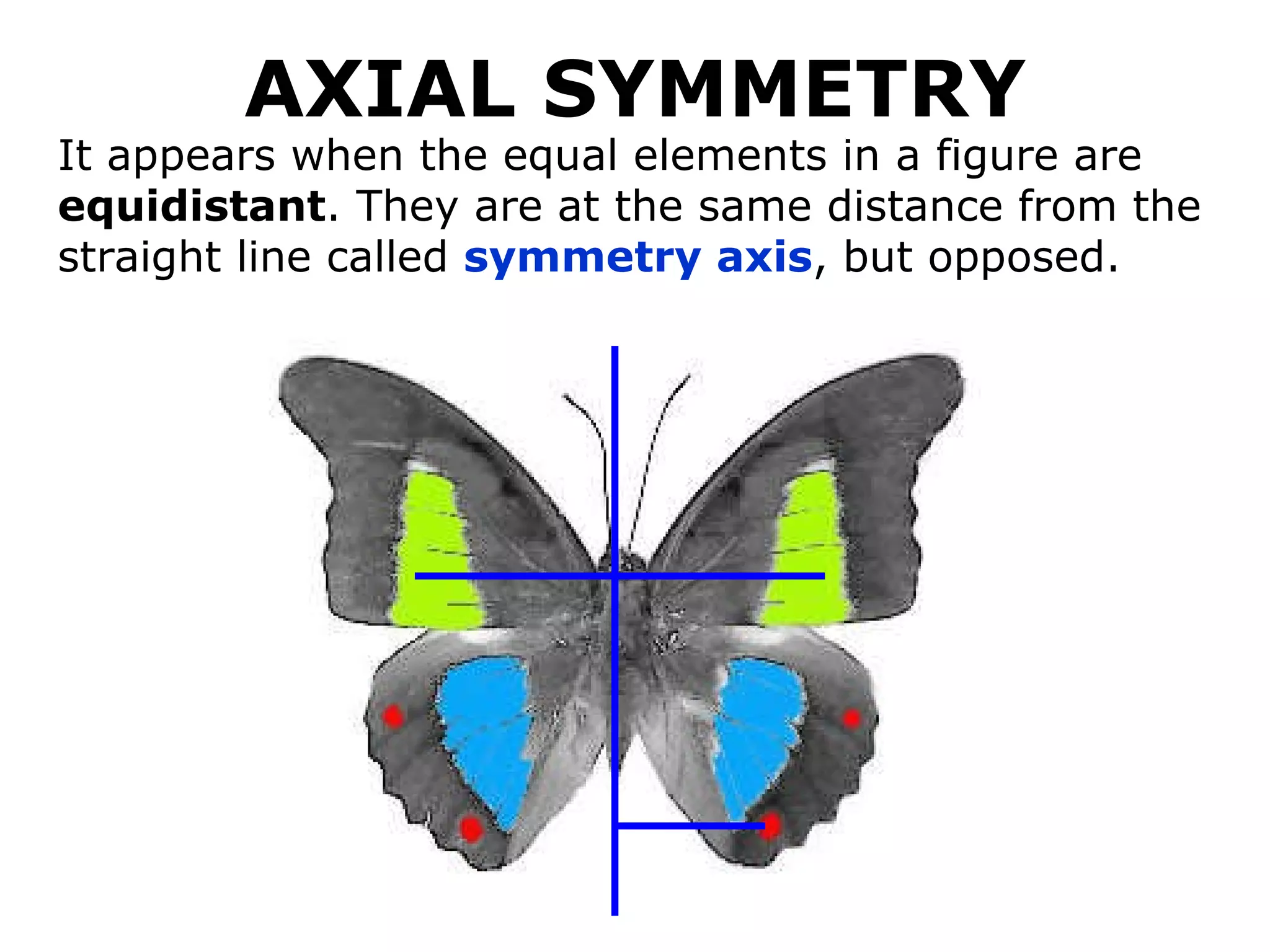
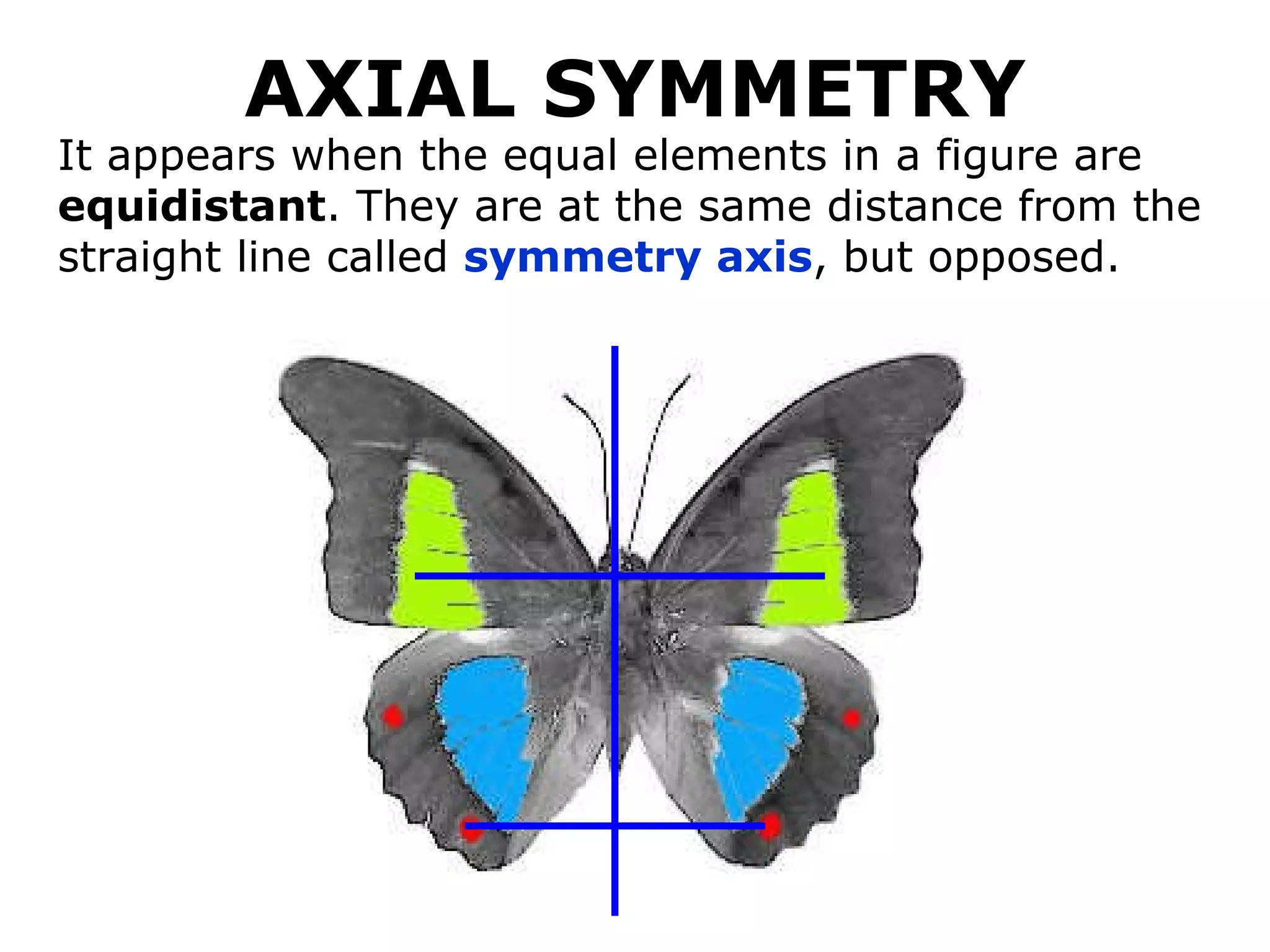
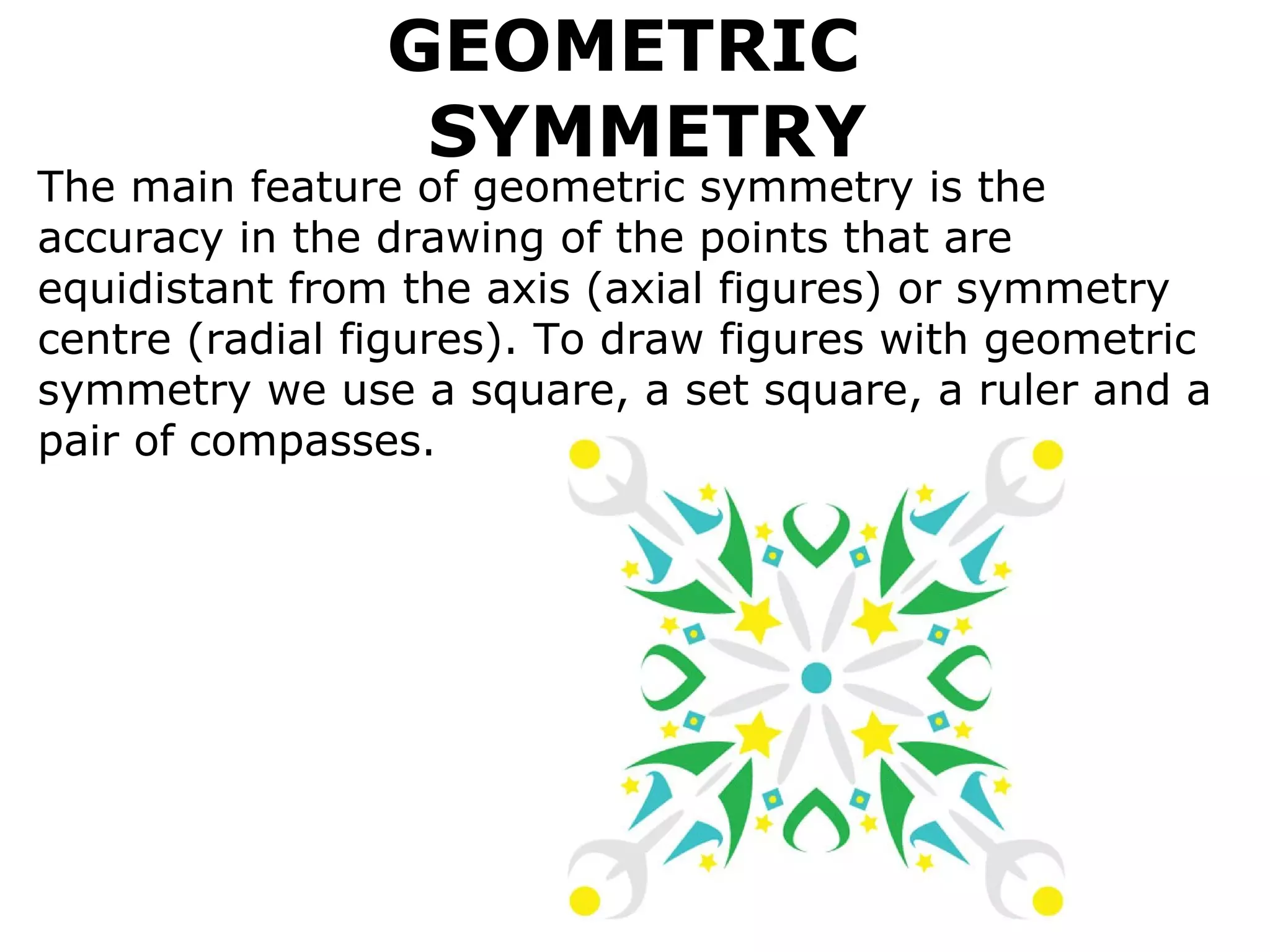
The document discusses symmetry in nature, architecture, and art. It defines symmetry as a spatial relationship where one half of a shape is the mirror image of the other half. There are different types of symmetrical lines including horizontal, vertical, and diagonal. Symmetry can be classified as axial or radial depending on whether equal elements are equidistant from a central axis or point.