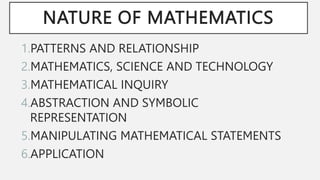
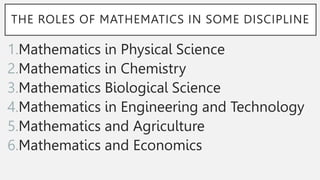
1) Mathematics exists everywhere and describes patterns found in nature. Many natural phenomena like the calendar, days of the week, and seasons exhibit regular repeating patterns.
2) Specific examples of patterns in nature discussed include symmetry, spirals, meanders, waves, foam, tessellations, cracks, and stripes. Fractals are also patterns in nature that are self-similar across scales.
3) The Fibonacci sequence and golden ratio are exhibited in seed heads, pine cones, tree branches, shells, spiral galaxies, and hurricanes. This demonstrates the mathematical patterns underlying forms in nature.