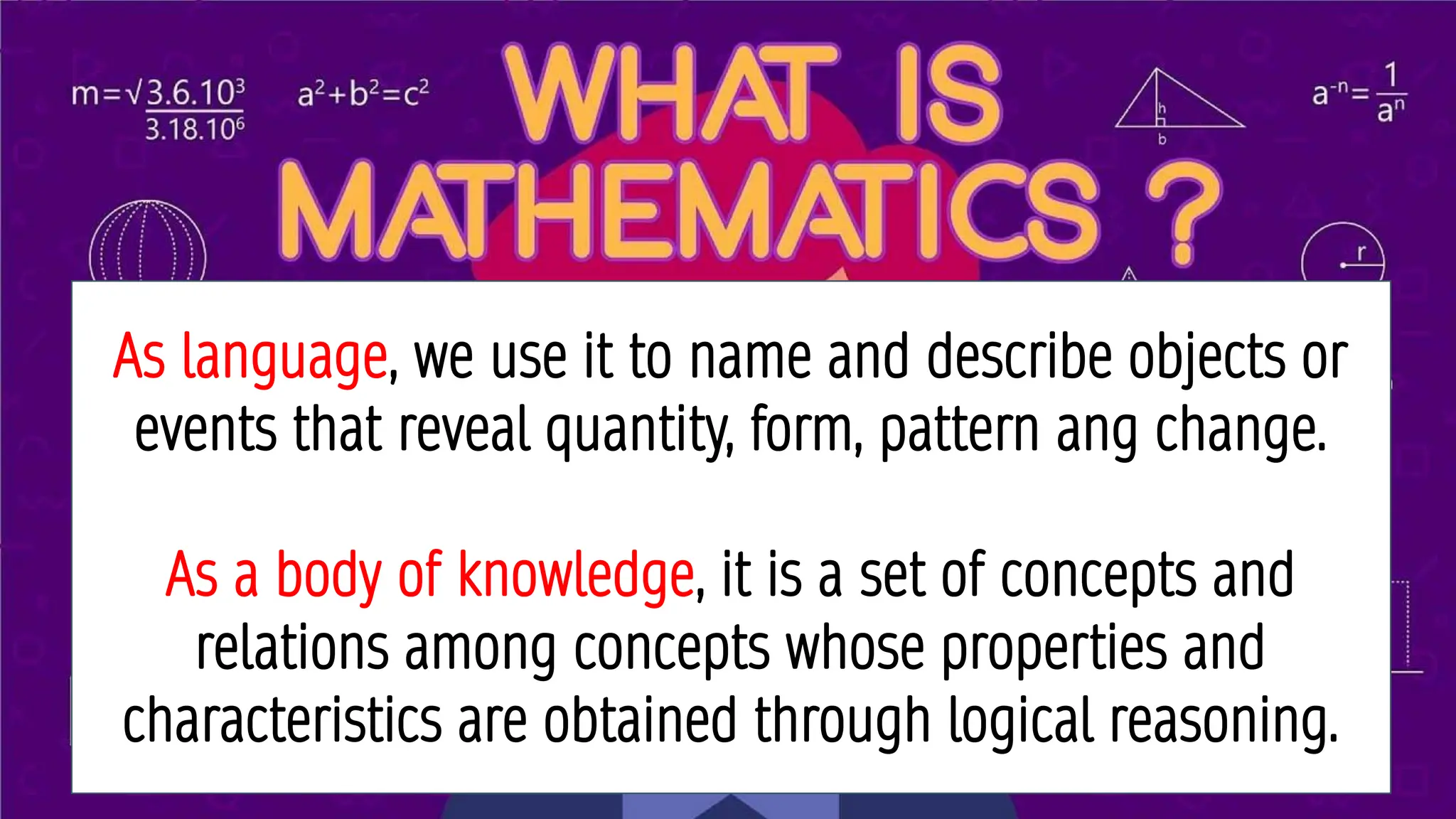
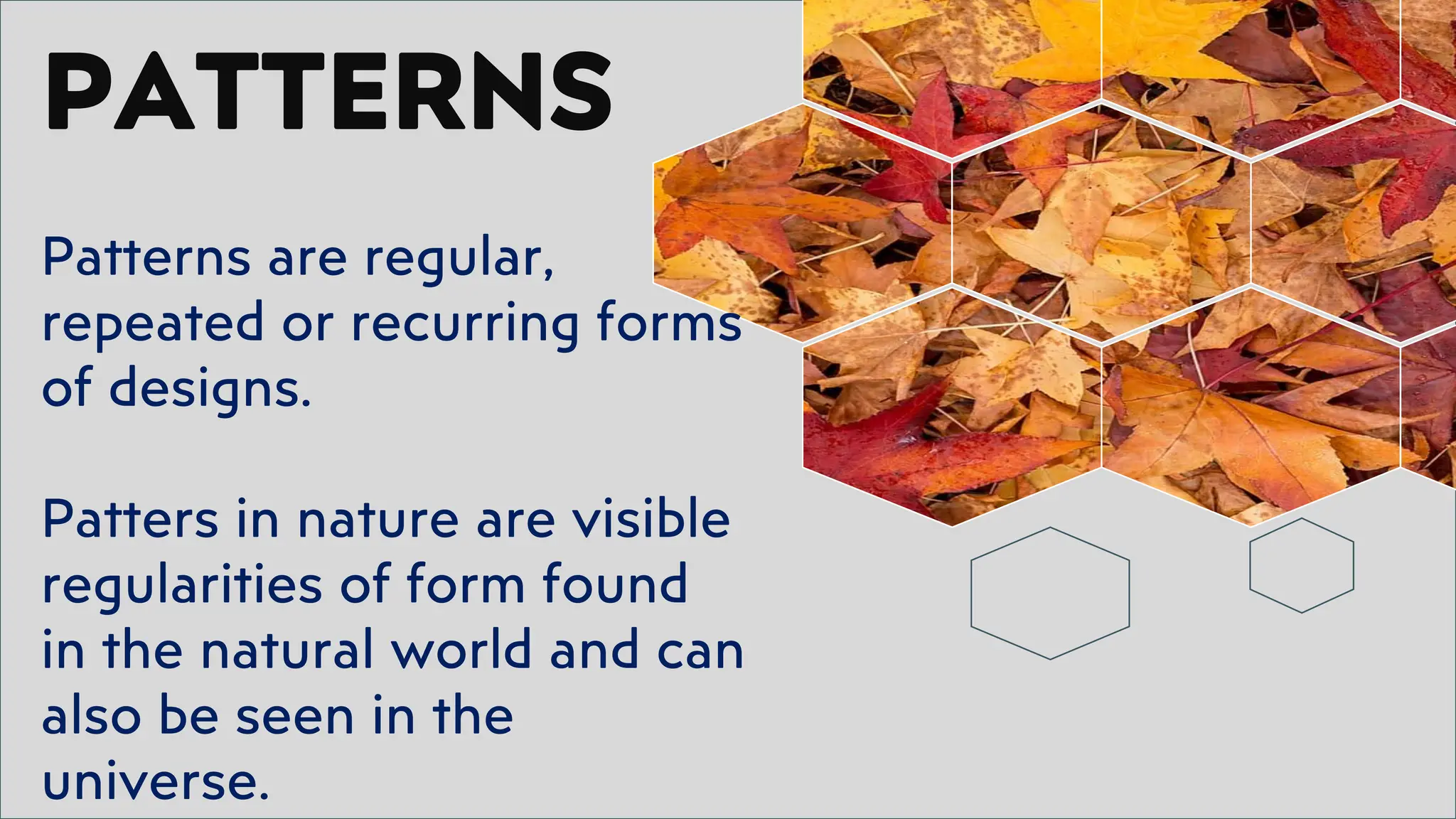
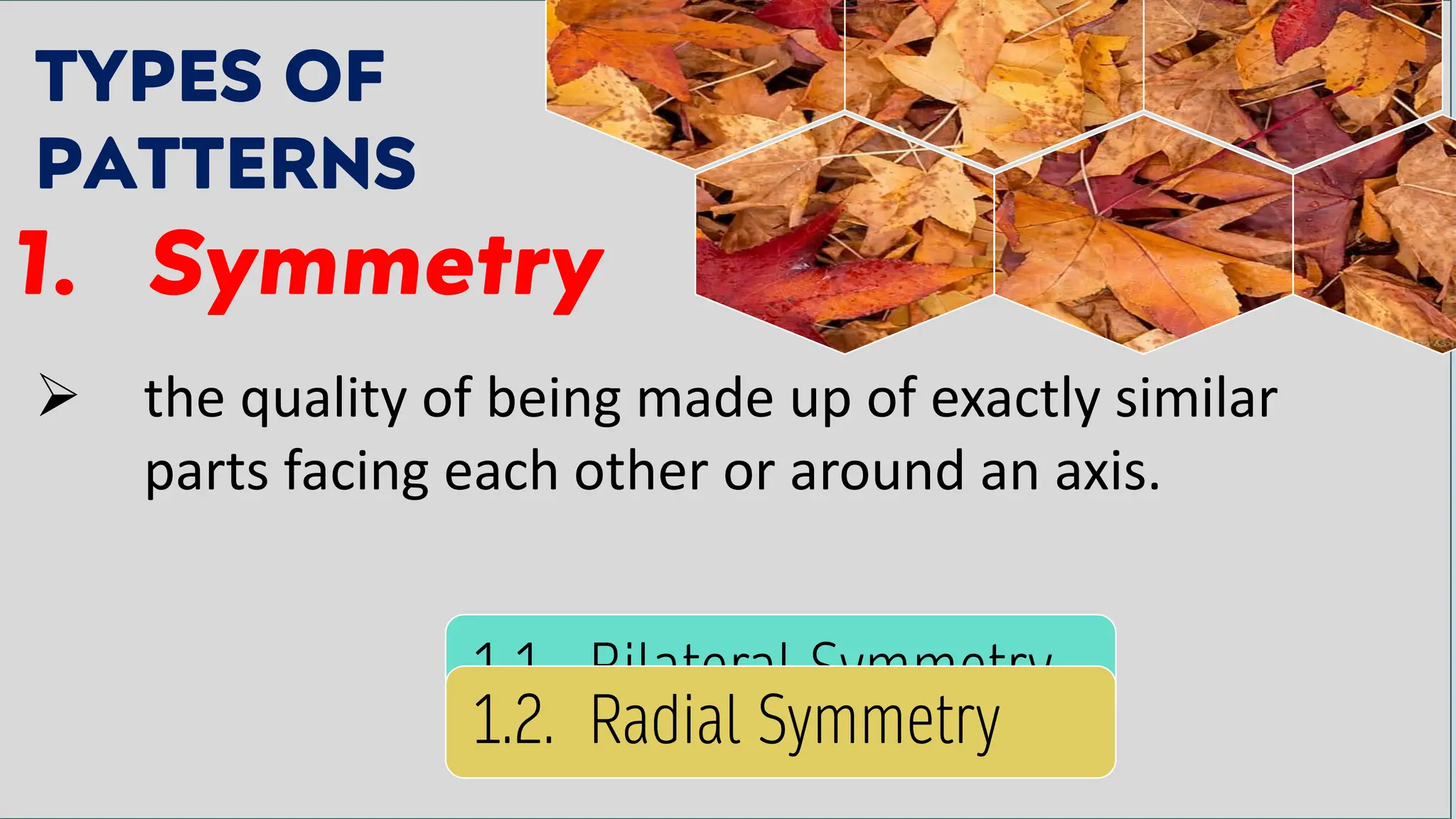
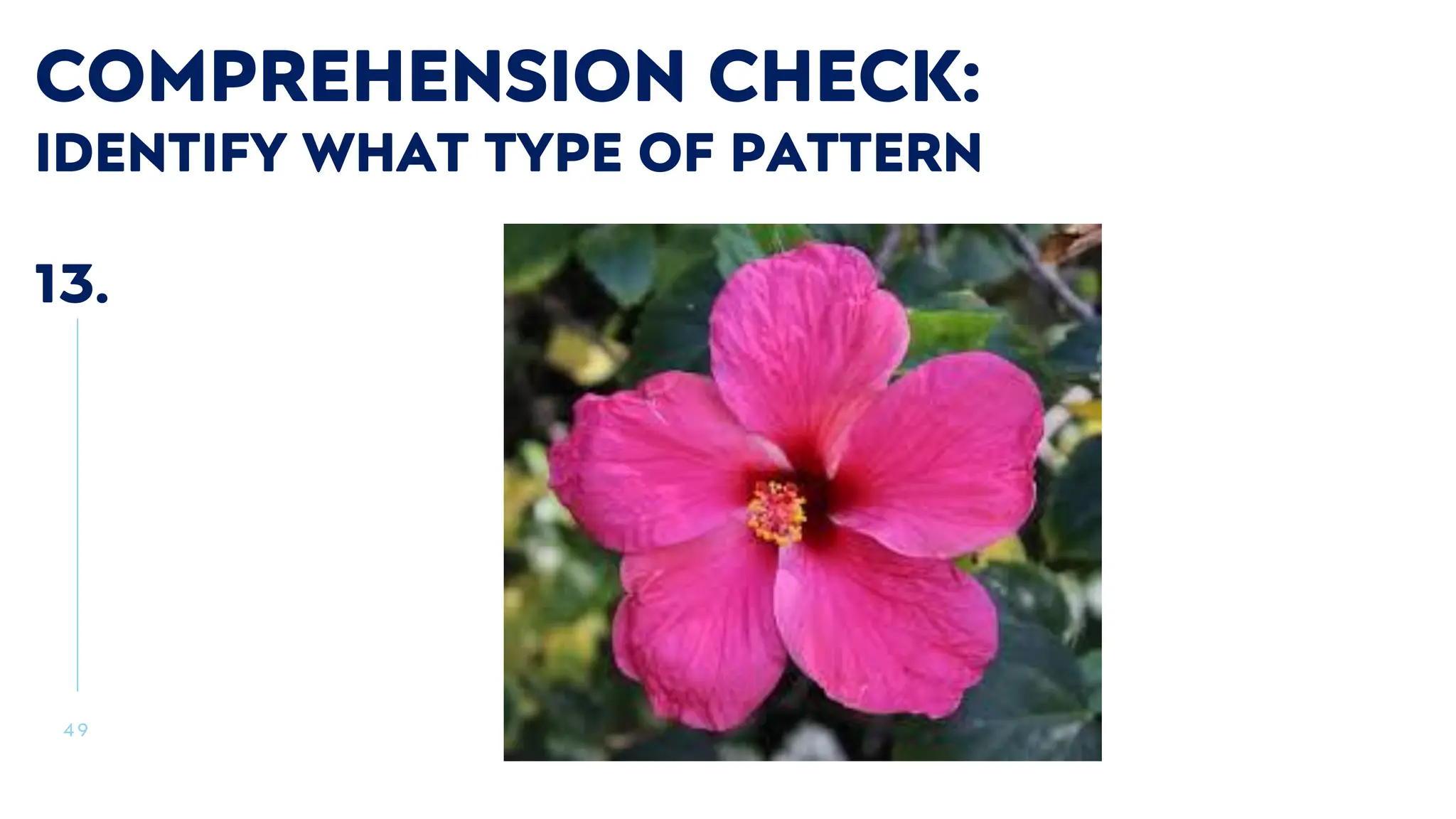
