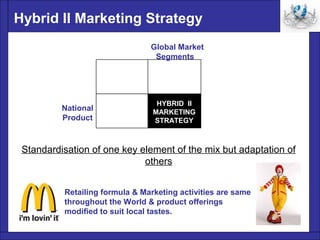
The document discusses different global marketing strategies and the standardization versus localization of the marketing mix elements of product, price, promotion, and place. It describes four main strategies: 1) an ideal global strategy of marketing a standard product using uniform programs worldwide; 2) an ideal national strategy of locally adapting the marketing mix in each national market; 3) a hybrid I strategy of standardized products but adapted other elements; and 4) a hybrid II strategy of standardizing one key element like retail format but adapting other elements like product offerings locally. The document emphasizes considering local tastes and regulations for different elements.