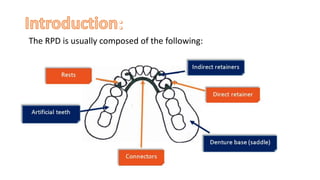
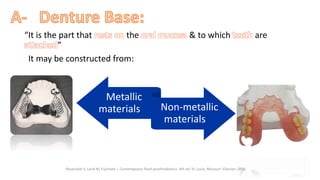
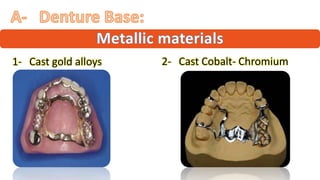
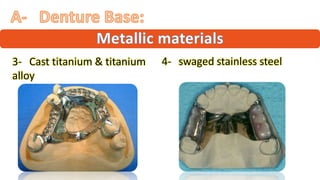
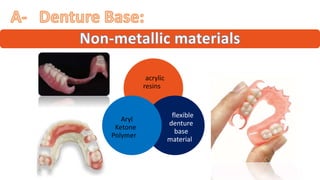
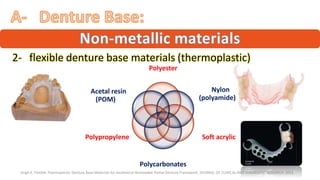
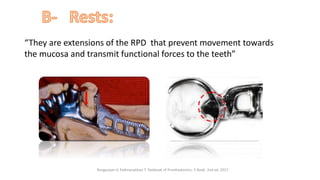
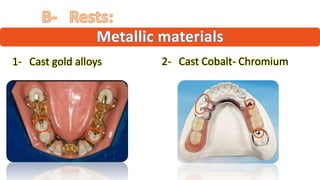
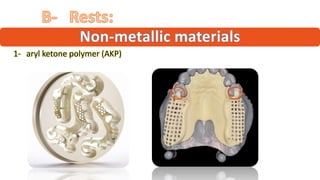
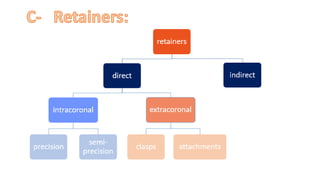
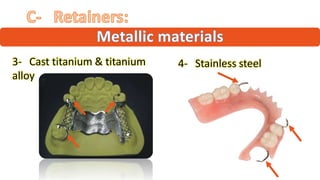
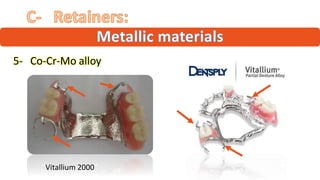
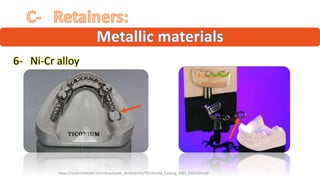
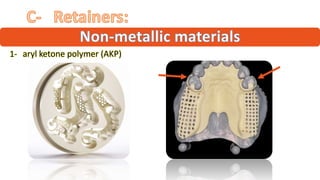
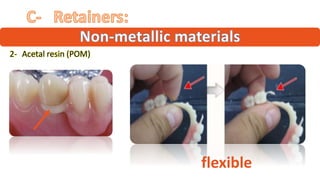
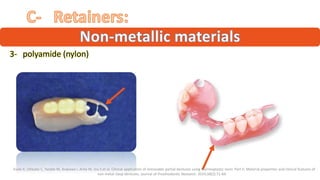
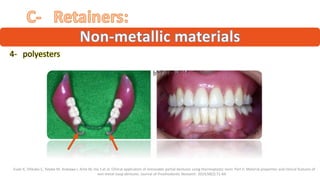
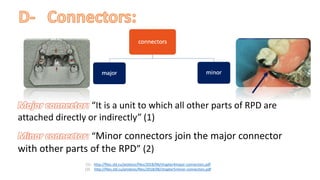
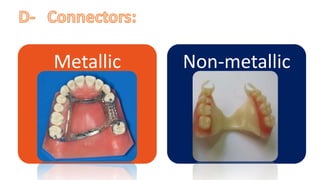
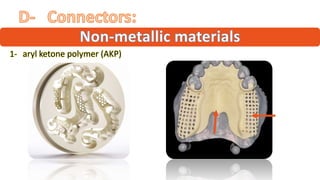
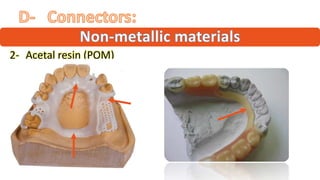
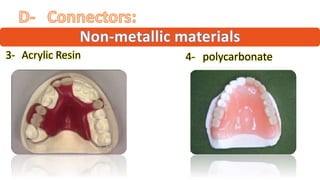
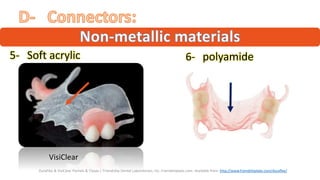
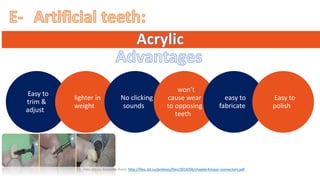
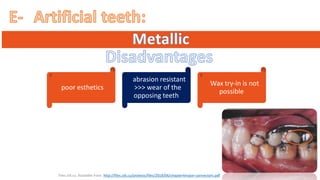
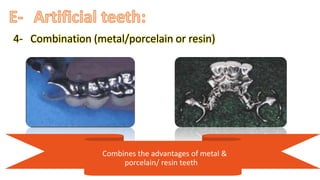
The RPD is composed of teeth, a major connector, and minor connectors. It can be constructed from various metallic materials like gold alloys, cobalt-chromium, titanium, or stainless steel. Non-metallic options include thermoplastics, acrylic resins, or aryl ketone polymer. Rest seats can also be made of similar materials and are extensions that prevent movement and transmit forces to teeth. Teeth can be porcelain, acrylic, metal, or a combination, with various advantages and disadvantages for each.