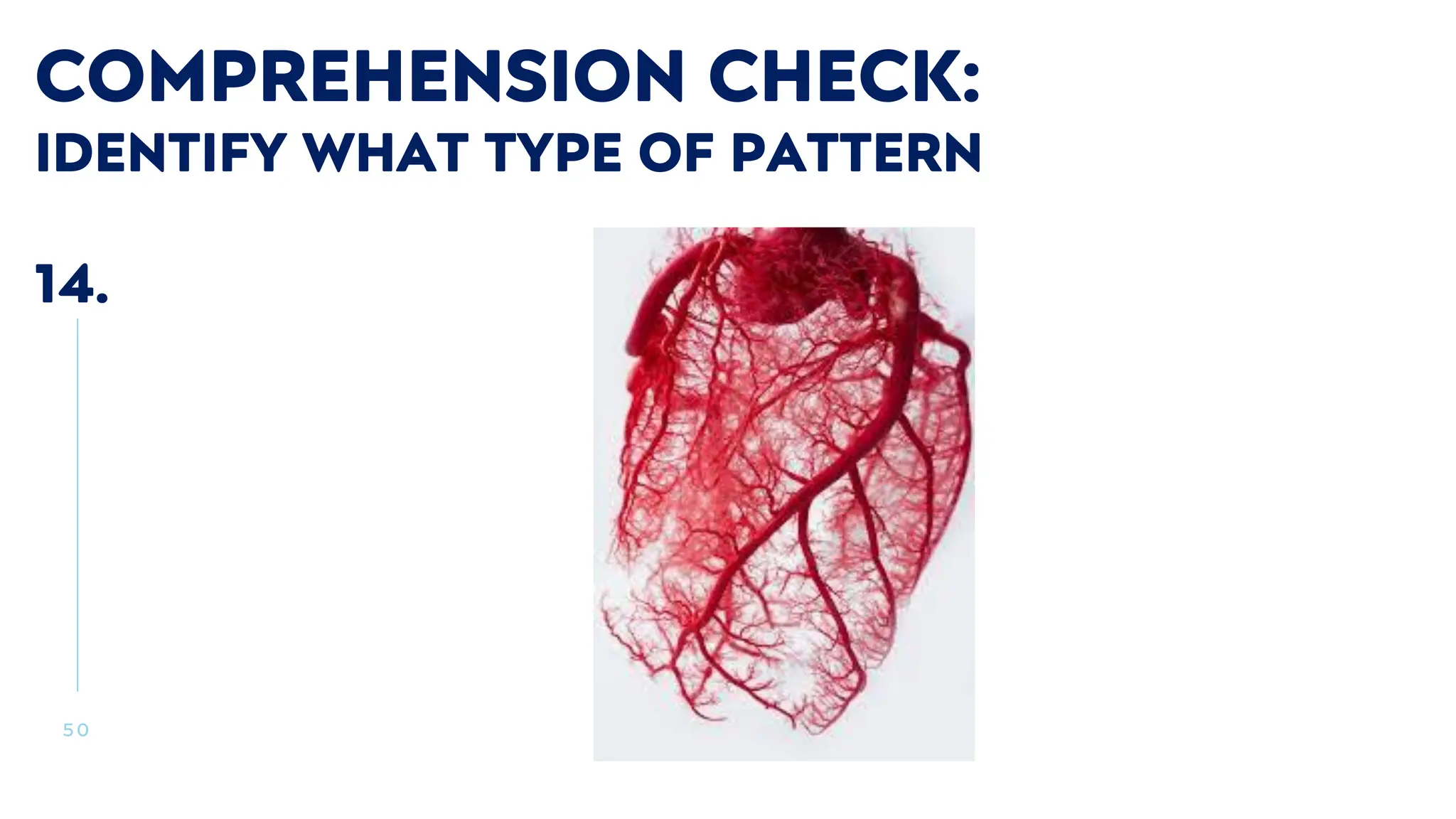
The document outlines a course titled 'Mathematics in the Modern World' which explores the nature and application of mathematics as a practical tool for understanding patterns in nature, employing both inductive and deductive reasoning. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing mathematical concepts in daily life and appreciating mathematics as a human endeavor through the study of various patterns such as symmetry, fractals, spirals, and tessellations. Learning outcomes include developing the ability to articulate the significance of mathematics, identify patterns in nature, and argue its representation and expression in the world.