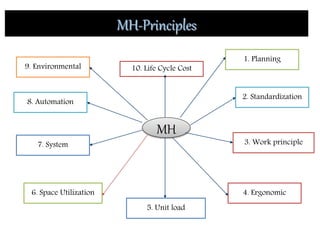
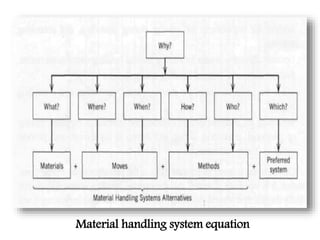
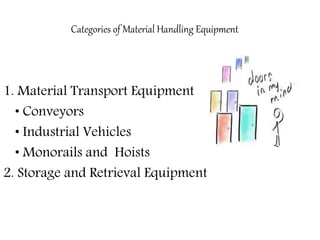
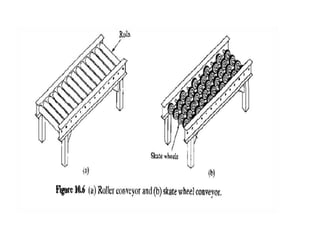
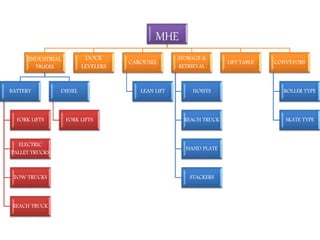
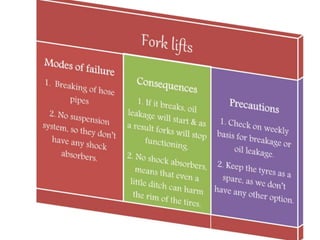
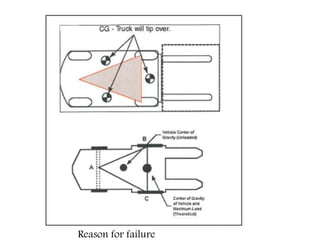
Material handling involves moving, storing, protecting and controlling materials. It includes various types of equipment like conveyors, industrial vehicles, hoists, forklifts and stackers. Proper planning, standardization, ergonomics, unit load design, space utilization, automation and life cycle costing are important principles of material handling. Questions around what, where, when, how, who and which materials and equipment should be considered to design an effective material handling system. Regular maintenance, safety training and use of personal protective equipment are crucial to safely operate material handling equipment.