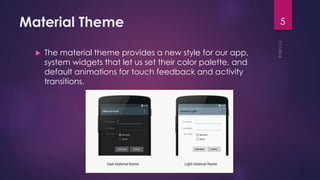
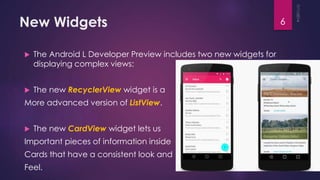
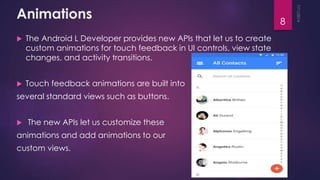
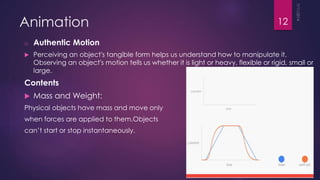
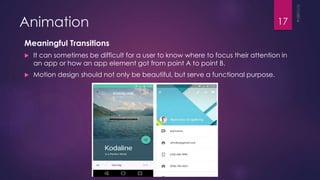
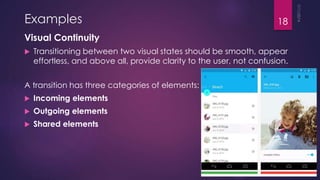
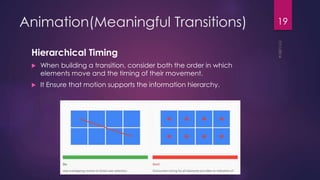
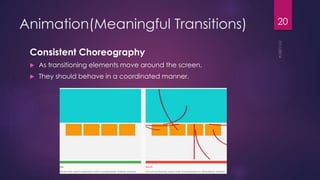
This document discusses the principles and elements of Material Design. It provides an overview of Material Design, including its goals of creating intuitive user experiences and harnessing technology capabilities. The key elements covered include the Material theme, new widgets like RecyclerView and CardView, view shadows, and animation APIs for touch feedback, view changes and activity transitions. The document also outlines the principles of Material Design, such as using motion to provide meaning and focus, and ensuring animations are authentic, responsive, meaningful and delightful.