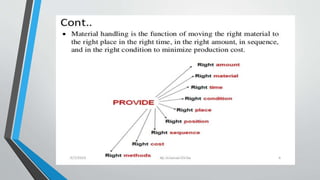
Material handling involves the movement of materials and products within an organization. It aims to reduce costs, waste, and improve workflow, distribution, warehouse capacity, and worker safety. There are principles related to planning, equipment selection, and operations. Material handling systems can be categorized as equipment-oriented, load-oriented, production-oriented, or function-oriented. Common material handling equipment includes conveyor systems, overhead cranes, forklifts, tractors, and pallets. Positioning this equipment properly is important for effective material movement.